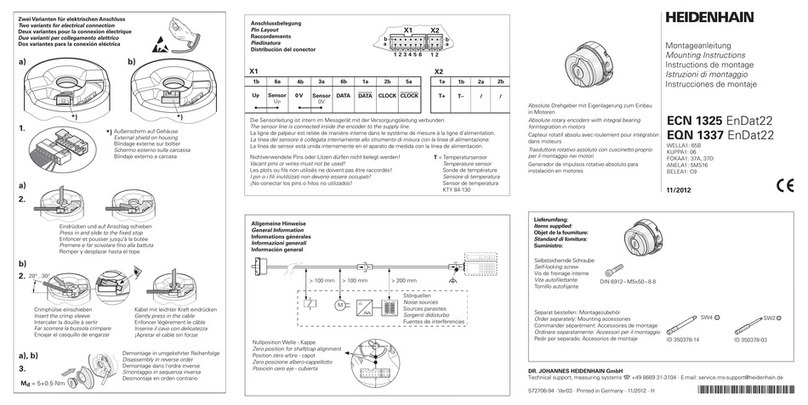
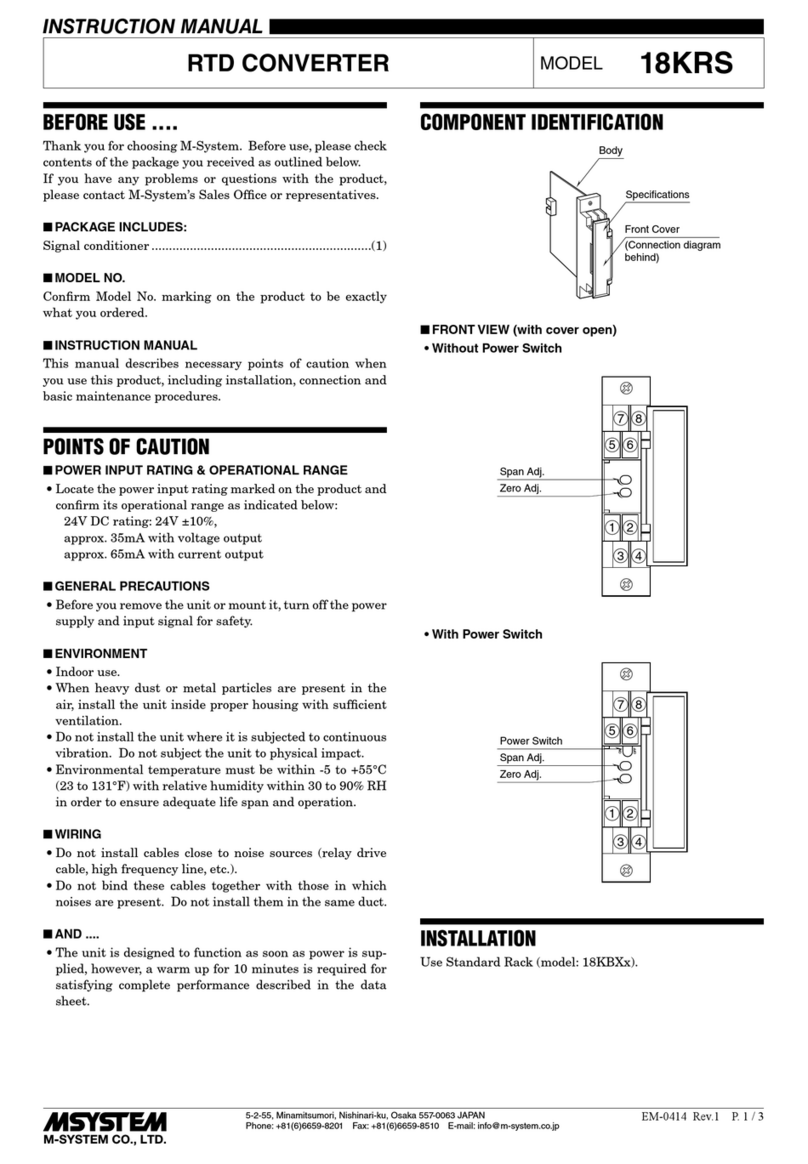
Equitel E411 User manual

