emitor Satlook Micro HD User manual

Satlook Micro HD
User Manual
______________________________________
______________________________________

2
Contents
Overview page 3
Quick Start page 4
EasyFind Mode page 6
Digital Mode page 7
Spectrum Mode page 13
nalog Mode page 15
Setup Functions page 19
Loading New Firmware page 24
Using PC to Transfer Transponder Data page 25
ppendix - Saved Parameters page 27
ppendix B - Universal LNB Primer page 28
ppendix C - DiSEqC Primer page 29
ppendix D - DVB-S and DVB-S2 Primer page 31
ppendix E – UniCable Primer page 32
ppendix F - Satlook HD *.smd File Structure page 34
ppendix G - Satlook HD Specifications page 35
Glossary page 36

3
Overview
The Satlook HD is Satellite Test Equipment for the professional made in
Sweden. It can receive both DVB-S and DVB-S2 satellite signals and using an
advanced demodulator can “lock” on transponders using automatic modulation
type, symbol rate and FEC selection. It is easily operated with just three
controls and the basic functions are easy to learn.
The instrument is provided with a 3" LCD which is used to display information
such as signal strength, Spectrum, or Digital information.
The Satlook HD can be used to measure satellite signals from two LNBs at the
same time. Signal strength is presented graphically on the LCD display in form
of thermometer scales.
It can also sound a tone which increases with signal level on an internal
loudspeaker.
The Spectrum Mode enables the measurement of the satellite spectrum in
resolution steps of 1 MHz to 10 MHz making it easy for the skilled installer to
know what satellite he is receiving and make more detailed measurements.
The Digital Mode shows extended information of Modulation, SIG, SNR, BER,
MER, and a constellation diagram. The Satellite Name and position are shown
using the Network Information Table in the MPEG transport stream. Channel
detail (or Service Information) can also be displayed for a transponder if
needed.
The Satlook can store 100 positions of Satellite transponder information.
The instrument can easily scan through the memory positions and identify the
various Satellite transponders.
The polarisation of the LNB is switchable by setting the LNB voltage to 13V or
18V and the High Low band with a 22 kHz signal. The DiSEqC function
controls all DiSEqC accessories such as LNBs, switches, and positioners.
The instrument is supplied with a built-in and rechargeable battery and a
carrying case for protection of the instrument in the installation environment.

4
Quick Start
Power On/Off Button
Menu Knob and Button
LNB- connector
LNB-B connector
Power Input for charging
RS232 Port
Reset Button
Power On
The Satlook HD is turned on by pressing and
holding the power on button for one second.
Power on tones indicate that firmware loading
has started. This takes about six seconds and
is shown by a progress bar on the display and
a pattern on the blue LEDs.
The Satlook HD initial mode can be set by the
user for convenience. Pressing and holding
the power button also turns off the Satlook
HD. The button must be held for more than
one second in order to turn the unit off. The Satlook HD also has an automatic
power down that is adjustable which will turn the unit off when there is no
activity. This can be set using the Setup Menu.
Navigation
The Menu Button and Menu Knob are the two controls used for navigation
through the menus and selection of functions. When the menu is off, pressing
the Menu Button shows the Menu. It is shown at the active mode, so if the
Satlook HD is in Digital mode, the menu is shown with the Digital entry at the
top.
Using the knob, the function that is to be executed is shown highlighted.
Pressing the Menu Button causes the function to be performed. For simple
functions such as switching the LNB Voltage with the 13V/18V function, the
Satlook HD performs this function, turns off the menu, and immediately returns
to the current mode.

5
For other functions, a new screen with choices is presented. Pressing the
Menu Button selects the highlighted item. Some of these other functions have
an exit function that is used to return to the current mode.
The Menu Knob is used for Frequency adjustment when in the Digital mode or
the Spectrum mode. When the Menu Knob is turned slowly, the frequency is
changed by 1MHz, but if rotated rapidly, the frequency step is increased
allowing for quick movement to the correct frequency.
Charging
Before using the Satlook HD, it should be fully charged.
To charge the Satlook HD, connect the external power supply or 12V Car
Cigarette Lighter Plug and then plug the external power supply into the DC
Input connector. The charging process will begin and the blue LED lights will
cycle indicating charging. The charging mode and time of charging are
displayed on the screen.
full charge can take up to 14 hours, but depending on the battery sate can be
competed earlier. When charging is complete, the bottom LED will be lit
indicating that the charging is complete. The Satlook HD can be operated using
the external power supply, but when the Satlook HD is on, no charging is being
performed.
The battery state is indicated on the nalog screen by a battery symbol.

