DG NVMeG4-IP User manual

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 1
NVMe IP with PCIe Gen4 Soft IP demo instruction
Rev1.1 20-Apr-20
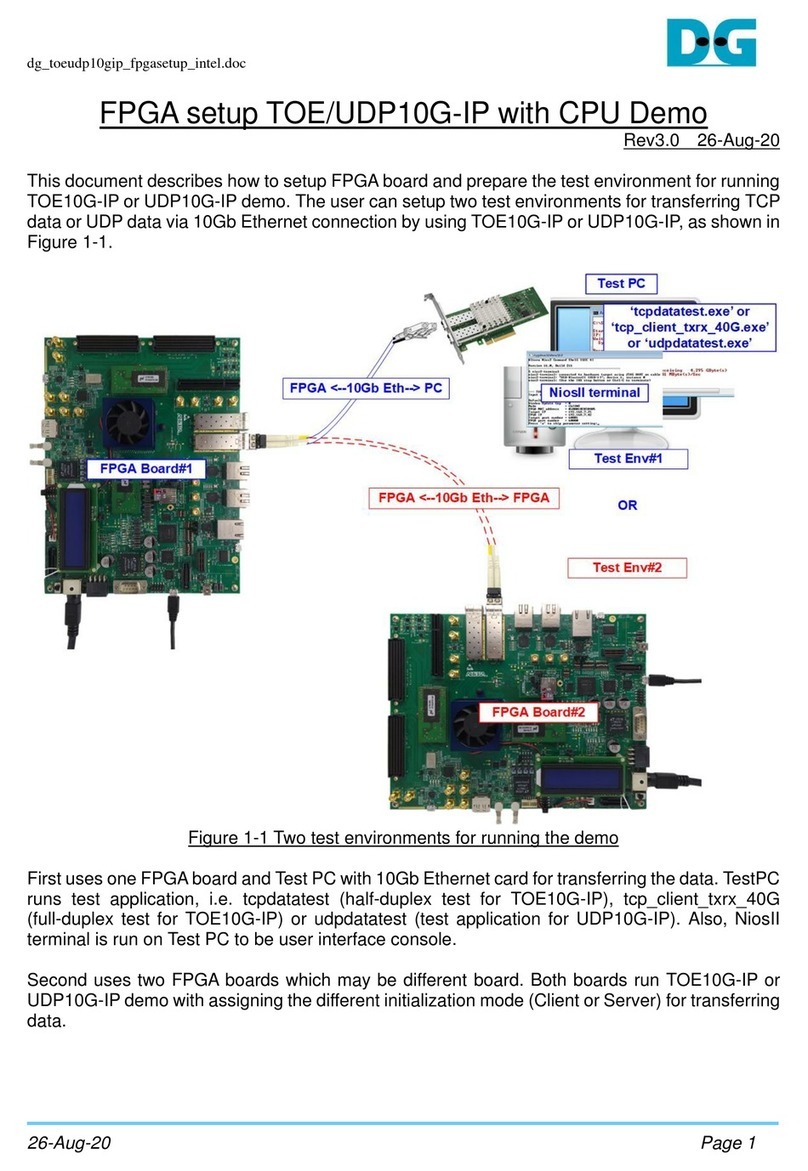
This document describes the instruction to run NVMeG4-IP demo on FPGA development board
by using the PCIe adapter board, AB18-PCIeX16 board. The demo is designed to write and verify
data with NVMe Gen4 SSD. User controls the test operation through Serial console.
1 Environment Requirement
To run the demo on FPGA development board, please prepare following environment.
1) Supported FPGA Development board: VCU118
2) PC installing Xilinx programmer software (Vivado) and Serial console software such as
TeraTerm
3) AB18-PCIeX16 board, provided by Design Gateway.
https://dgway.com/ABseries_E.html
4) ATX power supply for AB18.
5) Xilinx power adapter for FPGA board
6) PCIe Gen4 NVMe SSD
7) Two micro USB cables for programming FPGA and Serial console, connecting between
FPGA board and PC

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 2
Figure 1-1 NVMeG4-IP demo environment setup on VCU118