Audio over IP devices
EQUITEL Network Audio
Audio over IP decoders / mixers
E411, E413, E415 & E417
Technical Manual
Ed 2.1

This document is the technical reference for the decoders of the ENA Audio over IP family of devices. Includes the
E411, E413, E415 and E417 equipment.
It is valid for versions:
Hardware: EAIP1V133
Firmware: 3.06
© Equipos De Telecomunicación Optoelectrónicos, S.A.
Zaragoza, June 2015.
Ed 2.1

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual ii
Audio over IP decoders / mixers
Technical manual
Index
Chapter 1 : Introduction .....................................................................................................................................1
Chapter 2 : Functionality ....................................................................................................................................3
2.1 Audio source types ................................................................................................................................3
2.2 Audio layers...........................................................................................................................................5
2.3 Audio switching .....................................................................................................................................6
2.4 Digital I/Os.............................................................................................................................................6
Chapter 3 : Hardware description ......................................................................................................................7
3.1 External elements location....................................................................................................................7
3.2 Power supply .........................................................................................................................................8
3.3 Indicators...............................................................................................................................................8
3.4 IP address indication and default configuration recovery.....................................................................9
3.5 Ethernet.................................................................................................................................................9
3.6 Digital I/O ..............................................................................................................................................9
3.6.1. Inputs ..............................................................................................................................................9
3.6.2. Outputs .........................................................................................................................................10
3.7 Audio Outputs .....................................................................................................................................10
3.7.1. Headphone Output.......................................................................................................................10
3.7.2. Line Out ........................................................................................................................................10
3.7.3. Amplified audio output.................................................................................................................11
3.8 Audio inputs ........................................................................................................................................12
3.8.1. Mic input.......................................................................................................................................12
3.8.2. Line input ......................................................................................................................................12
3.9 USB connector .....................................................................................................................................12
3.10 Wall-mount remote control connector ...............................................................................................13
Chapter 4 : Configuration and control of the device ........................................................................................14
4.1 Accessing the device............................................................................................................................14
4.2 Configuration.......................................................................................................................................16
4.2.1. General Information .....................................................................................................................17
4.2.2. Audio.............................................................................................................................................17
Audio output ..............................................................................................................................17
Input Amplification ....................................................................................................................17
4.2.3. Audio Channels .............................................................................................................................18
‘RTP’ Source type configuration.................................................................................................21
‘SIP PBX’ Source type configuration...........................................................................................22
‘P2P SIP’ Source type configuration...........................................................................................23
‘SHOUTcast / ICEcast’ source type configuration ......................................................................24
‘Scheduled playlist’ Source type configuration..........................................................................27
‘Continuous playlist’ Source type configuration ........................................................................28
‘Microphone’ Source type configuration ...................................................................................29
‘Line’ Source type configuration ................................................................................................31
4.2.4. Network ........................................................................................................................................33
Static mode ................................................................................................................................33
Dynamic mode ...........................................................................................................................34
4.2.5. Firmware updates and device reset .............................................................................................35

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual iii
Reboot device ............................................................................................................................35
Restore default values ...............................................................................................................35
Firmware upgrade......................................................................................................................35
4.3 Control.................................................................................................................................................36
Chapter 5 : TMH60ENA wall-mount controller ................................................................................................37
5.1 Description ..........................................................................................................................................37
5.2 Connection ..........................................................................................................................................38
5.3 Operation ............................................................................................................................................38
5.3.1. Initial screen .................................................................................................................................38
5.3.2. No BGM sources screen................................................................................................................38
5.3.3. Default /control screen.................................................................................................................39
5.3.4. BGM channel selection .................................................................................................................39
5.3.5. ADV or EMG channel information ................................................................................................39
5.3.6. System info and configuration......................................................................................................40
BackLight level change ...............................................................................................................40
5.3.7. Link error screen ...........................................................................................................................40
Chapter 6 : Software.........................................................................................................................................41
Chapter 7 : Technical data................................................................................................................................42
7.1 Dimensions ..........................................................................................................................................42
7.2 Electrical Specifications .......................................................................................................................43
7.2.1. Power............................................................................................................................................43
7.2.2. Ethernet ........................................................................................................................................43
7.2.3. Audio.............................................................................................................................................44
7.2.4. Contacts ........................................................................................................................................44
7.3 Environmental conditions ...................................................................................................................44