6
EasyFind Mode
The EasyFind Mode is an easy way to point the dish at installation. When the
EasyFind Mode is entered, the Profile defined in the Setup EasyFind
Configuration is used. The five satellite transponders (or in the case of ll Sats,
all of the memory positions) which are in the Profile can be selected with the
knob.
Initially the display will appear as in the left diagram above and the RF signal
will be indicated on the display and by a tone with increasing frequency as the
RF signal increases. Turn the knob to select one of the five transponders in the
Profile. Point the dish in the approximate position, and move it slowly until the
Satellite is found as in the right picture above. There is an audible indication of
the correct satellite and a different audible indication if the wrong satellite is
found. If the indication is correct, then the screen will show the NIT data after a
few seconds for final confirmation. Now the Digital mode can be used for final
peaking. EasyFind Mode is exited by pressing the button.

7
Digital Mode
About Digital ode
When the user enters Digital Mode, the Satlook HD will attempt to receive a
DVB-S or DVB-S2 signal at the current frequency. The current frequency is
displayed in the centre of the screen and can be changed by the knob (within
the limits of the current LNB type and the 22 kHz setting).
When a signal is received, the Satlook HD is “locked” and the modulation mode
is displayed. This will be shown as QPSK, QPSK HD or 8PSK HD. The current
FEC and symbol rate are shown along with the LNB type definition being used.
If the signal is locked, then the frequency displayed includes the frequency
offset to the signal centre frequency. Usually, the Satlook HD will lock to a
signal up to 5MHz offset. When not locked, the frequency display contains no
offset and an utomatic Search is started in the direction given by the knob.
The Satlook HD checks the signal power at each 3 MHz interval and if the
signal is a peak, it will attempt to lock using the current Modulation settings
defined in the Setup/Modulations screen (DVB-S, DVB-S2, DVB-S Low Symbol
rate). The search will stop when a signal is locked. Turning the knob re-starts
the search in the direction of the knob turn. For Universal LNBs, if the
frequency reaches 11900 MHz in low band, the 22kHz signal will automatically
switch on and the search continues in high band. When searching down, when
the frequency reaches 11520 MHz in high band, the 22kHz will automatically
switch off and the search continues down.
The Search will end when a signal is locked or the frequency limits are reached.
Manual Tuning can be entered using the Digital Menu and is active until the
next press of the menu knob. To lock on signals when the signal symbol rate is
less than 15000 MSymbols/sec, the option “Low Symbol Rate” must be selected
in the Setup Modulations. For symbol rates below 7000 MSymbols/sec, the
signal identification may take several seconds.
Locked
Not Locked

