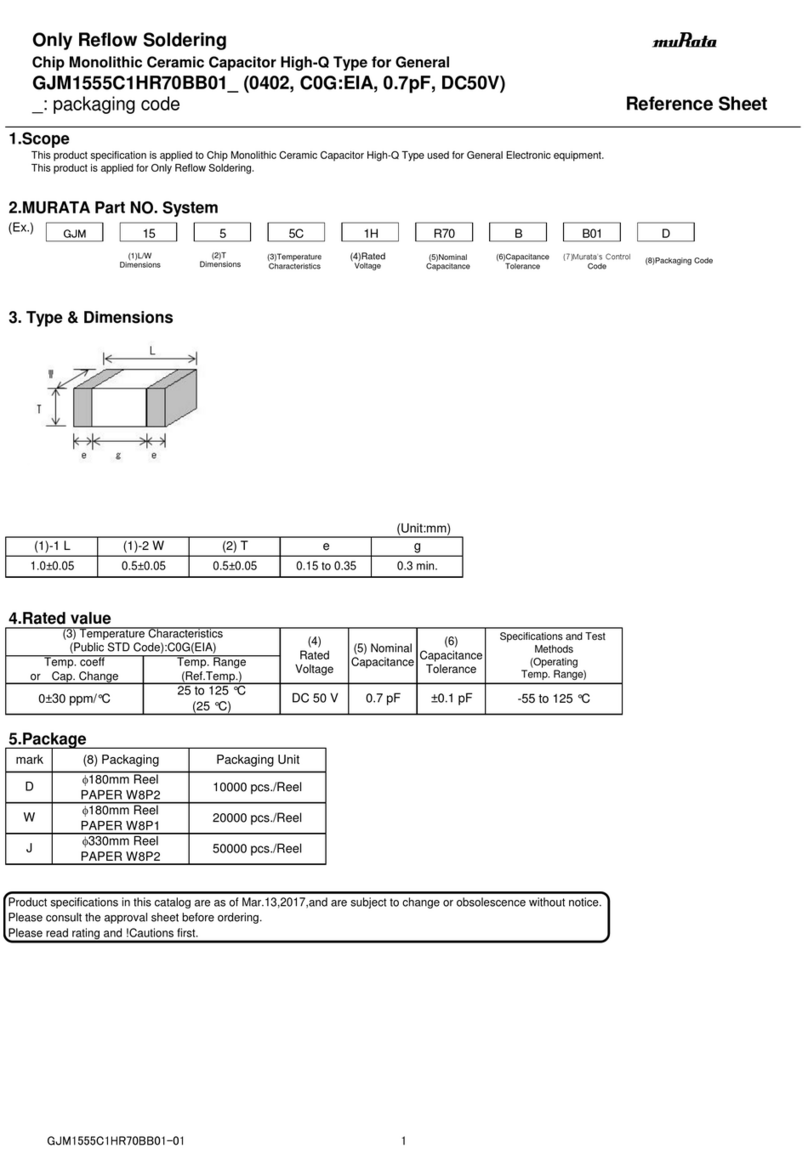
06
NWC1 Series Self-healing Low Voltage Shunt Capacitors
Table 7 Analysis and Troubleshooting of Faults
No.Faults Cause analysis Troubleshooting method
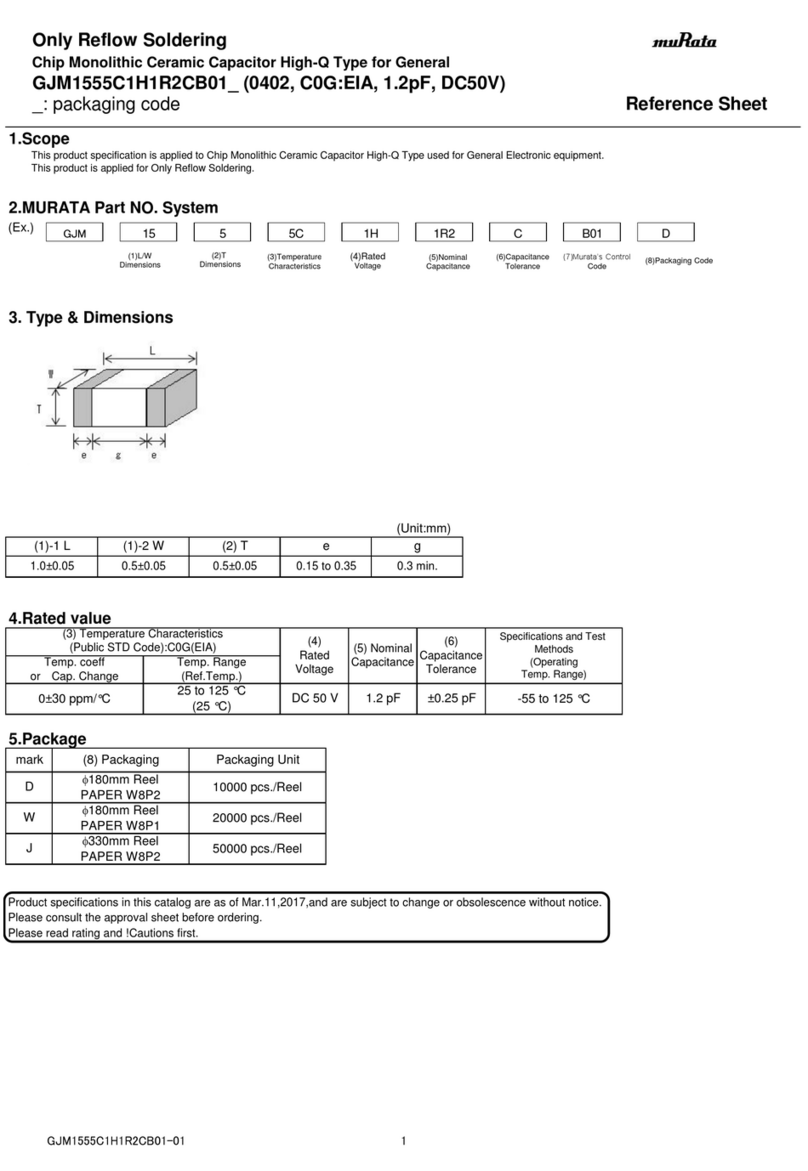
1
The measured current of a newly
connected capacitor is much
smaller than the rated current on its
nameplate (same for multiple
capacitors).
If a capacitor with higher rated
voltage is connected to 380V grid,
the actual output current will be
much smaller, which is normal.
There is nothing wrong with the
capacitor, it is just derated.
User should determine the status
of a capacitor based on its
