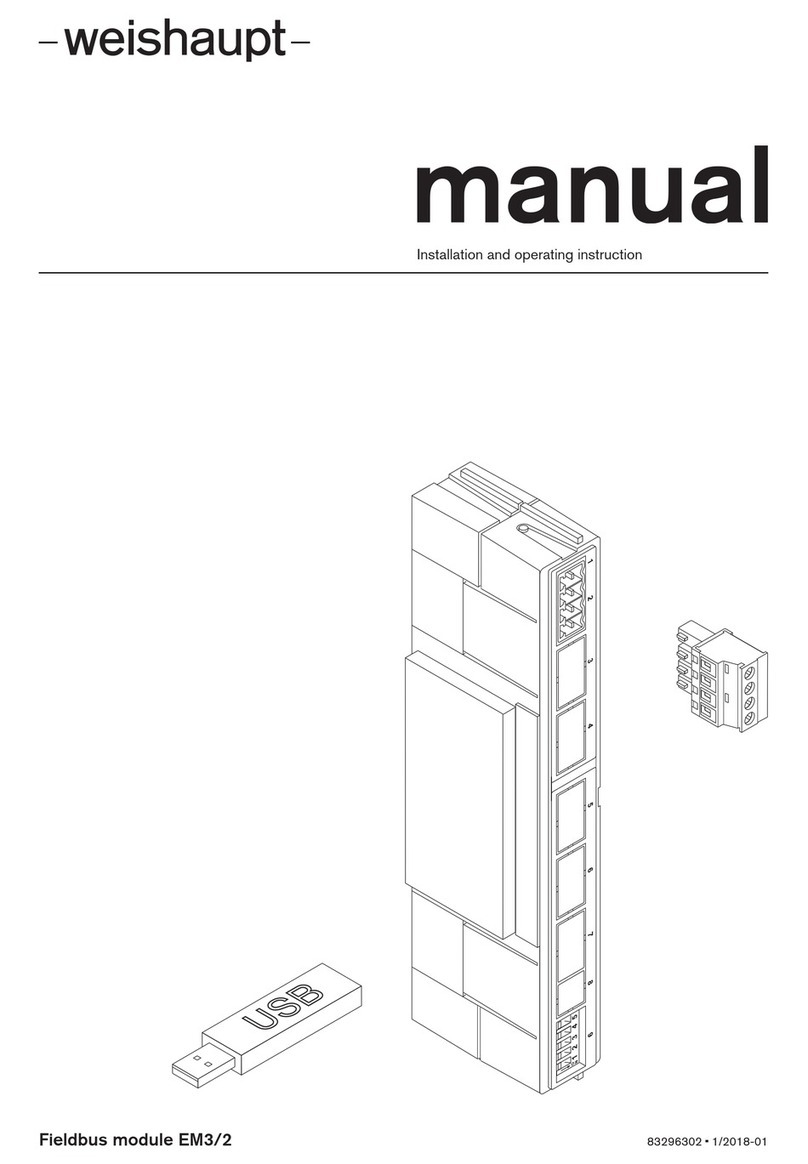
Bently Nevada 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface User manual

Part number 141706-01
Revision NC, August 1999
3500 Galvanic Isolator
Interface
Manual

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
ii
Copyright © 1999 Bently Nevada Corporation
All Rights Reserved.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
The following are trademarks of Bently Nevada Corporation in the United States and other
countries:
Actionable Information™, Actionable Information to the
Right People at The Right Time™, ADRE®, Bently
Nevada®, CableLoc™, Data Manager®, Decision
Support™, DemoNet™, Dynamic Data Manager®,
Dynamic Transmitor™, Engineer Assist™,
FieldMonitor™, FluidLoc™, FlexiTIM™, FlexiTAM™,
Helping you Protect and Manage All Your Machinery®,
HydroVU™, Key ∅®, Keyphasor®, Machine Condition
Manager™ 2000, MachineLibrary™, MicroPROX®,
Move Data, Not People™, Move Information, Not
Data™, Performance Manager™, PROXPAC®,
Proximitor®, REBAM®, Seismoprobe®, System 1™,
TDIXconnX™, Tecknowledgy™, TipLoc™,
TorXimitor®, Transient Data Manager®,
Trendmaster®, TrimLoc™, VAM™, Velomitor®,
Xlerometer™
The Bently Nevada Corporation Orbit Design is a
trademark of Bently Nevada Corporation in the United
States and other countries.
The following ways of contacting Bently Nevada Corporation are provided for those times
when you cannot contact your local Bently Nevada representative:
Mailing Address 1617 Water Street
Minden, NV 89423
USA
Telephone 1 775 782 3611
1 800 227 5514
Fax 1 775 782 9259
Internet www.bently.com

