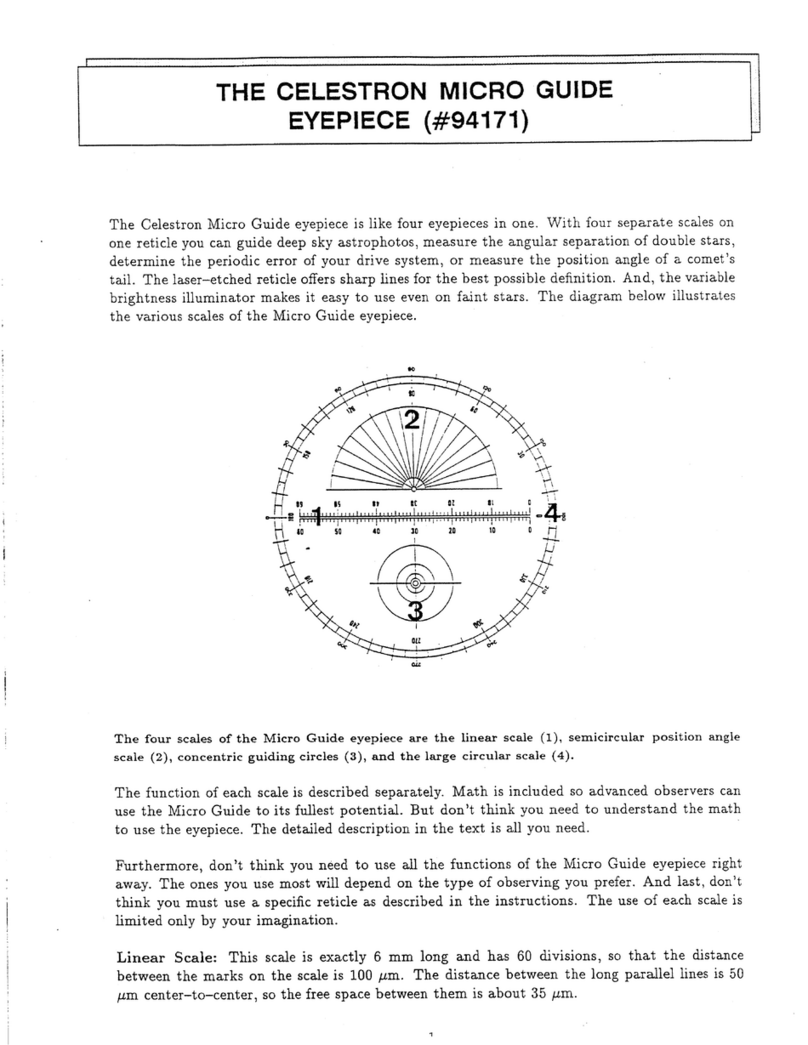
6
GLOSSARY
Altazimuth mount - the simplest type of mount, with two motions: altitude (up and down) and azimuth (side-to-
side). “Mount” refers to the parts of the telescope supporting the tube, which carries all the telescope’s optics. The
mount is made up of the ground plate, or base, and the rocker box.
Altitude clutch adjustment screw - used on the Star Hopper 4½to adjust the clutch tension on the altitude axis.
Altitude hubs - used on the Star Hopper 6and 8 to provide an axis of rotation for altitude adjustments.
Aperture - the diameter of the main optical element of the telescope; either the primary mirror or objective lens.
The larger the aperture, the more light the telescope collects. More light creates a brighter, sharper image.
Barlow lens - these lenses are optional accessories that double the magnifying power of your eyepieces by
increasing their effective focal length. For example, an 18mm eyepiece mounted on a 2x Barlow lens would have
the magnifying power of a 9mm eyepiece. It’s like having two eyepieces in one - an economical way to increase
your range of magnifications without buying new eyepieces.
Collimation - the proper alignment of the optical elements in a telescope, which is critical to achieving optimum
results. Poor collimation results in visual aberrations and distorted images. A full description of how to collimate
your telescope follows on pages 12 - 14.
Collimation cap - a tool for aligning the optics in a telescope. The optics to be aligned in the Star Hopper
telescopes are the primary mirror and the secondary mirror.
Deep-sky objects - celestial objects outside the boundaries of our solar system.
Dobsonian telescope - simple, azimuth mounted Newtonian telescope.
Extended objects - large celestial objects, other than stars, such as nebulae and galaxies.
Field of view - the size, in degrees, of the area you can see through the eyepiece of your telescope.
Finderscope - a low power telescope with cross hairs mounted to the side of a higher powered telescope, used to
locate objects more easily.
Focal length - the distance from the optical center of the lens to the point where the incoming light rays converge,
creating a clear, focused image.
Inner diameter - the measured diameter of the inside of the telescope tube.
Newtonian reflecting telescope - generally use a concave parabolic primary mirror to collect and focus incoming
light into a flat secondary mirror, which reflects the image into the eyepiece.
Off-axis coma - associated mainly with parabolic reflector telescopes, this is a blur caused by the spherical
aberration of oblique rays of light passing through a lens. The blur will be more pronounced near the edges of the
field of view and have a V-shaped appearance.
Pinnacle mirror cell - a stress free support for the primary mirror, made of aluminum to conduct heat away from
the mirror for quicker “cool down” time. The cell is designed to allow air flow within the telescope tube, assisting
the entire system to reach thermal equilibrium rapidly.
Primary mirror - gathers incoming light and forms a sharply focused image of the object being viewed.
Refracting telescope - a long, thin tube in which light passes in a straight line from the front objective lens
directly to the eyepiece at the opposite end of the tube.
Secondary mirror - reflects light from the primary mirror to the eyepiece. It’s also know as a diagonal mirror
because it is at 45°with respect to the optical axis.
“Seeing” or “seeing conditions” - refer to the stability of the atmosphere, transparency and sky illumination. See
pages 20 and 21 for a full description.
Thermal turbulence - turbulence caused by temperature variations. Some sources are differences in temperature
between the telescope tube and the air within it, or viewing near a heat source, such as a parking lot releasing
stored daytime heat.
Tube currents - convection currents within the telescope caused by differences in temperature between the air and
the telescope tube. These currents form near the wall of the telescope tube, therefore the Star Hopper’s oversized
tube is very beneficial in reducing interference caused by currents.
V-Spectrum Low Thermal Mass Optical System - a unique Celestron optical system utilizing a molded Pyrex
mirror for reduced thermal mass, in conjunction with the pinnacle mirror cell (see above).