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 1
Chapter 1: Introduction
The EQUITEL audio over IP devices family allows the transmission and reception of music channels and audio
messages over IP, using standard IP network hardware.
These devices provide a unified solution for transmitting audio signals such as background music, advertising and
informational messages, to one or more destinations.
By supporting multiple protocols and encoders, these devices are indicated in broadcasting applications, VoIP
and Internet radio. In addition to leveraging existing infrastructure and devices such as SIP phones.
Encoder (E421) sends audio input through the Ethernet network. This process is known as "streaming". Streams
can also be generated by other devices, like a PC running an application or a SIP phone.
The E495 and E497 desktop microphone consoles can also send vocal messages to the decoders for paging
applications. If more than one of these devices are used, they intercommunicate to avoid message collisions.
The E430 is a music and announcements server that can generate audio from internally stored files. It can be
used to generate background music channels and/or advertisements.
Decoders (E411, E413 or E415) can receive selected channels (i.e. "streams") from the network and convert it
back to an analog audio signal.
Mixer (E417), besides the same features than the decoders, includes the option to use audio coming from files
stored in a USB memory or analog signals in its MIC or LINE inputs.
The selection of the actual stream, local file or analog signal to be sent to the output is made based on a
powerful but very easy to configure priority schema.
The figure shows a schematic of this family of devices usage:
Figure 1: EQUITEL Audio over IP devices usage schema

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 2
This document is the user's manual for the decoding members of the family:
E411 - Decoder
Stereo output in line level (RCA) and headphones.
To be used with an external amplifier.
E413 - Decoder with digital I/O
Same features as E411 including two digital inputs and outputs for
external devices control.
Digital outputs can be used to switch ON/OFF the external amplifier.
E415 - Amplified decoder
Same as E413 and includes a high quality 25W audio amplifier.
Amplified output can be configured in mono or stereo.
Line-out output can be used simultaneously.
E417 - Decoder / Mixer
With the same characteristics as E415, it can also play sound from
files stored in an external USB memory and from its analog inputs.
Ideal to mix external background sources with local messages.
TMH60ENA
Wall-mount control for the ENA decoders.
Allows selection of the background music channel and volume control
in an easy way.

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 3
Chapter 2: Functionality
2.1 Audio source types
Decoders can play high quality stereo sound coming from several source types:
RTP:
Audio streams coming from E321 encoders, E495 or E497 paging consoles, E430 audio server, computer
applications or other devices, in the RTP format as defined in RFC 3550.
The RTP can be received also in multicast mode. So, many decoders can play the same RTP stream
without extra bandwidth consumption.
The allowable payload formats are:
oG711-A: (vocal quality, VoIP standard)
oPCM 16 bits/sample, 1 or 2 channels, 11025 Hz (voice/music –medium quality)
oPCM 16 bits/sample, 1 channel, 22050 Hz (voice/music –good quality)
oPCM 16 bits/sample, 1 channel, 32000 Hz (voice/music –very good quality)
oMP3 (quality according to emitter)
When using these RTP formats, as audio is not compressed, the latency is fairly low1.
RTP/SIP 2:
Audio streams coming from a standard SIP phone or PBX. The audio codec used is G711-A.
The decoder has an internal SIP agent that can be registered in an SIP PBX and acts as a standard
extension accepting calls.
Also, can be configured in “peer-to-peer” (P2P) mode if not PBX is used to accept calls directly from
phones.
When a call is received, is automatically answered and the audio is sent to the output if no other higher
priority channel is being played.
SHOUTcast / ICEcast 3:
High quality audio streams coming from local or internet servers (internet radios). These streams can
also be generated with the ENA software or the E430 audio server.
The device connects to the configured URL to acquire the compressed audio stream. The audio can be
sent in any of the following formats:
oMP3 up to 192 kb/s
oAAC+ up to 192 kb/s
oOgg-Vorbis up to 192 kb/s
Due to audio compression and buffering, this format has a very high latency, that can reach several
seconds.
1The minimum latency is obtained in a well dimensioned and configured network, and can be as low as 40 milliseconds.
2SIP is the most widely used protocol nowadays for session establishing in VoIP telephony. It is defined in RFC 3261 .
3SHOUTcast and ICEcast are both standards used to transmit music through Internet. There are many public radios in Internet
using these protocols, and is quite easy to create a proprietary radio using one ICEcast server provided by an ISE (Internet
Services Provider).