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 3
2 Demo setup
1) Power off system. Then, connect ATX power supply to AB18-PCIeX16 board and Xilinx
power adapter to FPGA development board.
Figure 2-1 Power connection
2) Confirm that,
•Two mini jumpers are inserted at J5 connector on AB18.
•Connect FPGA Side (A-side) on AB18 to PCIe connector on FPGAboard
•Connect Gen4 NVMe SSD (PCIe) to device side (B-Side) on AB18, as shown in
Figure 2-2.
Warning: Please confirm that NVMe SSD is inserted in the correct side of AB18
(B-side, not A-side) before power on system.
Figure 2-2 Connect Adapter board to NVMe SSD (PCIe) and FPGA board

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 4
3) Connect two micro USB cables between FPGAboard and PC for FPGAprogramming and
Serial console.
Figure 2-3 USB cable connection
4) Power on FPGA development board and AB18 adapter board.
Figure 2-4 Turn on power switch
5) On PC, the additional COM ports are detected after connecting USB cables to FPGA
board. There are more than one COM ports detected. Select Standard COM port, COM11
in Figure 2-5.
On Serial console, the setting is as follows.
Buad rate=115,200, Data=8-bit, Non-Parity, and Stop = 1.
Figure 2-5 Select and set COM port

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 6
7) Check LED status on FPGA board. The description of LED is as follows.
Table 2-1 LED Definition
GPIO LED
ON
OFF
0
Normal operation
Clock is not locked or reset button is pressed
1
System is busy
Idle status
2
IP Error detect
Normal operation
3
Data verification fail
Normal operation
8) After completely FPGA programming, LED[0] and LED[1] turn on until finishing the
initialization process. After that, LED[1] turn-offs.
Figure 2-7 LED status after finishing program configuration file and PCIe initialization
9) On the console, the message is displayed to show current status as follows.
•“Waiting IP initialization” is displayed when starting system initialization.
•After finishing IP initialization, Main menu is shown on the console as shown in Figure
2-8.
Figure 2-8 Main menu after finishing initialization

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 7
3 Test Menu
3.1 Identify Command
Select ‘0’ to send Identify command to NVMe SSD.
Figure 3-1 Test result when running Identify command
After finishing the operation, the SSD information outputfrom Identifycommand is displayed.
The console shows three values.
1) SSD model number: This value is decoded from Identify controller data.
2) SSD capacity: This value is signal output from NVMeG4 IP.
3) Data size per LBA: This value is signal output from NVMeG4 IP. Two values are
supported, i.e. 512 byte and 4 Kbyte.

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 8
3.2 Write Command
Select ‘1’ to send Write command to NVMe SSD.
Output performance
Input test parameter
Current transfer size
12
3
Normal Green: User input
Blue: Output to user
Figure 3-2 Input and test result when running Write command
User inputs three parameters as follows.
1) Start Address: Input start address to write SSD as 512-byte unit. The input is decimal unit
when user inputs only digit number. User can add “0x” to be a prefix for hexadecimal unit.
When LBA unit of SSD is 4 Kbyte, this input must be aligned to 8.
2) Transfer Length: Input total transfer size as 512-byte unit. The input is decimal unit when
user inputs only digit number. User can add “0x” to be a for hexadecimal unit. When LBA
unit of SSD is 4 Kbyte, this input must be aligned to 8.
3) Test pattern: Select test data pattern for writing to SSD. There are five patterns, i.e. 32-bit
increment, 32-bit decrement, all 0, all 1, and 32-bit LFSR counter.
After all inputs are valid, the operation begins. During writing data, current transfer size is
displayed on the console every second to show that system is still alive. Finally, total size,
total time usage, and test speed are displayed on the console after finishing the operation.

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 9
Figure 3-3 Example Test data of the 1st and 2nd 512 byte by using increment/LFSR pattern
Test data in SSD is split into 512-byte unit. For incremental, decremental, or LFSR pettern,
each 512-byte data has unique 64-bit header which consists of 48-bit address (in 512-byte
unit) and 16-bit zero value. The data after 64-bit header is the test pattern which is selected
by user.
The left window of Figure 3-3 shows the example when using 32-bit incremental pattern
while the right window shows the example when using 32-bit LFSR pattern.