8
constellation pattern is shown which is formed from a small subset of the IQ
decision points received by the demodulator. Occasionally, during an attempt to
lock, a calibration pattern can be observed momentarily. This is not a real
signal, but is an artefact of the demodulator process.
The current state of the 22 kHz signal and the LNB voltage are displayed at the
left. These are mirrored by the blue LED displays.
Once a transponder signal is locked, the Network Information is displayed at the
top of the screen. This can take some time to appear once the transponder is
locked. The transponder is supposed to send this data at least every 10
seconds, but sometimes there will be a transponder not sending any NIT data.
lso you should be aware that sometimes transponders send incorrect satellite
position data, because they are being used to repeat a transport stream used
on another satellite.
Visible Thermometer Bars
There are four thermometer bars displayed to indicate the state of the signal
being received. For all of these, the higher the thermometer bar, the better the
signal quality. Each of these thermometer bars has the recent maximum
displayed as a single bar. This maximum decays over time and so automatically
allows for peaking adjustments. The four thermometer bars are SIG, SNR, BER
and MER.
SIG
This is the power level of the signal at the current frequency. It is always
displayed whether the signal is locked or unlocked. This is not the same as the
display on the nalog screen.
SNR
This is the signal to noise ratio of the locked signal. This is a measure of the
meaningful power in the signal to the background noise of the signal. It is
shown in dB and is calculated by the demodulator using
SNR =
10log
10
(P
signal
/P
noise
)
BER
This is the bit error ratio of the signal. The lower this value is, the better the
signal. It is shown in reverse on the thermometer bar for convenience so that a
maximum can be easily found. For DVB-S QPSK signals, this is BER =
Error
preViterbi
/(Bit
Rate
Time
Lock
).
For DVB-S2 QPSK or 8PSK signals, the BER is estimated from the ratio of Un-
correctable blocks to Correctable blocks.
MER
This is the modulation error ratio in dB. It is calculated from the constellation
pattern and represents how close the I and Q decision points are to the ideal
position. typical MER value is 16 dB. higher value is better and represents
a closer spread of IQ decision points. sample of 200 points is used for the
calculation.
9
(
)
( )
+
+
=
∑
∑
22
22
10
log10
errorerror
idealideal
QI
QI
MER
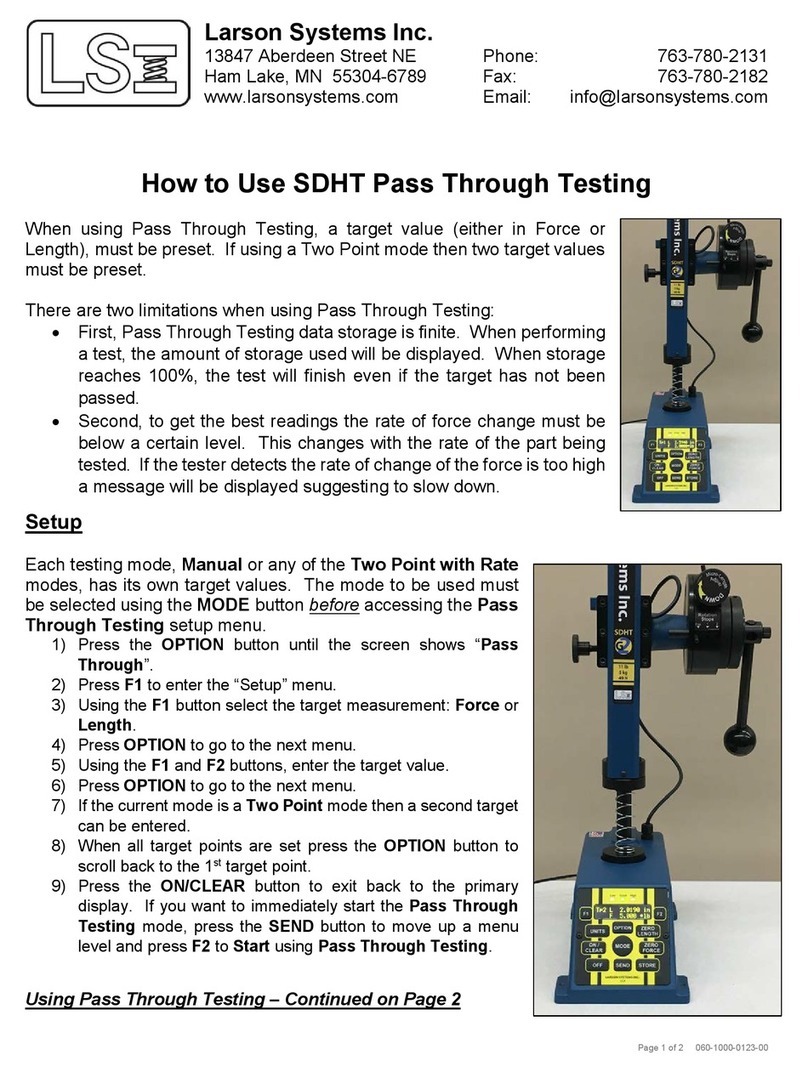
Accessing the Digital enu
When in the Digital Mode, turning the knob will change the current frequency.
The Menu button will activate the Digital Menu.
Tuning
This function enters Digital Mode with the Search function disabled. Tuning can
be performed manually using the knob. Pressing the knob button enables the
utomatic Search mode.
Constellation
This function shows a larger version of the constellation presentation for a more
detailed view. The current frequency is displayed at the top and rotating the
knob will allow this to be changed. If locked, the current modulation is displayed
along with the BER, SNR, and MER thermometer bars. The current Bit Rate of
the transponder is shown.