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 4
Audio files (in E417 only):
The E417 can decode and play audio files stored in an USB mass storage device.
The allowable formats are:
oMP3 up to 320 kb/s (Fixed bit rate)
Analog inputs (in E417 only):
The E417 has two analog inputs (microphone and line-in) than can be sent directly to the output.
Each input can be assigned only to one of the possible audio sources. See next point for more
information.

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 5
2.2 Audio layers
Decoders can accept up to 10 simultaneous sources or channels, grouped in three categories or “audio
layers”:
Background music:
The purpose of this layer is to be used for the ambience sound. Is the lowest priority layer and accepts
up to 6 sources (channels).
The allowable source types for this layer are: RTP, SHOUTcast / ICEcast, audio files (in continuous
playlist mode) and the analog inputs.
The selection of the channel to be played can be made manually with the web server of the device,
through an external application in a computer or mobile device and with the wall-mount control
TMH60ENA4.
It is also possible to allow the device to automatically change the channel being played if there are no
data to decode (for instance, a break-down in the connection to an internet radio).
The playing of a channel of this layer can be interrupted by the presence of audio in one channel of the
other two layers.
Advertisements:
This is the layer used to play advertisements. It accepts up to 3 channels, each one with its own priority
level.
Allowable source types are: RTP, RTP/SIP, Audio files (in periodic playlist mode) and the analog inputs.
Audio in this layer can interrupt the audio in the Background Music one and can be interrupted by
audio in the Emergency layer.
Emergency:
This is the highest priority layer and accepts only one channel. It is commonly used in PA systems for
evacuation or emergency messages.
The allowable source types for this layer are: RTP, RTP/SIP and the Analog inputs.
This is a summary of the allowable source types in each of the audio layers:
Audio layers
Background
music
Advertisements
Emergency
Source type
RTP
SIP/RTP
SHOUTcast / ICEcast
Audio files (E417)
Analog inputs (E417)
4The interface for the TMH60ENA wall-mount controller is available in all the models as an option. You must add “-R” to the
ordering code.

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 6
2.3 Audio switching
Only one of the 10 possible channels can be played at a time. The device chooses which one must be played
analyzing their status (active/inactive), the assigned priorities and the user selection (only for the
“Background Music”layer channels).
The activation of each channel depends on the source type configured for it:
For the RTP audio streams, the channel becomes active when there is data present during more than 70
ms and becomes inactive when there is no data for more than 1 second.
When the audio comes from an SIP phone, the channel becomes active or inactive attending to the SIP
protocol. When the call is established, the channel is activated. When the call is ended, the channel is
deactivated.
SHOUTcast or ICEcast sources are activated when the connection with the configured server can be
established. If the connection fails, the source is deactivated.
Sources based on local files for the advertisement layer are activated by a time scheduling. When used
for the background music layer, they are always active, being played continuously in a loop mode if the
channel is selected.
Analog inputs used for the “Advertisements” or “Emergency” layers are activated by one of the digital
inputs in the device. When used for background music, they are always active. Each one of the analog
inputs can be assigned only to one input channel.
2.4 Digital I/Os
The E413, E415 and E417 models have two digital inputs and outputs.
Inputs:
In all decoders, can be used to control the volume of the background music channel being played.
When input 1 is active (contact closed), volume increases in 2 db each 500 milliseconds. Contact 2
decreases the volume in the same way.
In the E417, can be also used to activate the analog audio sources.
Outputs:
Can be used for activation of external devices (i.e. an amplifier, a light, etc.) when one (or more) of
the input channels are being played.
Further this, both inputs and outputs can be managed through the control protocol of the devices from
external applications, for instance to read sensors, activate doors, etc.