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 10
When user runs Write or Read command with 4-Kbyte LBA SSD, there is the message
displaying on the console to show the input limitation which must be aligned to 8 as shown in
Figure 3-4. When the input does not align to 8, “Invalid input” is displayed and the operation
is cancelled.
Figure 3-5 shows the example when the input is out of the recommended range for each
parameter. The console displays “Invalid input” and then the operation is cancelled.
Figure 3-4 Error message when the input is unaligned for 4-Kbyte LBA SSD
Figure 3-5 Error message from the invalid input

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 11
3.3 Read Command
Select ‘2’ to send Read command to NVMe SSD.
Output performance
Input test parameter
Current transfer size
12
Normal Green: User input
Blue: Output to user
Test with all “0” pattern
3
Figure 3-6 Input and test result when running Read Command
User inputs three parameters as follows.
1) Start Address: Input start address to read SSD as 512-byte unit. The input is decimal unit
when user inputs only digit number. User canadd “0x” to be a prefix for hexadecimal unit.
When LBA unit of SSD is 4 Kbyte, this input must be aligned to 8.
2) Transfer Length: Input total transfer size as 512-byte unit. The input is decimal unit when
user inputs only digit number. User can add “0x” to be a prefix for hexadecimal unit.
When LBA unit of SSD is 4 Kbyte, this input must be aligned to 8.
3) Test pattern: Select test data pattern to verify data from SSD. Test pattern must be
matched with the pattern using in Write Command menu. There are five patterns, i.e.
32-bit increment, 32-bit decrement, all 0, all 1, and 32-bit LFSR counter
Similar to Write command menu, test system begins to read data from SSD when all inputs
are valid. During reading data, current transfer size is displayed on the console every
second to show that system is still alive. Total size, total time usage, and test speed are
displayed after finishing the operation.
“Invalid input” is displayed when some inputs are invalid or unaligned to 8 (when connecting
to 4-KB LBA SSD).
Note: The read performance result is measured by customized NVMeG4-IP core with
extended buffer size to achieve the best read performance of the SSD.

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 12
Figure 3-7 shows error message when data verification is failed. “Verify fail” is displayed with
the information of the 1st failure data, i.e. the error byte address, the expected value, and the
read value.
User can enter any keys to cancel the read operation or wait until finishing Read command.
Similar to the normal condition, the output performance is displayed on the console when
the user does not enter any keys to stop the operation.
After enter the key to cancel the operation, the read command operation still runs as the
background process. It is recommended to power-off/on AB18 and then press “RESET”
button to recover the error situation.
Verification error with cancellation
Message when operation is cancelled
User enters some keys to
cancel the operation
Wrong pattern
Message when
verification is failed
Output performance
Verification error without cancellation
Figure 3-7 Data verification is failed