10
X Polarity
This function can provide a visual reference of the signal level of the vertical
and horizontal polarisations at a frequency. This can be used to adjust the LNB
skew for maximum isolation. Many satellite transponders (like stra 28.2)
operate so that the vertical and horizontal polarisation signals are not usually at
the same frequency, but others (like Hotbird) have some transponders that
operate with vertical and horizontal polarisations at the same frequency. To
ensure that you use a “good” transponder for this isolation test, use the
Spectrum nalyzer to check the signals.
Transponder Chec
This function allows checking of all transponders for some satellites. The
satellites that are testable with this function are stra 28.2E, stra 23.5E, stra
19E, Hotbird 13E, Sirius 4.8E, and Thor 0.8W. When the function is started, the
satellite to be tested is shown on the screen. Turning the knob selects a
different satellite to be tested. Pressing the button starts the test. Each
transponder on the satellite is checked and if locked, then an upward vertical
line is shown. If the transponder is DVB-S2, then the vertical line is shown
slightly longer. If the transponder cannot be locked after three tries, then the
vertical line is downward. t the completion of the test, the knob can be used to
review any missing transponders and show the frequency and polarity for
further checking using the Spectrum or Digital modes. lthough all
transponders for a satellite are tested, failure to lock may occur for several
reasons. This is an accelerated test designed to run quickly and it is possible
that the demodulator may not lock in the short time allowed, or the transponder
may not have a broadcast “footprint” that covers your area.
11
13V/18V
The LNB voltage can be switched from the Digital Menu.
22 Hz
The 22kHz signal can be switched from the Digital Menu.
