PILOT’S OPERATING HANDBOOK
SECTION 0
Edition 0 -- October 31, 2013
Rev. 1
Page 0.5A
SOCATA MODIFICATIONS - INDEX
NOTE
The standardized name for SOCATA modifications is : MODXXX-XX
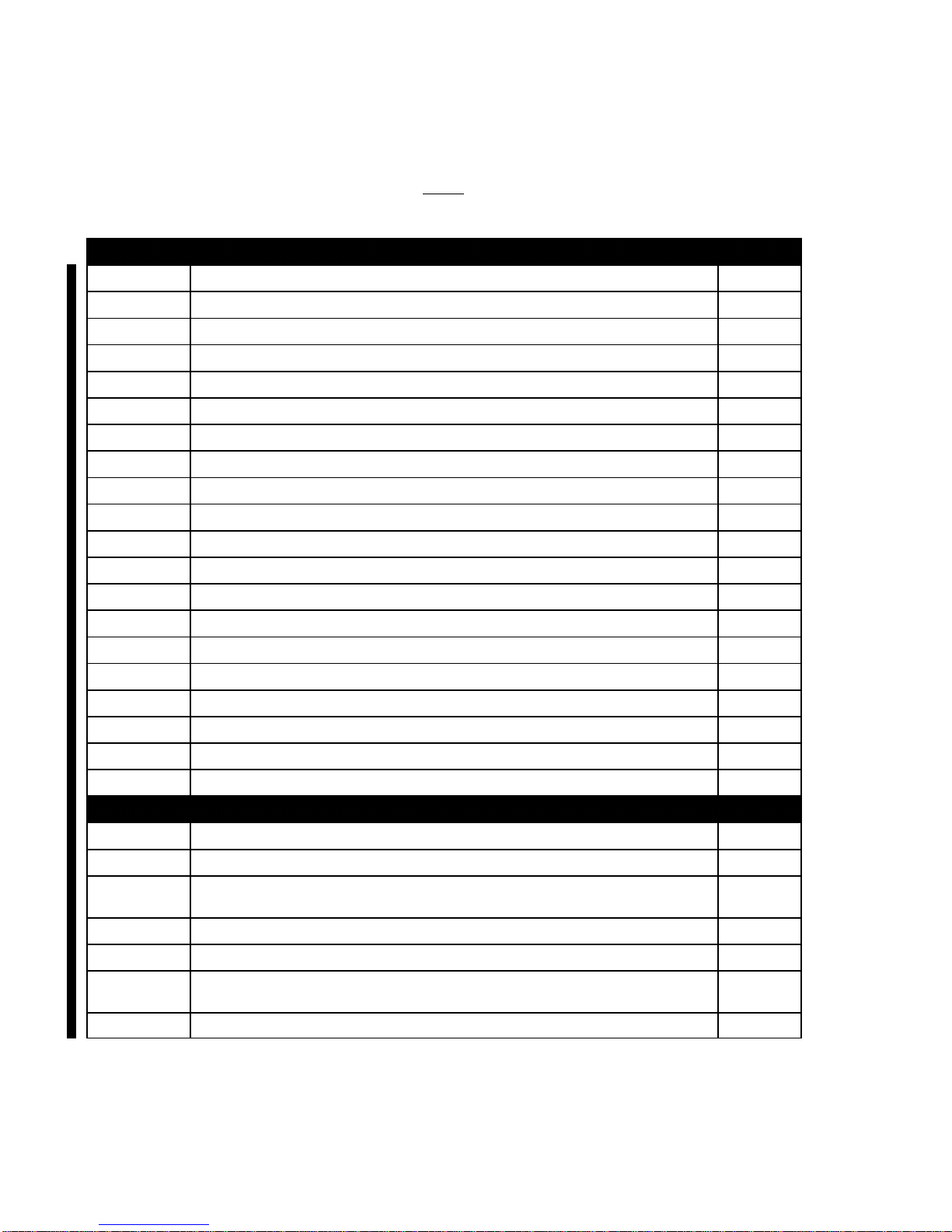
MOD70 No. SUBJECT CLASSIF.
70-0234-24 Electrical distribution and primary distribution Major
70-0322-00 Evolution of wing tips, tail cone and lights Major
70-0323-71 Propulsion efficiency improvement Major
70-0324-00 Modified pedestal and Single Lever Power Control Assy Major
70-0325-21 Automatic altitude cabin selection Major
70-0330-00 New metal-metal bonding Major
70-0336-26 Fire extinguisher relocation in cockpit minor
70-0341-32 New TBM700 Landing Gear Control and Display Panel minor
70-0342-52 Lower main landing gear doors minor
70-0346-55 New rudder ledge contour minor
70-0347-53 Improved G1000 instrument panel minor
70-0348-27 Control wheel CROUZET minor
70-0357-71 Takeoff and landing at 850shp - Increase of takeoff power Major
70-0359-71 Air inlet inertial separator actuator minor
70-0361-32 Landing gear wide washer minor
70-0364-25 Modified pylon upholstery minor
70-0369-25 Obsolescence of cabin lighting LED and lenses minor
70-0370-52 Wide door motor obsolescence minor
70-0372-33 Back lighted panels minor
70-0373-33 PL1 (Circuit breaker panel) lighting and label minor
70-0374-33 Servicing plugs minor
70-0375-28 Modification of MT40 fuel pressure sensor installation minor
70-0376-33 Pedestal lighting improvement minor
70-0379-23 Capability for future integration of the CPDLC (Controller Pilot Data Link
Communication) antenna minor
70-0381-31 M51 Hourmeter - Improvement of flight time calculation minor
70-0383-00 Software V14.01 - G1000 Integrated Flight Deck for TBM 850/900 Major
70-0384-77 TORQUE & IGNITION functions maintained during switching of S1 from
"NORMAL" position to "EMERGENCY" position minor
70-0385-23 AVIONICS MASTER and GROUND CLEARANCE architecture modification minor