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 13
3.4 SMART Command
Select ‘3’ to send SMART command to NVMe SSD.
Figure 3-8 Test result when running SMART command
After finishing the operation, SMART/Health Information (output from SMART command) is
be displayed as shown in Figure 3-8. The console shows six parameters, described as
follows.
1) Temperature in °C unit.
2) Total Data Read decoded as GB/TB unit. Additionally, raw data without decoding is
displayed in 128-bit hexadecimal unit. The unit size of raw data is 512,000 Byte.
3) Total Data Written decoded as GB/TB unit. Additionally, raw data without decoding is
displayed in 128-bit hexadecimal unit. The unit size of raw data is 512,000 Byte.
4) Power On Cycles: Display the number of power cycles.
5) Power On Hours: Display the period of time in hours to show how long the SSD has been
powered on.
6) Unsafe Shutdowns: Display the number of unsafe shutdowns of SSD
dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 14
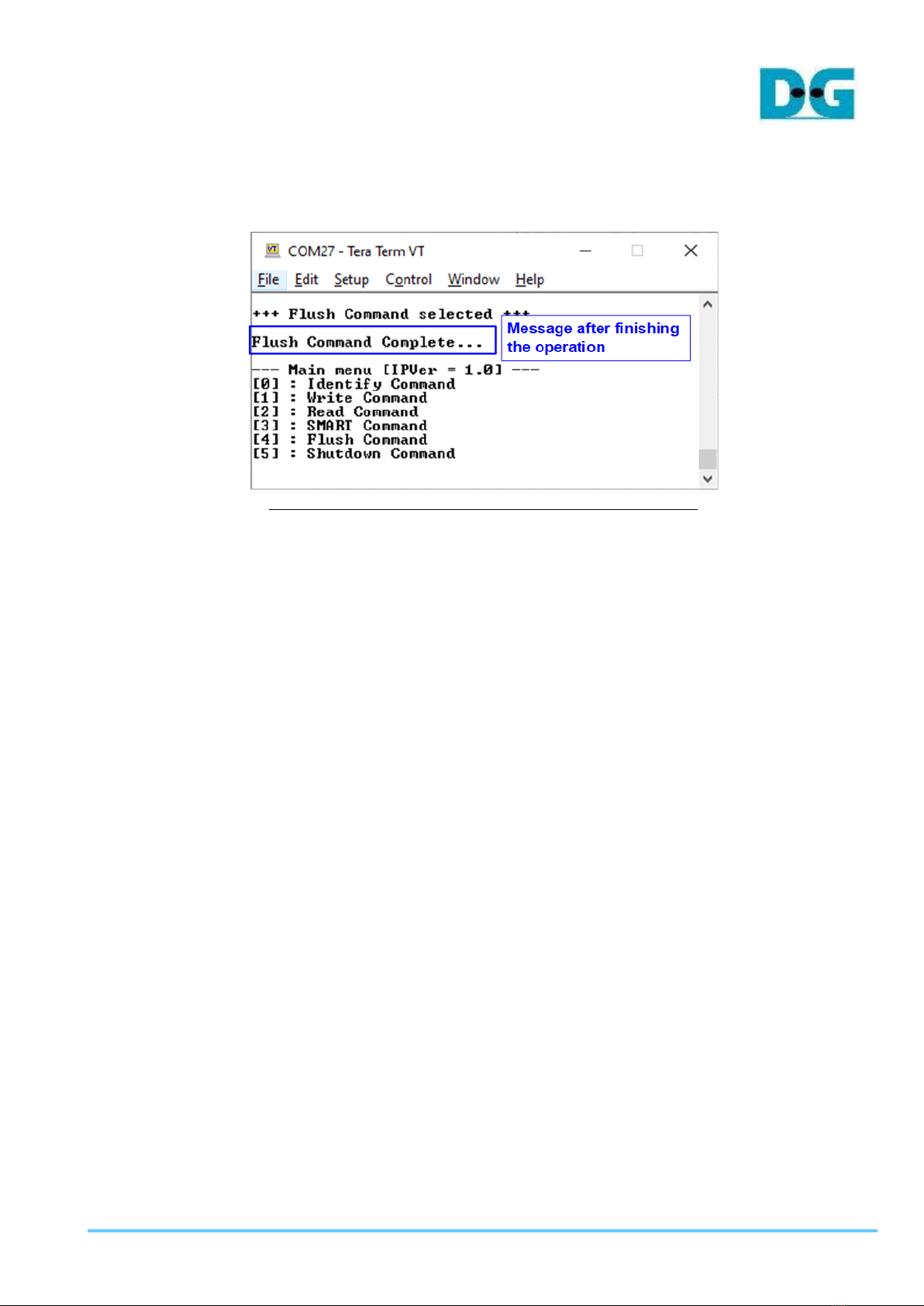
3.5 Flush Command
Select ‘4’ to send Flush command to NVMe SSD.
Figure 3-9 Test result when running Flush command
“Flush Command Complete” is displayed after finishing Flush operation.

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 15
3.6 Shutdown Command
Select ‘5’ to send Shutdown command to NVMe SSD.
Figure 3-10 Shutdown Command with confirmation
The confirmation message is displayed on the console. User enters ‘y’ or ‘Y’ to continue the
operation or enters other keys to cancel the operation.
After finishing Shutdown operation, “Shutdown command is complete” is displayed on the
console as the last message. Main menu is not displayed anymore. User needs to power
off/on test system to start new test operation.

dg_nvmeg4ip_instruction_xilinx_en.doc
20-Apr-20 Page 16
4 Revision History
Revision
Date
Description
1.0
29-Jan-20
Initial version release
1.1
20-Apr-20
Remove power adapter cable from AB18
Table of contents
Other DG Motherboard manuals