SNR Beeper
This function starts the beeper with a frequency depending on the current SNR
reading. s the SNR increases, so does the frequency of the tone.
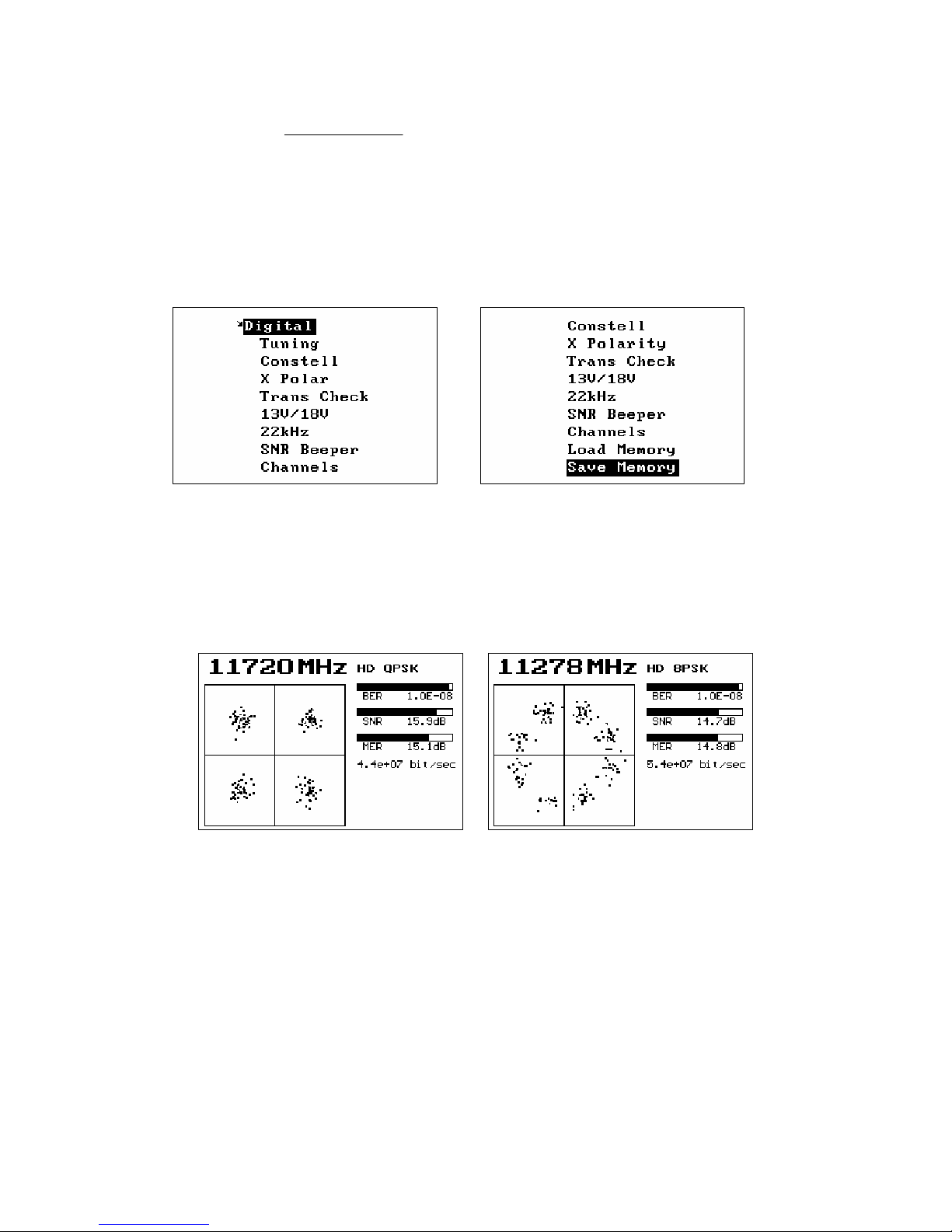
Channels
This shows the services available on the current transponder. The type of
service is shown in the first column. R is a radio service, TV is a standard
definition service and HD is a High Definition service. Other service types are
listed by number. The Service ID number, Service Name and Service Provider
are shown. The services shown will update as more services are found. The
knob can be used to scroll up and down to see all of the services.
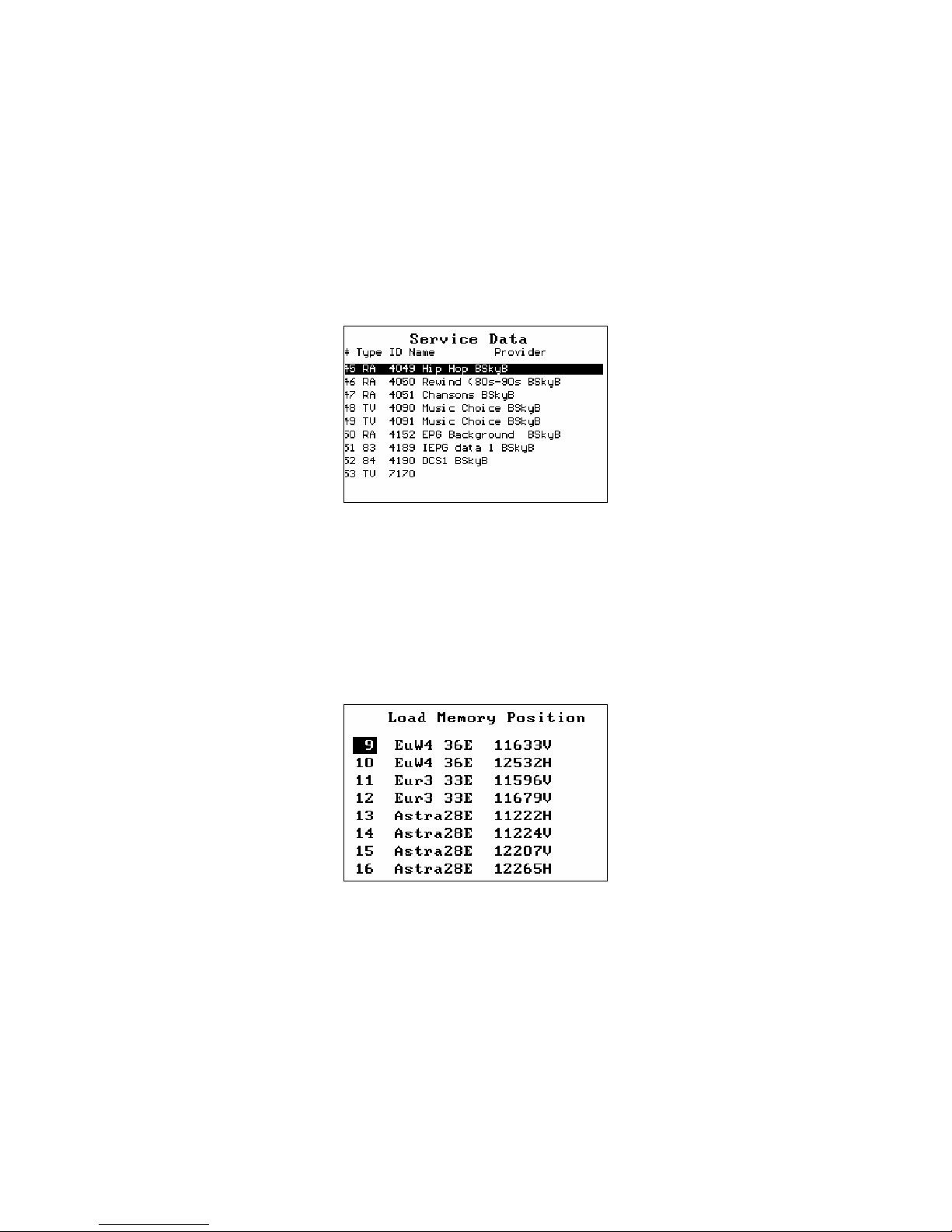
Load Memory
The Load Memory function is used to load the settings for frequency,
polarisation, and band from the permanent memory. The knob is used to select
the desired memory and the knob button loads this memory.
12
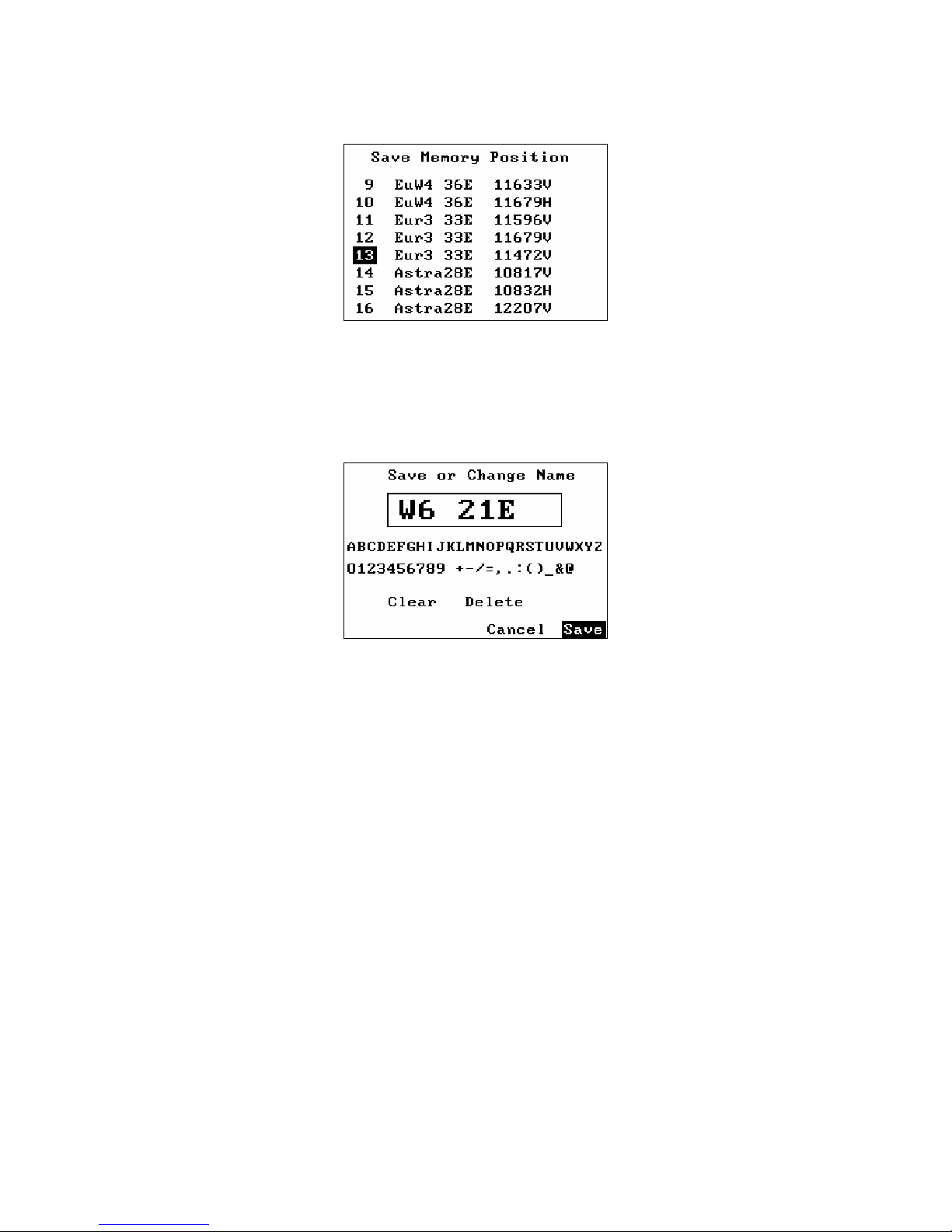
Save Memory
The Save Memory function saves the current Frequency, Polarity (13V/18V),
Band (22kHz signal state), and LNB Type in the selected location. The knob
can be turned to select the desired memory position to change. If a new name
is needed for the memory position, then it can be entered on the next screen
when the menu button is pressed to select the memory position number.
If the memory location name is already correct, then press the menu button
again to save the frequency data in this memory position. If the name needs to
be changed, use the knob to make the changes. Characters can be added by
selecting the character with the knob and then pressing the menu button.
Characters can be deleted by selecting the “Delete” function with the knob and
then pressing the menu button. “Clear” will erase the name, and “Cancel” will
abort saving the memory position.