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 7
Chapter 3: Hardware description
3.1 External elements location
The following figure shows the external elements of the E417. Not all of the elements are present in all the
models, as shown in the table below:
Figure 2: External elements
Element
Description
Applies to
Indicators
All models
USB connector
E417
Microphone input
E417
Audio line input
E417
Audio line out
All models
Headphone out
All models
Ethernet
All models
Terminal for I/O contacts
E413, E415, E147
Amplified audio output terminals
E415, E147
IP recovery and reset default button
All models
Power supply connector
All models
Remote wall-mount control connector
All models with “-R” option
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
11
10
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
1
12

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 8
3.2 Power supply
The devices can be powered by an external 12 or 24 volts DC power supply (connector in the Figure 2) or
by PoE 5(Power over Ethernet) using the Ethernet cable.
The PoE versions can be powered also through the connector . If both supplies are simultaneously
present, the PoE is not used.
The external power supply connector needed is 5.5 x 2.1 mm, with the polarity shown in the figure:
Figure 3: Power connector
The minimum power requirements depend on the device and the usage, as shown in the table:
Amplifier not used
Amplifier up to
7W + 7W
Amplifier up to
12W + 12W
E411
12V / 1A
---
---
E413
12V / 1A
---
---
E415
12V / 1A
12V / 2A
24V / 2A
E417
12V / 1A
12V / 2A
24V / 2A
E411-P
12V / 1A or
PoE (802.3af)
---
---
E413-P
12V / 1A or
PoE (802.3af)
---
---
E415-P
12V / 1A or
PoE (802.3af)
12V / 2A or
PoE+ (802.3at)
24V / 2A
E417-P
12V / 1A or
PoE (802.3af)
12V / 2A or
PoE+ (802.3at)
24V / 2A
IMPORTANT NOTE: Decoders with amplified audio output (E415 and E417) need to be powered with an
external 24V / 2A supply to achieve the maximum output power to the loudspeakers, even in the ‘-P’ version.
PoE+ can’t supply as much power as the device needs.
3.3 Indicators
There are four LEDs in the front plate of the device ( ) with the following meaning:
ON (Green): indicates that the device is powered.
RUN (Green) when flashing indicates that the device is working properly.
OUT (Green): indicates active audio output.
ERROR (Red): Indicates some kind of error. It can be a network error, a malformed audio source or a
serious system failure.
5All the devices can be ordered with the “-P” option for PoE powering.
1
11
11

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 9
3.4 IP address indication and default configuration recovery
The devices have an internal pushbutton ( ) with two functions:
To indicate the IP address: When pressed momentarily (1 second), the IP address is said via the
audio outputs. Simply connect a headset to the output to listen to the IP address.
To Reset to default settings: When pressed for more than 6 seconds, the default settings will be
restored.
To access the internal switch, use a small screwdriver or a wire (a paper clip can serve, for example).
3.5 Ethernet
The 10/100 Ethernet port has Auto-MDIX capability.
The Auto-MDIX automatically switches from MDI to MDI-X and vice versa, allowing the connection of any
type of cable (straight or crossover) regardless of whether the module is connected directly to a computer, to
a switch / hub or other device.
There are two LEDs in the connector:
Green LED: indicates line activity. When blinking, the line is OK. If the LED is OFF, there is no link.
Amber LED: indicates the speed of the connection. If the LED is ON, the link is established at
100 Mb/s.; if OFF, at 10 Mb/s.
3.6 Digital I/O
The E413, E415 and E417 models have two digital inputs and two digital outputs located in terminal .
The inputs can be used to trigger some audio sources activation. One of the most typical applications would
be to connect the “push to talk” button of a console to trigger the audio input in the E417.
Also can be used to control the volume of the background music being played as following:
Input 1, when activated (closed), increases the volume in 2 dB steps each 500 milliseconds.
Input 2 decreases the volume in the same way.
The outputs can control external devices triggered by the activation of one or several audio sources. For
instance, to control the power of an external amplifier in PA applications when audio is emitted and a
flashlight when the emergency channel is active.
3.6.1. Inputs
Inputs are designed to be connected to a switch or dry contact and are optically isolated, as seen in the
schema:
GND
+5v
A
B
1K
Figure 4: Digital inputs
8
1
6
10