iii
Additional Information
Notice:
This manual does not contain all the information required to operate and maintain the
3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface. Refer to the Following manuals for other required
information.
3500 Monitoring System Rack Installation and Maintenance Manual (129766-01)
•general description of a standard system
•general description of a Triple Modular redundant (TMR) system
•instructions for installing the removing the module from a 3500 rack
•drawings for all cables used in the 3500 Monitoring System
3500 Monitoring System Rack Configuration and Utilities Guide (129777-01)
•guidelines for using the 3500 Rack Configuration software for setting the operating
parameters of the module
•Guidelines for using the 3500 test utilities to verify that the input and output terminals on
the module are operating properly
3500 Monitoring system Computer Hardware and Software Manual (128158-01)
•instructions for connecting the rack to 3500 host computer
•procedures for verifying communication
•procedures for installing software
•guidelines for using Data Acquisition / DDE Server and Operator Display Software
•procedures and diagrams for setting up network and remote communications
3500 Field Wiring Diagram Package (130432-01)
•diagrams that show how to hook up a particular transducer
•lists of recommended wiring

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
iv
Contents
1. Receiving and Handling Instructions ........................................1
1.1 Receiving Inspecting .........................................................................................1
1.2 Handling and Storage Considerations...............................................................1
1.3 Disposal Statement ...........................................................................................1
2. General Information....................................................................2
2.1 The Parts of the Interface System.....................................................................3
3. Installing the Hardware...............................................................5
3.1 Before You Begin..............................................................................................5
3.1.1 Verifying that the Installation will Meet Approval Requirements..........5
3.1.2 Checking the Accuracy of the Output Signal.......................................5
3.2 Installing Backplane Hardware..........................................................................6
3.2.1 Installing the Vibration Transducer Interface Modules ........................7
3.2.2 Installing the Hazardous-area Screw Clamp Connector......................7
3.2.3 Connecting the Power Supplies..........................................................8
3.2.4 Installing the Earth Rail.......................................................................9
3.2.5 Installing the Backplane....................................................................11
3.2.6 Installing the Backplane onto a Surface............................................11
3.2.7 Installing the Backplane onto a DIN-rail............................................11
3.2.8 Installing the Backplane into an Enclosure .......................................13
3.3 Backplane Dimensions (Vibration)...................................................................15
3.4 Backplane Dimensions (Keyphasor)................................................................15
4. Wiring the Hardware .................................................................16
4.1 Location of Terminals on the Vibration Transducer Interface Module ..............17
4.2 Location of Terminals on the Backplane..........................................................18
4.2.1 Vibration Backplane..........................................................................18
4.2.2 Keyphasor Backplane.......................................................................19
4.3 Connecting Single or Redundant Power Supplies in a Ring Main System.......19
4.4 Precautions about Connecting the Screw Clamp Connectors..........................22
4.5 Connecting Cable Assemblies to Backplanes..................................................23
4.5.1 Cable Pin Outs.................................................................................25
4.6 Connecting Special Alarm Inhibits...................................................................28
4.7 Configuring the 3500 Monitoring System.........................................................28
5. Maintenance and Troubleshooting..........................................29
5.1 Maintenance....................................................................................................29
5.2 Troubleshooting...............................................................................................30
5.2.1 Bench Testing Isolators....................................................................31
5.2.2 Replacing Faulty Isolators ................................................................32

Section 1 — Receiving and Handling Instructions
1
1. Receiving and Handling Instructions
1.1 Receiving Inspecting
The Bently Nevada 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface module is shipped with
Vibration Transducer Interface modules installed on the backplane and in the
enclosure or as separate units depending on ordering information. Carefully
remove all equipment from the shipping containers and inspect the equipment for
shipping damage. If damage is apparent, file a claim with the carrier and submit
a copy to Bently Nevada Corporation. Include part numbers and serial numbers
on all correspondence. If no damage is apparent and the equipment is not going
to be used immediately, return the equipment to the shipping containers and
reseal until ready for use.
1.2 Handling and Storage Considerations
Store the 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface module and any other Bently Nevada
equipment in an environment free from potentially damaging conditions such as
high temperature, excessive humidity, or a corrosive atmosphere.
Circuit boards contain devices that are susceptible to damage when exposed to
electrostatic discharge. Damage caused by obvious mishandling of the board will
void the warranty. To avoid damage, observe the following precautions in the
order given.
!Do not discharge static electricity onto the circuit board. Avoid tools or
procedures that would subject the circuit board to static damage. Some
possible causes include ungrounded soldering irons, nonconductive plastics
and similar materials.
!Personnel must be grounded with a suitable grounding strap (such as 3M
Velostat No. 2060) before handling or maintaining a printed circuit board.
!Transport and store circuit boards in electrically conductive bags or foil.
Use extra caution during dry weather. Relative humidity less than 30% tends to
multiply the accumulation of static charges on a surface.
1.3 Disposal Statement
Customers and third parties that are in control of product at the end of its life or
at the end of its use are solely responsible for proper disposal of product. No
person, firm, corporation, association or agency that is in control of product shall
dispose of it in a manner that is in violation of United States state laws, United
States federal laws, or any applicable international law. Bently Nevada
Corporation is not responsible for disposal of product at the end of its life or at
the end of its use.

