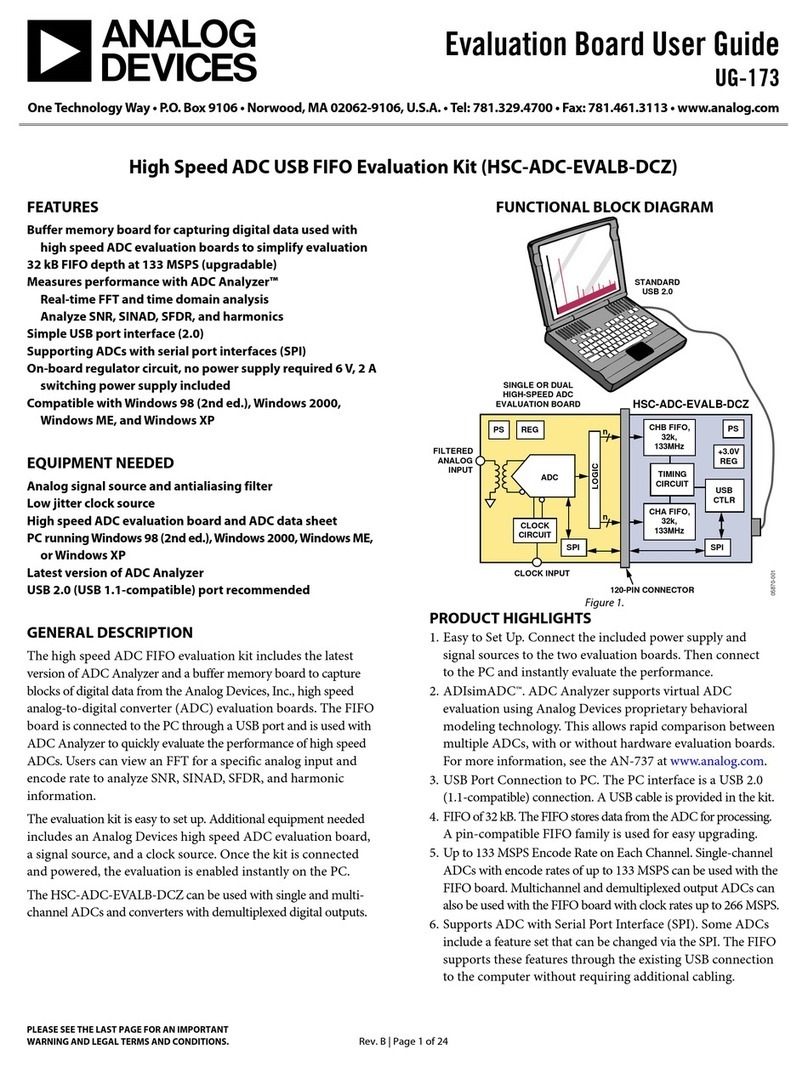
UG-348 EVAL-AD5162SDZ User Guide
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 16
TEST CIRCUITS
The EVA L-AD5162SDZ incorporates several test circuits to
evaluate the AD5162 performance.
DAC
RDAC1 can be operated as a digital-to-analog converter (DAC),
as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. DAC
Tabl e 4 shows the options available for the voltage references.
Table 4. DAC Voltage References
Terminal Link Options Description
A1 A20 AC + DC Connects Terminal A1 to
(VDD − VSS)/2.
VDD Connects Terminal A1 to VDD.
W1 BUF_W1 Connects Terminal W1 to an
output buffer.
B1 A21 DC Connects Terminal B1 to
(VDD − VSS)/2.
GND Connects Terminal B1 to
analog ground.
The output voltage is defined in Equation 1.
(1)
where:
RWB1 is the resistor between the W1 and B1 terminals.
VA1 is the voltage applied to the A1 terminal (A20 link).
VB1 is the voltage applied to the B1 terminal (A21 link).
However, by using the R34 and R35 external resistors, the user
can reduce the voltage of the voltage references. In this case, use
the A1 and B1 test points to measure the voltage applied to the
A0 and B0 terminals and recalculate VA0 and VB0 in Equation 1.
AC Signal Attenuation
RDAC1 can be used to attenuate an ac signal, which must be
provided externally using the AC_INPUT connector, as shown
in Figure 3.
Figure 3. AC Signal Attenuator
Depending on the voltage supply rails and the dc offset voltage
of the ac signal, various configurations can be used as described
in Tabl e 5.
Table 5. AC Signal Attenuation Link Options
Link Options Conditions
A20 AC + DC No dc offset voltage.
AC signal is outside the voltage supply rails
due to the dc offset voltage.
DC offset voltage ≠ VDD/2.1
AC All other conditions.
A21 DC Use in conjunction with ac + dc link.
GND All other conditions.
1Recommended to ensure optimal total harmonic distortion (THD) performance.
The signal attenuation is defined in Equation 2.
+
×=
−− ENDTOEND
WWB1
R
RR
nAttenuatio log20)dB(
(2)
where:
RWB1is the resistor between the W1 and B1 terminals.
RWis the wiper resistance.
REND-TO-END is the end-to-end resistance value.
In addition, R36 can be used to achieve a pseudologarithmic
attenuation. To do so, adjust the R36 resistor until a desirable
transfer function is found.
W1_BUF
A1
RDAC1
AC + DC
VDD
A1
B1 BUF_W1
GND
DC
2
VDD – VSS
VDD
2
VDD – VSS
R34
R35
W1
W1
B1
10366-002
W1_BUF
A1
RDAC1
AC + DC
AC_INPUT
AC
A1
B1 BUF_W1
GND
2
V
DD
– V
SS
R34
R35
W1
W1
B1
1µF
R36
DC
2
V
DD
– V
SS
10366-003