measured capacitance value (μF).
The actual operating current IC=
Uc/UN ×IN
2
The current of the capacitor is
closed to rated current when it is
first put into operation, but the
current drops after a period of time.
The current drops as the
capacitance value of the
capacitance decreases.
There are several reasons for
capacitance decrease such as
improper use, large harmonic or
quality defect.
Find out the reason and solve the
problem. User must replace the
capacitor if the capacitance value
drops below 50%.
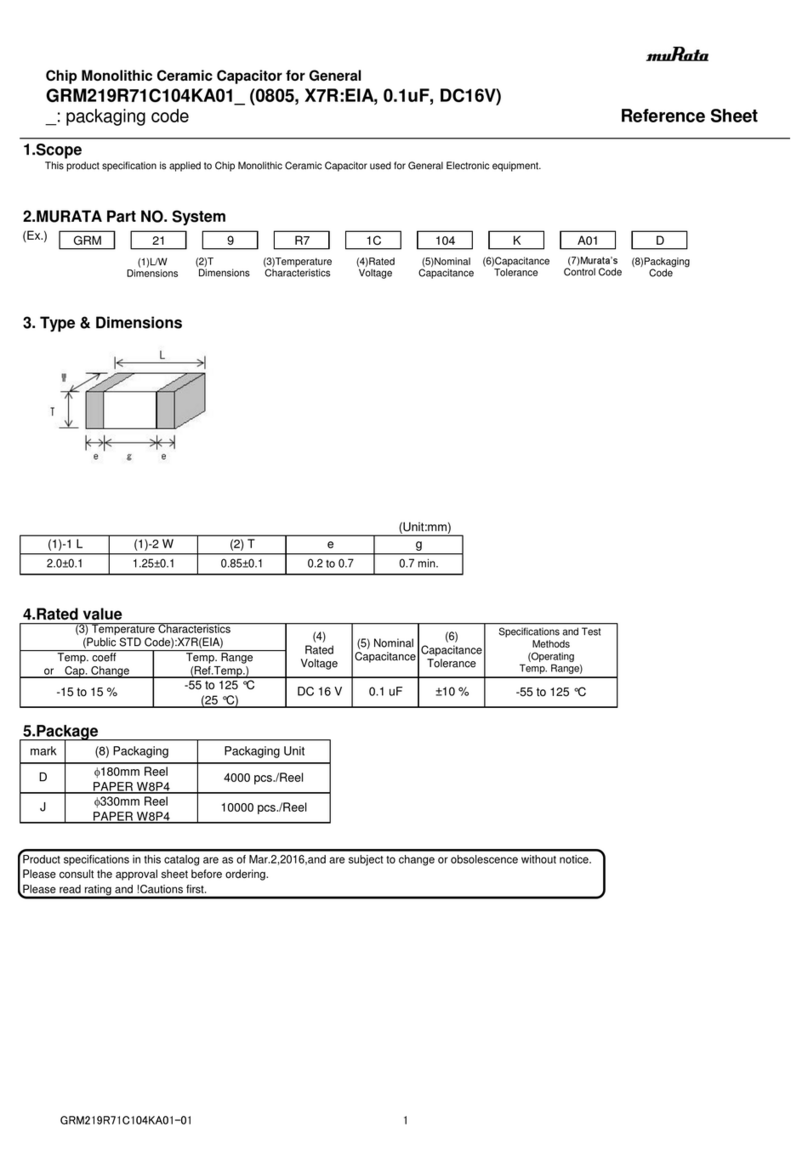
3
The terminal screws of the capacitor
generate heat or even turn into
black during operation.