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
2
2. General Information
This section describes the Bently Nevada 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface
system and lists the Bently Nevada 3500 Monitors and transducer systems with
which it is designed to be used.
A Vibration Transducer Interface works in an intrinsically safe system as a
galvanic isolator. This isolator acts as an interface between a transducer
installed in a hazardous environment and a 3500 monitoring system installed in a
safe environment.
Although a galvanic isolator and a zener barrier are both intrinsically safe
interfaces that provide the same level of protection, they work differently. A
zener barrier works by shunting excess current and voltage to ground. A
galvanic isolator provides intrinsic safety by isolating power, ground, and signal
in the hazardous area from the safe area. This isolation removes the need to
provide an earth ground in the hazardous environment. With the exception of the
Aeroderivative Interface Module, all transducers can "float" in the hazardous
environment.
A drawback to using galvanic isolation instead of zener barriers is that galvanic
isolation introduces a small amount of noise and signal inaccuracy to the
transducer output as listed in the data sheet at the end of this manual. This error
can cause some concern in certain applications as described in the section
Checking the Accuracy of the Output Signal, page 5.
The Bently Nevada 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface can receive inputs from the
following approved Bently Nevada transducers:
•3300 XL ProximitorTransducer
•3300 5 mm/8 mm ProximitorTransducer
•7200 5 mm/8 mm ProximitorTransducer
•Accelerometer Interface Module (part number 23733-03)
•Aeroderivative Interface Module (part number 86517) (Velocity Only)
•3300 REBAMMicroPROXTransducer
•7200 REBAMMicroPROXTransducer
The 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface system can be used in thrust, DC,
Keyphasor and vibration systems. The following 3500 monitors have been
tested with the 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface system:
•3500/25 KeyphasorMonitor
•3500/40 ProximitorMonitor
•3500/42 Proximitor/Seismic Monitor
•3500/44 Aeroderivative Monitor
•3500/50 Tachometer Monitor
Note: The I/O modules of the above 3500 monitors must be External
Terminations.

Section 2 — General Information
3
2.1 The Parts of the Interface System
Part Part Name Function of the part
Vibration
Transducer
Interface Module
A galvanic isolator that isolates safe-area
circuitry from hazardous-area circuitry.
Backplane
(Vibration)
Backplane
(Keyphasor)
A circuit board that distributes power to
the Vibration Transducer Interface
modules and sends transducer output
signals to the 3500 Monitoring System.
The backplane is a safe-area component.
An 8-position backplane for proximity and
acceleration measurements is used with
the 3500/40, 3500/42, 3500/44 and
3500/50 Monitors. A 4-position backplane
for Keyphasormeasurements is used
with the 3500/25 Keyphasor Monitor.
Hazardous Area
Connector A screw clamp connector for attaching
transducer wiring to the hazardous area
terminals at the top of the Vibration
Transducer Interface module.
Interface Cables Cables that interface the backplanes to
the 3500 Monitoring System. Order these
separately.
Earth Rail An accessory that comes with the
backplane and provides a convenient
earth termination point.
Also included with the standard interface system package are a mounting kit and
a manual. The mounting kit contains the following parts:
Item Qty Where Used
Pan head self tapping screw 4 DIN-rail mount
Spacer 4 DIN-rail mount
DIN-rail mounting foot 4 DIN-rail mount
Plain washer, M4 4 Surface/DIN-rail mount
Locking washer, M4 4 Surface/DIN-rail mount
Retaining Washer 4 Surface/DIN-rail mount
M4x20 screw 4 Surface mount

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
4
M4x10 spacer 4 Surface mount
Retaining washer, M4 4 Surface mount
Power supply Connectors 2 Power Input
An enclosure is also available with the isolator system as optional accessories.

