Embedos EM User manual

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
1
User Manual and Installation
EM
IO Data Logger + 4G Gateway
April 2022
Version 1.0.0

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
2
DISCLAIMER
Copyright © 2022 by Embedos Engineering LLP
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or
by any means, including photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the
prior written permission of the publisher. For permission requests, write to the publisher, addressed
“Attention: Permissions Coordinator,” at the address below.
Embedos Engineering LLP
Mumbai
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
3
Document Revisions
Date
Version Number
Document Changes
16-05-2022
1.0.0
Initial draft

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
4
Contents
1) Preface:................................................................................................................................................. 5
2) IO description: ...................................................................................................................................... 6
3) Connection diagram:.............................................................................................................................7
4) Application Overview:..........................................................................................................................8
5) Web utility Overview: .......................................................................................................................... 9
a. Connecting to IO logger using WiFi:....................................................................................................9
b. Dashboard page description:...............................................................................................................10
c. Configuration page description:..........................................................................................................13
i. Parameter configuration overview table:........................................................................................13
ii. Configuration of parameters settings:.............................................................................................13
iii. Calibration Diagnostic section:.......................................................................................................14
iv. Analog Input Calibration Section:..................................................................................................15
v. Logging Interval configuration:......................................................................................................19
vi. RPM Scan time configuration: .......................................................................................................19
vii. Output delay configuration:............................................................................................................20
viii. Debounce time configuration: ........................................................................................................21
d. Reports page description:....................................................................................................................23
e. Networks and RTC configuration page description: ..........................................................................25
i. Wifi Configuration section: ............................................................................................................25
ii. Wifi Status section:.........................................................................................................................26
iii. RTC configuration section:.............................................................................................................27
iv. MQTT configuration section:.........................................................................................................28
v. OTA firmware update section:........................................................................................................29

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
5
1) Preface:
Purpose of Document
The document covers Installation and usage of Embedos EM IO Data Logger and 4G
gateway.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
6
2) IO description:
IO logger is currently provided with the following configuration.
Digital Inputs:
1) Pulse Input (To measure RPM value input as digital pulse)
Analog Input:
1) Analog Channel 1 Input (User configurable analog parameter 4 –20 mA)
2) Analog Channel 2 Input (User configurable analog parameter 4 –20 mA)
3) Analog Channel 3 Input (User configurable analog parameter 4 –20 mA)
4) Analog Channel 4 Input (User configurable analog parameter 4 –20 mA)
Digital Outputs:
1) Digital Output for Analog Channel 1 Set point.
2) Digital Output for Analog Channel 2 Set point.
3) Digital Output for Analog Channel 3 Set point.
4) Digital Output for Analog Channel 4 Set point.
5) Digital Output for RPM Set point.
HMI:
1) 1.5” OLED display.
2) Web based utility to view real-time data, download reports and configure device
setting/parameters.
Data Storage(Logging):
1) SD card for local data storage and logging.
Connectivity:
SIM card for 4G connectivity.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
7
3) Connection diagram:

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
8
4) Application Overview:
The IO data logger is designed to log data to device as analog inputs, a pulse input which
is to be converted to RPM value. The logger is able to also display real-time data on a
webpage based utility. The user can interact with the data-logger to configure and view
all the settings and device parameters currently running on the device. The logger can
store real-time data and send the same data via MQTT to a broker.
The IO data logger is provided with following connectivity interfaces:
i. Wifi to connect to an SSID for MQTT data transmission and access to webpage.
ii. 4G to connect to a network for MQTT data transmission.
The device is configured to monitor and log data of five parameters.
Parameter 1 to 4 are analog input parameters corresponding to the devices 4 Analog
inputs respectively. These parameters can be user configurable.
Parameter 5 is RPM parameter and will always output calculated RPM value measured
through the devices Digital Input 1.
Note: Parameter 5 value RPM cannot be interchanged with other parameters.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
9
5) Web utility Overview:
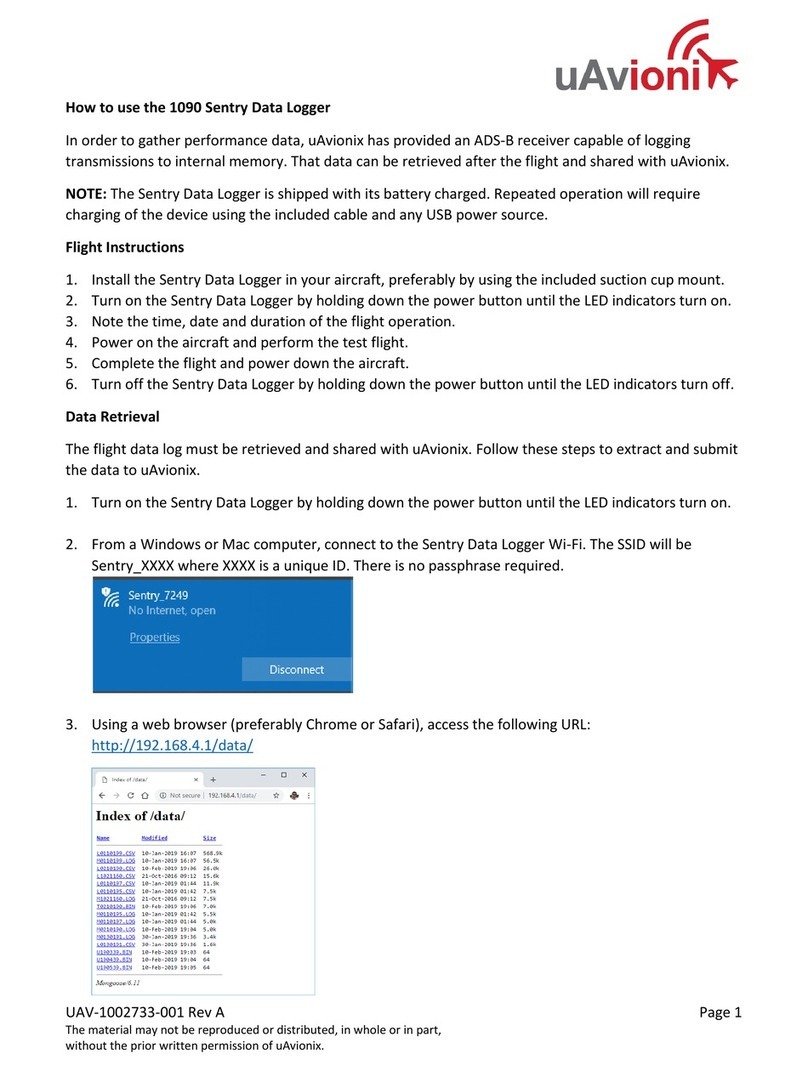
a. Connecting to IO logger using WiFi:
To access the devices web utility page the user can either connect the computer/laptop to
the WiFi AP (Hotspot) generated by the device.
The default credentials for his AP are as follows:
SSID : EM-7C:87:CE:09:DA:D8
Password : Edge@12345
Default IP : 192.168.4.1
On successful connection to the AP, the web based utility of the device can be accessed by
typing the default IP (192.168.4.1) in any web browser.
The device will then load the web utility on the browser.
To access the devices web utility when the device is connected to a WiFi network, the
computer must also be connected to the same network.
The device will display the SSID it is connected to on the OLED display. The device will
also display an IP address which it has acquired.
The user can access the web utility by entering this IP address in the computer.
The device will then load the web utility on the browser.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
10
b. Dashboard page description:
The Dashboard page is loaded when the user enters the devices IP (Default station IP
192.168.4.1 if connected to WiFi AP or Assigned DHCP IP when connected to an SSID) on
the browser.
The User can use the navigation side bar on the left side of the web utility to switch to
different pages of the web utility. It can be accessed by hovering over the side bar on the
extreme left side of the webpage.
The navigation side bar is shown in the below picture.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
11
.
The dashboard page provides the user with real-time data of all parameters the device is
currently monitoring. This data is displayed in graphical format using a gauge and an output
status indicator for each parameter.
Each gauge displays the name of the parameter on the top.
Each gauge displays the units of the parameters at the bottom.
The numerical value of the parameter is also displayed at the bottom of the gauge.
The user configured range of the parameter is also displayed above the numerical value of

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
12
parameter.
The graphical gauge represents the value of data in the given user range. The gauge is
divided into three sections.
The orange coloured section in the middle indicates the set-point and hysteresis region.
The set-point configured by user is displayed on top of the orange region.
The digital output associated with each parameter is turned on or off on crossing the set-
point and hysteresis region. The green coloured region indicates where the digital output
will be off and the red coloured region indicates where the digital output will be on.
The output indicator associated with each gauge provides the user with the current status of
the digital output of that parameter.
The output indicator will be green when the digital output is off and red when the digital
output is on.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
13
c. Configuration page description:
The configuration page is provided so the user can configure details about the parameters
that the device is currently connected to monitor or log data. The configuration page also
provides the user with options to calibrate the devices analog input channels.
i. Parameter configuration overview table:
The parameter configuration overview tables displays the current parameter
configuration settings.
The table provides the user with following options:
Parameter Name
Parameter User Ranger (Low value and High value)
Parameter Set-point
Parameter Hysteresis
Parameter Units
ii. Configuration of parameters settings:

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
14
To configure the parameter settings the use must click on the “Edit Table” button.
On clicking the button the utility will open a configuration section the right side of
the table.
To configure the parameter the user has to first select the ID which corresponds to
the serial number present in the configuration table.
After selection of the ID the previous configuration will be loaded in the fields of the
configuration section.
The user can configure the required parameters settings and click on submit button to
save the configuration.
After the user clicks the submit button the device will save the parameter changes
and refresh the webpage.
The new configuration will now be visible on the configuration table.
*Note:
The configuration of parameters have the following constraints:
Parameter name must not exceed 100 characters
Parameter unit must not exceed 5 characters
Set-point value must be between low and high values.
Set-point and hysteresis region must not exceed low and high range values.
iii. Calibration Diagnostic section:
The calibration section is provided so that user can calibrate the analog channels of
the device as per the requirements.
To display the calibration diagnostic section the user can click on the Show/Hide
button.
The calibration diagnostic sections is provided so the user can view the current
calibration setting of each of the analog channels.
The Scaling Factor and Offset of each analog channel is displayed.
The RAW value of analog channels is also displayed for user reference.
The device is internally calibrated to convert analog input values in range from 0 to
100.
When a sensor is connected to analog input channel its raw value can be checked in
range from 0 to 100.
The user can check if the analog channel is working as expected by verifying the raw
value and change in raw values when the actual analog input is varied.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
15
iv. Analog Input Calibration Section:
The Analog Input Calibration section is provided for the user to configure the

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
16
calibration of each analog input as per the user requirements.
Analog calibration can be done by the any of the following three methods:
Zero Span calibration:
Zero Span calibration is a calibration method wherein the user knows the range of
measurement of the respective parameter. The user must be aware of the lowest
possible value of the parameter and highest possible value of parameter that the
analog input represents.
For example, if a sensor is used to measure a physical quantity then the minimum
and maximum value that the sensor can measured is to be noted.
While configuration this minimum and maximum value has to be entered as sensor
low range and sensor high range values.
When the user clicks on submit button after entering these values the device will then
calibrate the selected analog channel to display calibrated values.
Two Point Calibration:
Two point calibration method is used when the parameter to be measured is used
when the exact range of measurement of the sensor is not known. The way two
point calibration works is that user firsts sets the sensor input to a known value
which is towards the lower end of the measuring range.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
17
When the sensor is set the user enters in the low value field what value of parameter
corresponds to the sensor input. Example, if 4 mA sensor output value represents
0 degree Celsius.
The user then clicks the submit button to configure the low range value.
Now the user sets the sensor input to a known value which is towards the higher end
of the measuring range.
When the sensor is set the user enters in the high value field what value of
parameter corresponds to the sensor input. Example, if 20mA sensor output values
represents 100 degree Celcius.
Now the user can click on the submit button. After this the device will calibrate the
selected channel with reference to the two points used for configuration.
Manual Calibration:
Manual calibration method is used when the user has knowledge about the
sensor output range and the sensor measurement range. The user can manually
calculate the required multiplying factor (scaling factor) and offset value from
the above data.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
18
The user can then enter these two values in the multiplying factor and offset
fields provided.
The user can click submit button to calibrate the selected channel based on the
above configuration.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
19
v. Logging Interval configuration:
The user can configure the amount of time in which the device logs data onto the
on-board SD card.
The Logging interval configuration section provides user to enter the time delay
between two successive log entries.
The value of logging time can be set to any value between 1 second to 100000
seconds (approximately 24 Hrs).
The user can enter the desired value in the field and click submit to update the
configuration.
vi. RPM Scan time configuration:
The user can configure the scan time duration for RPM counting.

IODataLogger +4GGateway
info@embedos.io
www.embedos.io
20
The device measures input digital pulses, where each pulse represents one
rotation.
The device calculates the number of pulses in a particular time interval, this
interval is the scan time interval.
The user is recommended to keep RPM scan time interval as 1 seconds if the
measuring RPM value is greater than or equal to 60 RPM.
If the measurement of RPM values lower than 60 RPM is needed then the user
must enter a larger value than 1 second for RPM scan time.
It is not recommended to keep the value of RPM scan time greater than 60
seconds.
vii. Output delay configuration:
The device is provided with a provision to delay the turning on of the digital
output when the value crosses the set-point hysteresis region.
If delayed output is required the user can select the channel (referring to
configuration table) for which the output is to be delayed.
The user can then enter the delay interval in seconds and click on submit to
configure the channel delay.
On crossing the set-point hysteresis region the digital output will be turned on
only if the parameter value is in this region for the set delay duration.
If the value crosses back into the green region of the gauge the output will not be
triggered and reset to off state.
If delayed output is not required the user can set the value of delay to 0 to
disable the delayed output on the particular channel.
Table of contents
Other Embedos Data Logger manuals
Popular Data Logger manuals by other brands

Lascar
Lascar EasyLog EL-CC-2-001 quick start guide
MadgeTech
MadgeTech UltraShock-5-EB Product Information Card

Davis Instruments
Davis Instruments Perception II Getting started guide

Chauvin Arnoux
Chauvin Arnoux PEL 106 quick start guide

Axiometrix Solutions
Axiometrix Solutions imc SPARTAN Getting started

Gemini
Gemini Tinytag Plus LAN manual