AG2500Series Software User’s Guide June 2002 iii
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
1.1 Introduction .........................................................................................................................1
1.2 Features ...............................................................................................................................1
1.3 Package Includes .................................................................................................................1
1.4 Minimum System Requirements ........................................................................................1
1.5 Management Interface Options ...........................................................................................2
1.5.1 HTML Interface (Web-based) ............................................................................. 2
1.5.2 SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) ................................................ 2
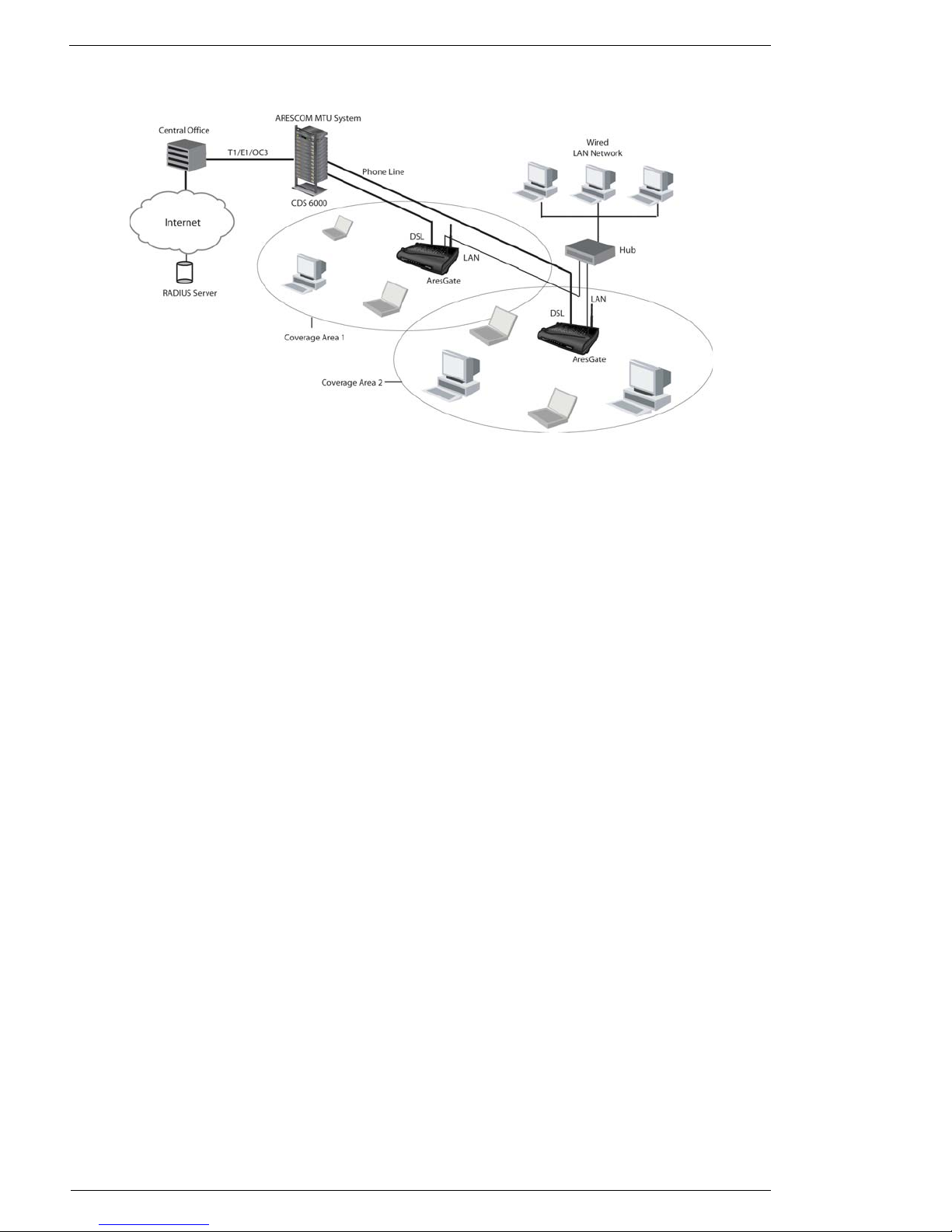
1.6 Network Scenario ...............................................................................................................3
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.1 Front Panel Information ......................................................................................................5
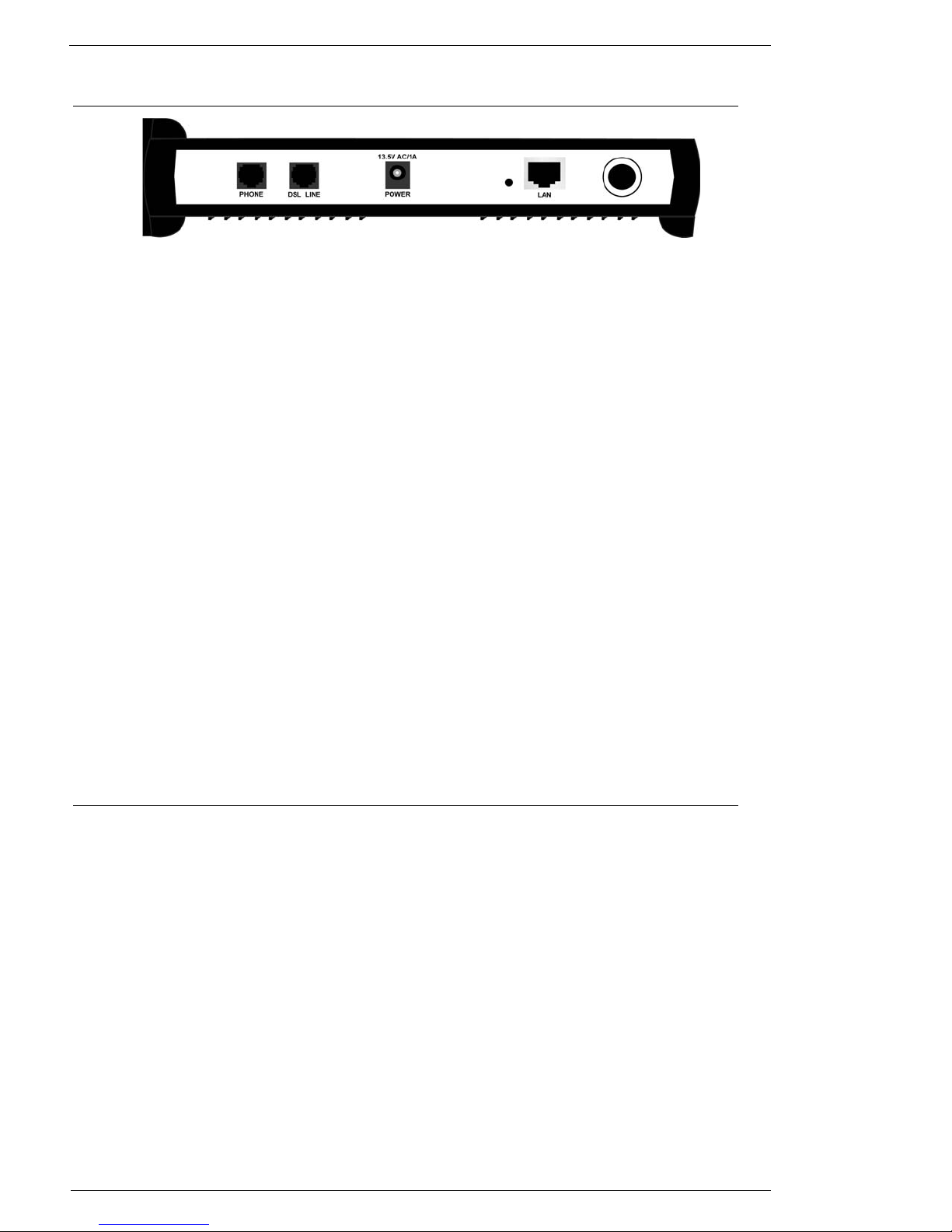
2.2 Back Panel Information ......................................................................................................6
2.3 Location & Placement ........................................................................................................6
2.4 Setup Instructions ...............................................................................................................7
CHAPTER 3 BEFORE YOU START
CHAPTER 4 SOFTWARE CONFIGURATION
4.1 Open Your Browser ..........................................................................................................11
4.2 Basic - SETUP ..................................................................................................................12
4.3 Basic - WIRELESS ...........................................................................................................14
4.4 Basic - AUTHENTICATION ...........................................................................................16
4.5 Basic - DHCP ....................................................................................................................18
4.5.1 Reserved IP Table ............................................................................................. 19
4.6 Basic - USER STATUS ....................................................................................................20
4.6.1 Current Log-on User Status ............................................................................. 20
4.7 Basic - STATUS ...............................................................................................................21
4.8 Advanced - ADMINISTRATION ....................................................................................23
4.8.1 Administration .................................................................................................. 23
4.9 Advanced - IP ROUTING ................................................................................................25
4.9.1 Current IP Routing Table ................................................................................. 25
4.9.2 Add Route ......................................................................................................... 25
4.9.3 Delete Route ..................................................................................................... 25
4.10 Advanced - SNMP ............................................................................................................26
4.10.1 Current SNMP Table ........................................................................................ 26
4.10.2 Add SNMP Entry .............................................................................................. 27
4.10.3 Delete SNMP Entry .......................................................................................... 27
4.11 Advanced - UPGRADE ....................................................................................................28