Section 3 — Installing the Hardware
5
3. Installing the Hardware
This section shows how to install the parts of the 3500 Galvanic Interface onto
the backplane and then how to mount the backplane on a surface or in an
enclosure. The next section, Wiring the Hardware, shows how to connect the
installed interface to vibration transducers, monitors, and power supplies.
3.1 Before You Begin
Before you install the 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface, use the following two
checklists to verify that the installation will meet approval requirements and to
check the accuracy of the output signal.
3.1.1 Verifying that the Installation will Meet Approval
Requirements
•Make sure all installation work is carried out in accordance with all relevant
local standards, codes of practice, and site regulations.
•Check that the hazardous-area equipment complies with the descriptive
system document.
•If you cannot verify that the system meets approval requirements, refer to the
certificate for clarification of any aspects of intrinsic safety or contact Bently
Nevada or your local Bently Nevada representative for assistance.
•Refer to the General Information section for appropriate applications.
3.1.2 Checking the Accuracy of the Output Signal
Before installing a 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface system, use the information in
Section 3.1.2.1., Section 3.1.2.2. and the Specifications, to evaluate how the
Vibration Transducer Interface module will affect your instruments.
Note:
The 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface can introduce additional ac and dc errors.
3.1.2.1 Affects on Monitors
The 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface system could affect the following types of
monitors. We recommend that you verify the vibration levels in the field after you
install the 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface system.
!3500/25 KeyphasorMonitor
!3500/40 ProximitorMonitor
!3500/42 Proximitor/Seismic Monitor
!3500/44 Aeroderivative Monitor
!3500/50 Tachometer Monitor

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
6
3.1.2.2 Affects on Diagnostic Systems
Be aware of the additional phase, gap, and vibration errors that will be present
(refer to the Specification sheet at the end of this manual). The following
measurements are affected by the additional voltage errors:
•Shaft centerline plots are affected by the dc offset.
•Gap measurements are affected by the dc offset.
•The additional phase error could affect orbit plots. The amount of error
depends on the frequency of the vibration.
•The additional ac error will affect vibration measurements.
3.2 Installing Backplane Hardware
These procedures show how to attach Vibration Transducer Interface modules,
connectors and the earth rail to the backplane. Before you begin, take note of
the following precaution about installing components in hazardous areas:
WARNING
Do NOT install a backplane or
other safe area components in a
hazardous environment. An
explosion may occur if safe
area components are installed
in a hazardous environment.
Install the 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface in a safe environment unless the
modules are protected by a locally acceptable explosion proof technique.

Section 3 — Installing the Hardware
7
3.2.1 Installing the Vibration Transducer Interface Modules
Install Vibration Transducer Interface modules on the backplane (refer to the
3500 Field Wiring Package (130432-01)). To install a Vibration Transducer
Interface module:
1. Attach a position label (NOT supplied) where shown if necessary. The label
identifies the location of the module on
the backplane.
2. Position the Vibration Transducer
Interface module onto the appropriate
safe-area/power supply connector on
the backplane as shown and insert it
onto the connector. This connects the
module to the appropriate safe-area
connector (pins 7 and 8) and to the
power supply.
3. Tighten the two mounting screws
where shown.
1) Position Label
2) Mounting Screw
3) Safe Area/Power Supply Base
Connector
4) Backplane
3.2.2 Installing the Hazardous-area Screw Clamp Connector
1. Trim the insulation of the wire back 12 mm. The wire
should be between 16 and 22 AWG.
2. Insert the wires according to the socket assignment
(see the 3500 Field Wiring). Tighten the screws of the
connector as shown.
3. Attach a tag label where shown if necessary.
4. Position the hazardous area connector over the
appropriate Vibration Transducer Interface module
and insert as shown.

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
8
1
3
2
4
0V
V2
0V
V1
0V
V2
0V
V1
V1
0V
V2
0V
0V
V2
0V
V1
3
3
3
4
4
4
3.2.3 Connecting the Power Supplies
Power is supplied to the backplane through two power supply connectors. To
install the power supply connectors:
1. Connect the power supply connectors to the independent supply sources as
illustrated and according to the 3500 Field Wiring Package (130432-01).
Each connector can provide connection for both primary and secondary
power supplies to the backplane. Both connectors are functionally equivalent
so that either or both of these connectors can be used as shown. Be aware
that the maximum wire gauge is 12 AWG (2.5 mm2).
1) Vibration Backplane
2) Keyphasor Backplane
3) Power Supply
4) Power Supply Connector
To check the power supply status:

Section 3 — Installing the Hardware
9
1
23
3
Verify that at least one power supply LED is on. One LED will be on for each
power supply that is installed.
1) Vibration Backplane
2) Keyphasor Backplane
3) Power Supply LEDs
3.2.4 Installing the Earth Rail
An earth rail provides a termination point for shield and spare wires. It also
provides a grounding location for transducers if local wiring codes require an
earth ground. Reference local wiring codes for any wiring restrictions.
The 3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface system does not require a high integrity
earth and the transducers can be left floating or be earthed at any one point.
Refer to the 3500 Field Wiring Package (130432-01). Do not wire transducer
common to earth. A "floating" system is recommended, except for the
Aeroderivative Interface Module (part number 86517) which requires a grounded
system for noise immunity.