The wire nuts are loose or not
tightened properly during
installation.
If the nuts are tightened properly,
the reason might be long-term
overcurrent due to harmonic
current amplification in the grid.
Tighten the nuts, replace nuts, flat
gaskets, elastic washer if necessary.
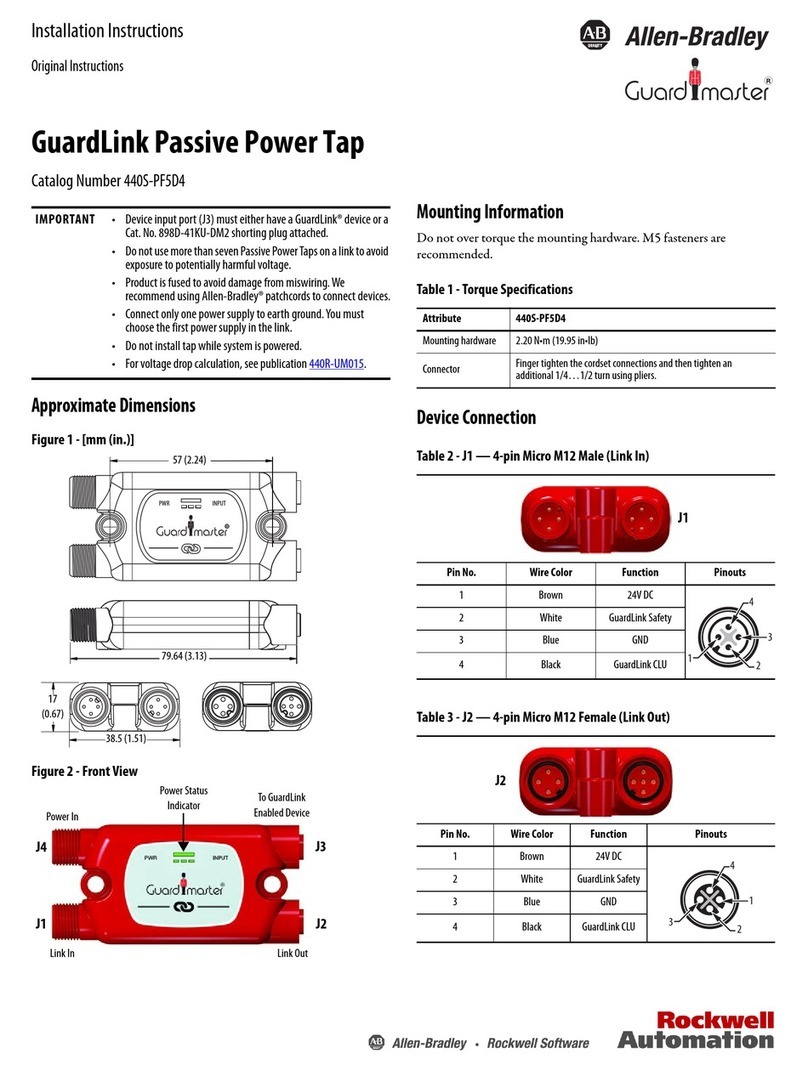
4
The fuse in branch circuit blows
frequently (or miniature circuit
breaker trips frequently); the CJ19
contactor fuses; the current-limiting
resistance burns frequently; the
surface of XD1 current-limiting
reactor case cracks, etc.
These symptoms are typical when
the grid harmonic is too big or
there is intermittent resonance in
the grid.
