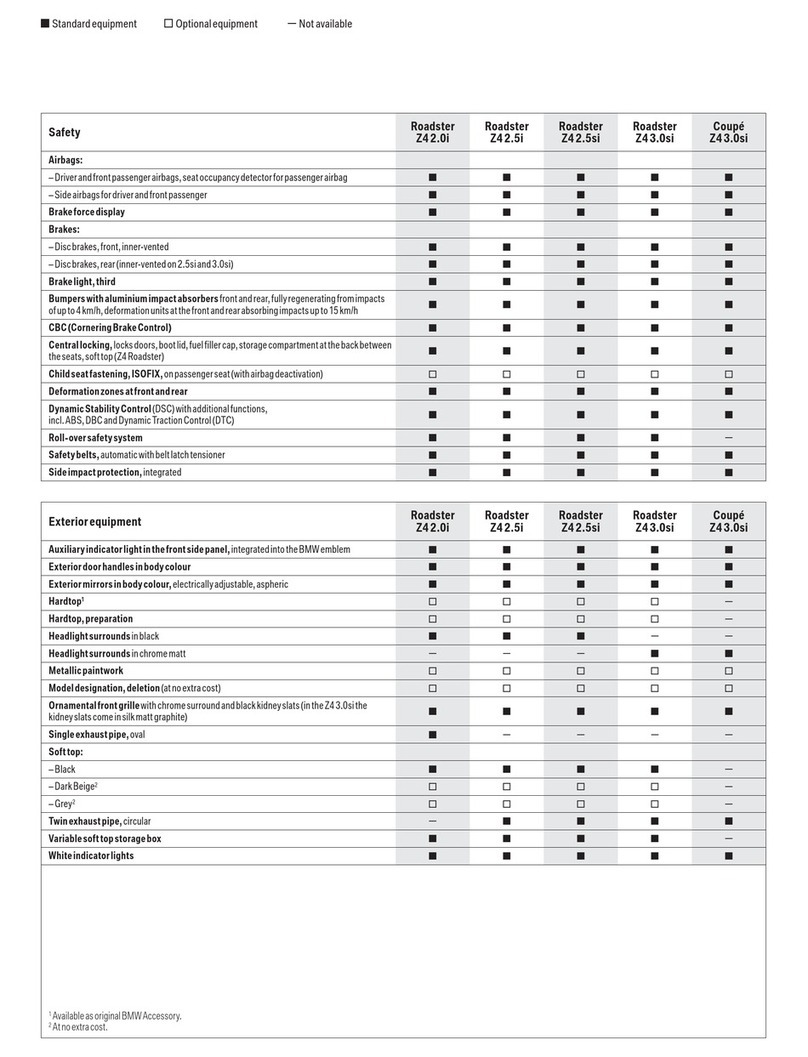
F12�Chassis�Dynamics
Contents
1. Introduction.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................1
1.1. Driving�dynamics�and�comfort..........................................................................................................................................................1
1.2. Bus�system�overview....................................................................................................................................................................................... 2
2. Models...............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................5
2.1. Comparison..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
3. Chassis�and�suspension................................................................................................................................................................................................. 6
3.1. Front�axle............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
3.1.1. Technical�data............................................................................................................................................................................7
3.1.2. Service�Information........................................................................................................................................................... 7
3.2. Rear�axle...............................................................................................................................................................................................................................8
3.2.1. Technical�data........................................................................................................................................................................10
3.2.2. Service�Information.......................................................................................................................................................10
3.3. Suspension/dampers................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
3.3.1. Electronic�Damper�Control�(EDC)..........................................................................................................11
3.4. Wheels�&�Tires......................................................................................................................................................................................................12
3.5. Tire�Pressure�Monitor�System..................................................................................................................................................... 13
3.5.1. System�function................................................................................................................................................................. 13
3.5.2. System�overview............................................................................................................................................................... 15
3.5.3. System�wiring�diagram............................................................................................................................................16
3.5.4. Notes�for�Service............................................................................................................................................................. 17
4. Brakes............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................19
4.1. Service�brakes........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 19
4.2. Electromechanical�Parking�Brake�(EMF)...................................................................................................................... 20
4.2.1. System�overview............................................................................................................................................................... 21
4.2.2. System�wiring�diagram............................................................................................................................................23
4.2.3. System�structure.............................................................................................................................................................. 24
4.2.4. System�function................................................................................................................................................................. 24
5. Steering......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................33
5.1. Basic�steering..........................................................................................................................................................................................................34
5.1.1. System�overview............................................................................................................................................................... 34
5.1.2. System�wiring�diagram............................................................................................................................................36
5.2. Integral�Active�Steering........................................................................................................................................................................... 37
5.2.1. Functional�ranges............................................................................................................................................................ 38
5.2.2. System�wiring�diagram............................................................................................................................................41
5.2.3. EPS�with�24�V.......................................................................................................................................................................43
5.2.4. Rear�axle�slip�angle�control�HSR............................................................................................................. 50