13
Spectrum Mode
About Spectrum ode
The Spectrum Mode shows the signal power versus frequency around the
current frequency. On entry to the Spectrum Mode, the spectrum cursor is in
the centre of the display and the centre frequency is set to the last used
frequency. Turning the knob changes the cursor frequency, and the flag shows
the current cursor frequency and for a Universal LNB also shows the Polarity. If
the cursor frequency is adjusted to a position that would be offscreen, the
screen is cleared and the spectrum plotted with the cursor at the new frequency
in the centre. The current frequency is used for other modes, so the Spectrum
Mode can be used to find a signal of interest, and then the Digital Mode can be
used for more complete examination. The user can exit Spectrum Mode by
pressing the button.
Accessing the Spectrum enu
The Menu is activated by pressing the button. t this time, the Spectrum
options can be changed or other functions in the menu can be used.
Sweep
The Spectrum Sweep can be changed from 1 MHz per increment to 10 MHz per
increment. The user setting for the Spectrum Sweep increment is then saved
and restored on power up.

14
13V/18V and 22 Hz
From the Spectrum Menu, the Polarity and Band can be changed with the
13/18V and the 22kHz signal.

15
nalog Mode
About Analog ode
The screen in nalog mode shows the relative RF level for the two LNB inputs
on a thermometer bar. This is the RF level for the IF band from 920 MHz to
2150 MHz. For a Universal LNB, the Satellite band will be selected from one of
the four quadrants by the 13V/18V and the 22 kHz signal. The LNB voltage of
13V or 18V is displayed by the blue LEDs and also on the screen. The LNB
signal 22kHz is displayed by the blue LEDs and also on the screen. The
ttenuator state is shown on the screen and is displayed by the blue LEDs.
The LNB Current is displayed. Typical LNB current will range from 90 to 175
m . If there is a short in the satellite cable to the LNB, the screen will show an
overcurrent condition. When both LNB- and LNB-B are connected, you will
see the combined LNB Current. If the LNB Current exceeds about 450m , then
the LNB Voltage of 13V/18V will be turned off.
Power Display
The battery charge level is shown approximately by the battery symbol. When
the Satlook HD is connected to a power supply, the battery symbol is replaced
by “Ext Power”.
Accessing the Analog enu
When in the nalog Mode, turning the knob or pressing the knob button will
activate the nalog menu for the nalog functions.

