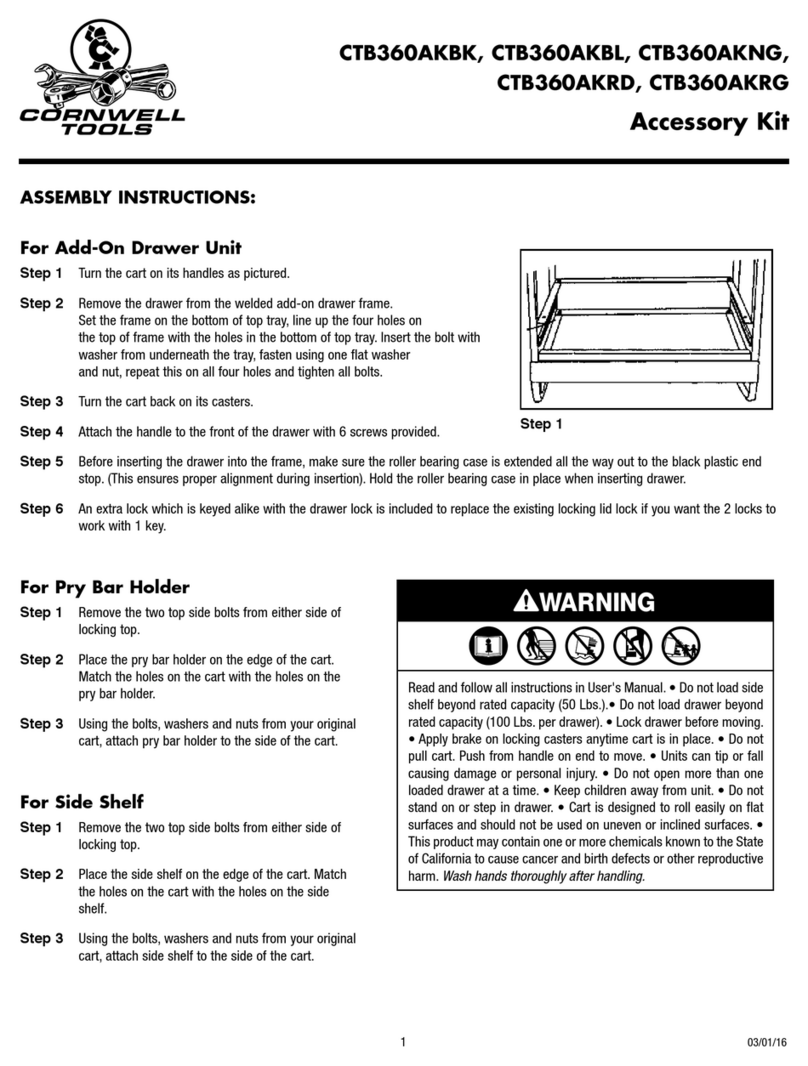
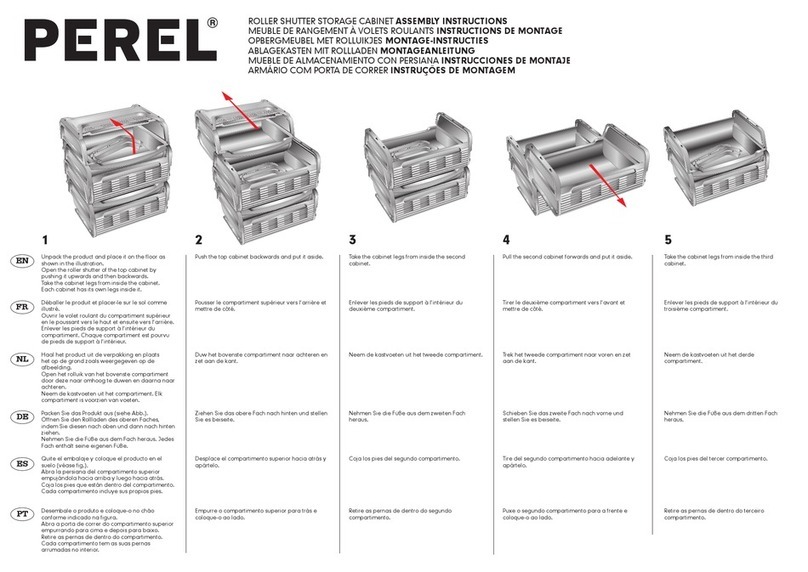
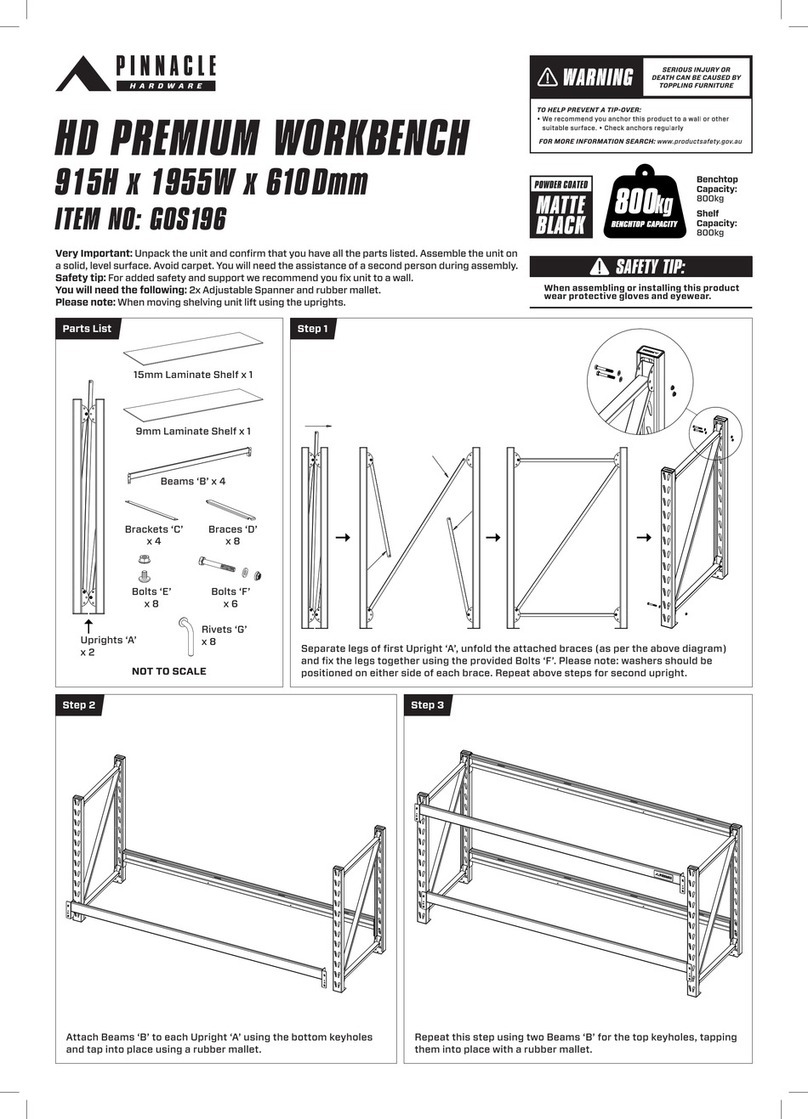
Spectrum Mill Workbench Quick Start Guide 3
Protein/Peptide
Summary
Spectrum Viewer support for c- and z-ions, which are prominent in ETD spectra
Retention time in peptide summaries
Fragmentation mode in peptide summaries, so you can ascertain the mode for
each spectrum (for example, CID versus ETD)
Enhanced protein grouping based upon shared peptides
Ability to align sequences of proteins within a protein group
Ability to sort and filter by peptide pI
New capability in the Spectrum Viewer to type your own sequence and have it add
to the list of available sequences that the software shows when you click the Rank
arrow buttons
Ability to sort peptides by the numerical position of their first amino acid in the
protein sequence
Capability to distinguish in results tables between true mass errors and mass
differences produced by peptide modifications
Support for more
amino acid modi-
fications
Support for Deamidated (N) and Deamidated (Q) as variable modifications. The
software displays the first by default; system administrators can add the second by
copying a definition from smconfig.misc.xml to smconfig.custom.xml.
Expanded iTRAQ support, to include data from the Generic Extractor and the
*.raw (LCQ/LTQ) Extractor. The latter uses merged MS3spectra.
Support for both original iTRAQ (which assumes complete labeling) and iTRAQ
Partial-mix, which allows you to check for incomplete labeling
Miscellaneous New Easy MS/MS Search form that simplifies use of the software and streamlines
the data processing steps
New Multiple Sequence Aligner utility to align sequences of proteins from a
database and highlight amino acid differences
Support for Web-based interaction with GeneSpring MS
Easier, faster input of mass lists into Manual PMF, with MH+/M selection that
allows you to input either protonated or neutral species (directly compatible with
output from a variety of instrument data systems)
Faster selection of data folders
Sherenga de novo sequencing support for the Agilent Q-TOF and ETD data from
the Agilent ion trap