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
10
12
33
3
3
44
To attach the earth rail:
1. Locate the earth rail over the "C" holes of the backplane.
1) Vibration Backplane
2) Keyphasor Backplane
3) “C” Holes
4) Earth Rail Post Positions
2. Mount the earth rails to the backplane
with four M3x12 screws and washers.
1) Earth Terminal
2) Plastic Rivet
3) Earth Rail
4) Earth Rail Post
5) M3 x 12mm Screw and
Washer (2 places per post)
6) Backplane
7) “C” Holes

Section 3 — Installing the Hardware
11
3.2.5 Installing the Backplane
Install a backplane to one of the following:
•A flat surface
•A "G" or "T" type DIN-rail
•A Bently Nevada enclosure
If you order an enclosure with the interface system, the system will be shipped
with the backplane installed within the enclosure. This installation will use some
mounting kit hardware, specifically, those parts pertaining to a surface
installation.
3.2.6 Installing the Backplane onto a Surface
1. Drill and tap holes into the surface that the backplane will mount at the
locations marked "A". See page 15 for backplane dimensions.
1) Mounting
Hole “A”
2) M4 x 12mm
Screw
3) Locking
Washer
4) Plain Washer
5) Backplane
6) M4 x 10mm
Spacer
7) M4
Interference
Washer
8) Tapped
Mounting
Surface
2. Mount the backplane using the spacers and screws as shown.
3.2.7 Installing the Backplane onto a DIN-rail
The mounting hardware kit will have a combination "G" and "T" DIN-rail mount.
For simplicity, only a T-section illustration is shown. Both "G" and "T" DIN-rail
mounts follow the same procedure.
To attach the backplane to a "G" or "T" DIN-rail:

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
12
1. Attach the DIN-rail mounting feet onto two lengths of "G" or T-section DIN
rails.
1) Mounting
Hole “A”
2) DIN Rail
Mounting
Foot
3) M4 x 20mm
Screw
4) Locking
Washer
5) Plain
Washer
6) Backplane
7) M4 x 10mm
Spacer
8) M4 Interference Fit Washer
2. Position the screws and washers through the backplane mounting holes
marked "A" as shown.
3. Attach the backplane to the mounting feet with the fixing screws as shown.
Dimensions: Millimetre (inch)

Section 3 — Installing the Hardware
13
3.2.8 Installing the Backplane into an Enclosure
The Bently Nevada enclosure includes a mounting plate with tapped holes that
correspond to the "A" holes of the backplane. Position and install the backplane
as shown using the surface mount portion of the mounting kit.
Dimensions: Inch (millimetre)

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
14
3.2.8.1 Installing the Enclosures to a Surface
Install the enclosure to a surface use the following procedure:
1. Attach wall-mounting lugs to the underside of the enclosure as shown.
Dimensions: Inch (millimetre)
1) Wall Mounting Lug
2) Alternate Position
2. Secure with a fixing screw. Slide the screw into the TOP of the enclosure
and screw it into the mounting lug. This requires a long screwdriver.
3. Mount the enclosure on a surface at the appropriate centers. Refer to the
data sheet at the end of this manual.

Section 3 — Installing the Hardware
15
3.3 Backplane Dimensions (Vibration)
Dimensions: Inch (millimetre)
3.4 Backplane Dimensions (Keyphasor)
Dimensions: Inch (millimetre)

3500 Galvanic Isolator Interface Manual
16
4. Wiring the Hardware
The 3500 Field Wiring Package (130432-01) shows how to connect transducers, power
supplies, and monitors to the interface modules. This section shows the location of the
connecting terminals and contains important precautions about safe and hazardous
area connections that you must consider before you use the drawings to connect
components.
WARNING
NON-Intrinsically Safe and Intrinsically Safe wiring MUST be separated by
50 mm minimum. Reference local wiring codes before wiring the
installation.
Table of contents
Other Bently Nevada Control Unit manuals