16
Rotating the knob will scroll through the menu items. To select a menu item,
press the menu button. If the enu Timeout function (set using Setup mode) is
set, then the display will revert to the nalog Mode display after a timeout,
otherwise the nalog menu will continue to be displayed until an nalog
function is selected from the nalog menu.
Analog enu Functions
13V/18V
This function toggles the LNB voltage. If the voltage is 13V, it is changed to
18V and vice versa. The LNB voltage is used to select the Polarity for a
Universal LNB. 13V selects Vertical Polarity and 18V selects Horizontal Polarity.
The user setting for the LNB voltage is saved and restored on power up.
22 Hz
This function toggles the LNB 22kHz signal. If the signal is off, it is turned on
and vice versa. The 22 kHz signal selects the band for a Universal LNB. If the
22 kHz signal is off, then a Universal LNB selects the low band (10670 MHz to
11900 MHz). If the 22 kHz signal is on, the high band is selected (11520MHz to
12750MHz). The overlap region from 11520MHz to 11900MHz can be received
with the 22 kHz signal either on or off. The user setting for the 22 kHz signal is
saved and restored on power up.
Beeper
This function toggles the RF signal beeper to one of three modes. The
frequency of the beeper increases with RF signal strength.
- if off, it is set to use the RF signal from LNB-
- if currently LNB- , then it is set to use the RF signal from LNB-B
- if LNB-B, it is set to off
Attenuate
This function toggles the RF attenuator on or off. This inserts about 3dB into
the RF path. It attenuates both LNB- and LNB-B. There is no effect on signals
in Digital Mode.
MaxHold
This toggles the MaxHold function from off to on and vice versa. When the
MaxHold function is on, the maximum RF signal value for LNB- and LNB-B is
displayed as a line on the thermometer bar.
DiSEqC Cmd

17
This function sends a DiSEqC command. Turning the knob shows the DiSEqC
command selected and pressing the knob button sends this command. The Exit
position returns the user to nalog mode. The DiSEqC commands that are sent
are detailed in appendix C (DiSEqC Primer).
Positioner
This function sends a DiSEqC command to a positioner. Turning the knob
shows the DiSEqC command selected. Pressing the knob button will then send
this command. The Exit position returns to the nalog Mode. The DiSEqC
commands that are sent are detailed appendix C (DiSEqC Primer).
Go East: This sends the DiSEqC command to move the positioner to the East.
Go Home: This sends the command to “Home” the positioner. (This command
is Goto Pos 0) This is normally due South, but for some positioners may be the
extreme easterly limit.
Go West: The DiSEqC command to move the positioner to the West.
SetEast: Set the East “soft” limit for the positioner at the current position.
Clr Lim: Clear the “soft” limits.
SetWest: Set the West “soft” limit for the positioner at the current position.
Goto Pos: This sends the DiSEqC command to the positioner to move to a
stored position from 1 to 31. The knob selects the position number to move to
and pressing the knob button sends the command.
Save Pos: This sends the DiSEqC command to the positioner to save the
current position as a “stored” position from 1 to 31. The knob selects the
position number that this will be called and pressing the knob button sends the
command.
Goto X: This sends the DiSEqC command to move to a position calculated by
the Satlook HD for the Satellite ngle desired. The knob selects the Satellite
ngle that will be used and pressing the knob button sends the command. To
move the positioner to HotBird for example, the command to send would be