Conduct grid harmonic test or
check if there are harmonic
sources such as frequent
converter, rectifier, intermediate
frequency furnace or electric-arc
furnace installed at load end. See
3.3.2 for harmonic suppression
measures.
5
Sometimes there is buzzing sound
in the cabinet during operation.
There is harmonic current passing
through the capacitor.
User must take harmonic
suppression measures if the
harmonic current is too big
(same as 4)
6
There is significant current increase
when adding a capacitor into a
group.
Either abnormal power frequency
resonance (underloading), or
harmonic current amplification or
there is resonance.
Same as 4
7
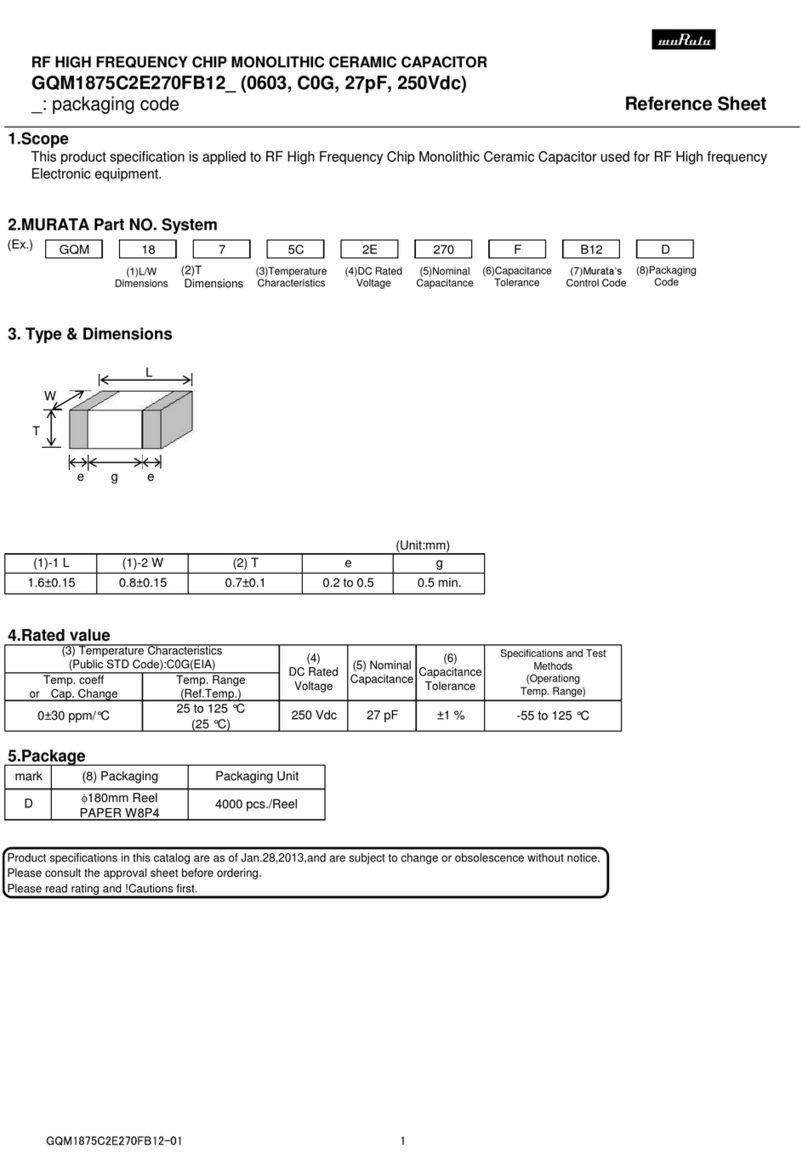
Slight deformation occurs to the
capacitor case after the capacitor
has been used for a period of time,
and no current can be detected.
Long-term overtemperature or
overcurrent operation of the
capacitor which cause self-healing
breakdown of internal components
that generates gases and increases
internal pressure. When the
overpressure protector breaks,
slight deformation can occur to
the capacitor case.
Use heat dissipation measures to
lower the ambient operating
temperature of the capacitor.
Select products with higher rated
voltage. Harmonic suppression
measures are the same as
described in 4.
9 Warranty Period, Environmental Protection and Law & Regulations
9.1 Warranty period
The warranty period of the product is 30 months from production (delivery) date if the product is kept
under normal storage conditions and the package or the product itself is in good condition. If the warranty
period has expired, please inspect the product and make sure it meets all the requirements before installing
and using the product. The following circumstances are not within the scope of warranty (excluding repair
or replacement):