18
Goto X 13.0 E. The Goto X function calculates the amount to move the
positioner from the Satellite ngle and the user Latitude and Longitude. In
order for the command sent to be correct, the Latitude and Longitude must be
set for the user location.
MyLat: This function is for the entry of the Latitude of the user location. Turning
the knob will show the selected latitude from 90.0
o
South to 90.0
o
North and
pressing the knob button will save this setting. This setting will be restored on
power on.
MyLong: This function is for the entry of the Longitude of the user location.
Turning the knob will show the selected Longitude from 180.0
o
East to 180.0
o
West and pressing the knob button will save this setting. This setting will be
restored on power on.
19
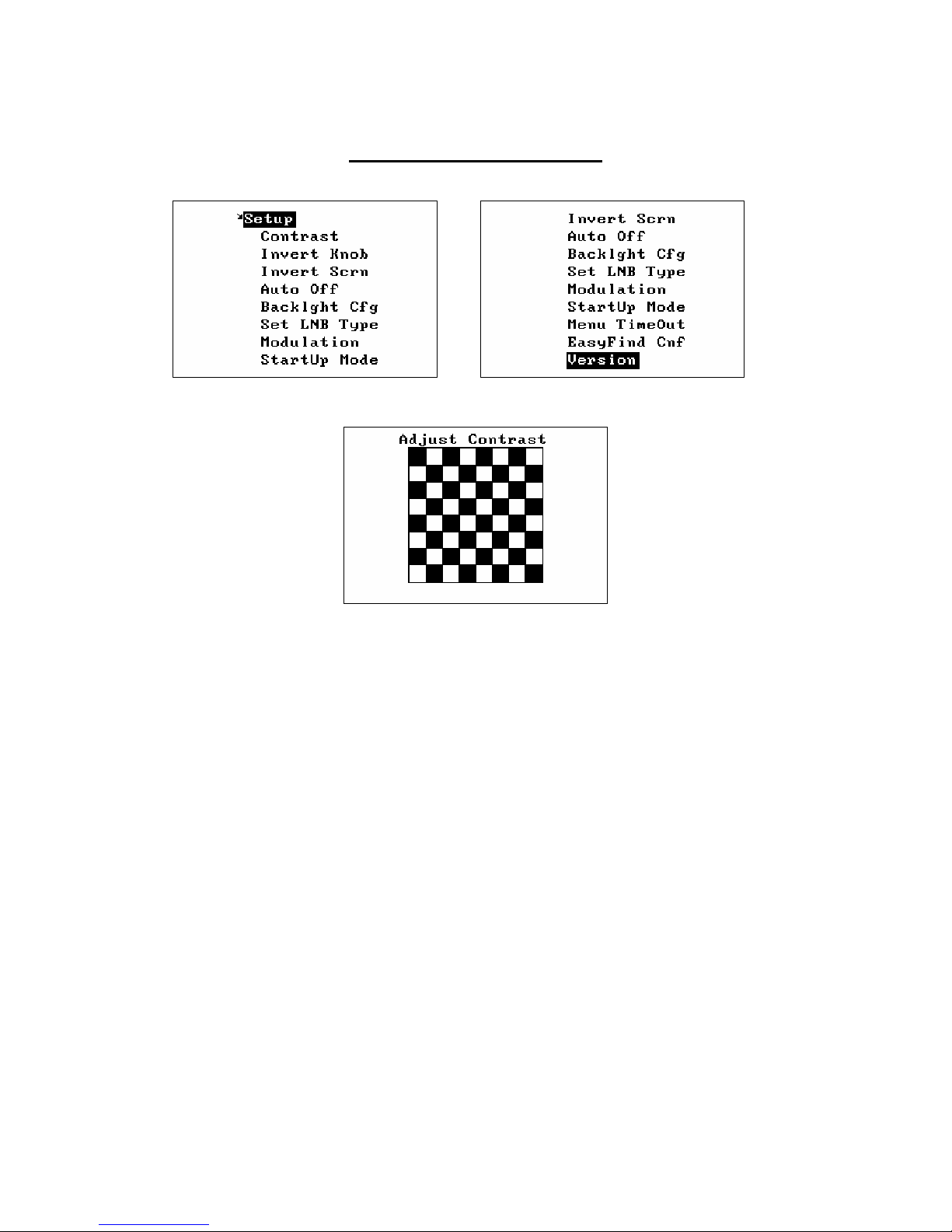
Setup Functions
Contrast
The Contrast function shows a black and white grid and allows the adjustment
of the display contrast for best viewing using the knob. Pressing the knob
button exits the contrast adjustment and saves the current contrast settings.
Invert Knob
Pressing the Knob button for the Invert Knob function changes the way the knob
rotation is interpreted. t default, rotating the knob clockwise means that
frequency will increase and the menu selection will move down to the next
selection. This is saved as a power on parameter.
Invert Scrn
Pressing the knob button for the Invert Scrn function will invert the screen, black
to white and vice versa. This is then saved as a power on parameter.

20
AutoOff Timeout
This function sets the utoOff timeout if required. If the knob button or knob is
not used for the timeout period, then the Satlook will display “ utoOff” and
power down. This setting is then saved as a power on parameter.
Backlight Configuration
The backlight can be set so that it will turn off after a delay. The setting is then
saved as a power on parameter.
Set LNB Type
The LNB used can be set so that the frequency displayed is correct and the
stored transponders are correctly used.
The “Universal” entry sets the LNB so that two local oscillator frequencies
(9750MHz and 10600MHz).are used for conversion. These are switched using
the 22kHz signal to select the 9750MHz local oscillator when the 22kHz is off
and the 10600MHz local oscillator when the 22kHz is on. The LNB
downconverts the satellite signal to the Intermediate Frequency as:
IF = Frequency
Satellite
- Frequency
LO
Other manuals for Satlook Micro HD
1
Table of contents