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 10
When the “A” and “B” terminals are connected, the input is considered active.
As said, the inputs are designed to be driven by dry contacts (i.e. switches), but can also be controlled by
other interfaces like open collector. In those cases, special care must be taken to assure that the input is
activated properly. If needed, please, contact us at support@equitel.es for more information.
3.6.2. Outputs
Each output has a SPDT relay. So, it can be used as “normally open” or “normally closed”.
The drawing in the rear plate of the device show the status when the output is inactive: The center
terminal is connected to the right one:
C
NO NC
Figure 5: Digital outputs
The characteristics of the relays are:
Maximum operating current: 1A
Maximum operating voltage: 125VAC or 60VDC
3.7 Audio Outputs
As previously said, decoders accept several audio input channels, but can only play one at a time.
The resulting audio output is sent simultaneously to the three possible audio outputs: Headphone, line out
and amplified output (only in E415 and E417).
3.7.1. Headphone Output
All models have a 3.5 mm stereo jack headphone output ( ). This output is particularly useful to retrieve
the IP address of the decoder by pressing the internal button 'IP / RD' ( ).
3.7.2. Line Out
The stereo audio line out, also present in all decoders, is accessible via two RCA connectors ( ), with a
level of 1.8Vpp on 10kΩ.
The white connector corresponds to the left channel and the red one to the right channel.
5
10
6

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 11
3.7.3. Amplified audio output
The E415 and E417 models have an internal amplifier to drive speakers directly. The amplified output is in
the rear plate of the device ( ). It can be used in stereo or mono mode. Also, it can be disabled, if not
used, to reduce the device consumption.
The speakers must be connected as shown in the figure:
SPKL+
SPKL-
SPKR+
SPKR-
8 Ω
+
-
8 Ω
+
-
SPKL+
SPKL-
SPKR+
SPKR-
4 Ω
+
-
Stereo mode Mono mode
Figure 6: Amplified output connections
Remember that besides choosing the appropriate connection, the device must be configured in
accordance. (See point 4.2.2)
The maximum output power obtained depends on the power supply chosen, as shown in point 3.2 .
There are two internal potentiometers in the device to limit the maximum output power sent to the
speakers:
Figure 7: Internal volume potentiometers
Devices are shipped with this potentiometers set to maximum value.
If the used speakers’ power is smaller than the maximum output of the device, the potentiometers must
be adjusted accordingly in order to prevent the speakers destruction.
In this case, care must be taken to adjust both potentiometers to approximately the same value.
The adjustment must be done experimentally, configuring the device to play a channel at maximum level
and adjusting the potentiometers to obtain a good sound without distortion in the speakers.
9

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 12
3.8 Audio inputs
The E417 model has two audio inputs that can be used as a local audio source: a stereo line level and a mono
microphone level.
3.8.1. Mic input
The microphone input connector ( ) is a 3.5 mm 3-terminal Jack.
The simplified schematic is shown in the figure:
3.3V
1K
Figure 8: Microphone input
The maximum input level is 143mVpp, with an impedance of 45kΩ.
The input accepts directly the standard microphones designed for computers.
3.8.2. Line input
The line input ( ) is a stereo RCA, with a level of 2.5Vpp and an impedance of 80kΩ.
The white connector is the left channel and the red, the right one.
3.9 USB connector
The E417 has a type A USB connector ( ) to connect a mass storage device to store audio files that can be
decoded and played locally.
It’s an USB 2.0 interface that supports devices formatted in the FAT32 file system, with a maximum capacity
of 64 GB.
It is very important to not unplug the USB memory while it is in use to avoid file corruption or even its
destruction.
The device is accessible through the network using the FTP protocol to change its content remotely 6.
6Contact us at [email protected] if you are interested in the access method.
2
4
3

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 13
3.10 Wall-mount remote control connector
All decoders with the “-R” option include a 3.5 mm jack ( in Figure 2) to connect the TMH60ENA wall
mount remote control.
In this case, a 3.5 mm jack to terminal adapter is supplied to easily connect the 3 wires needed for the remote
control, as shown in the figure:
Terminal
Wire
D
Data
+
5V output
-
Ground
Figure 9: Adapter for wall-mount remote control connector
These 3 wires must be connected to the TMH60ENA wall mount controller corresponding terminals.
12

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 14
Chapter 4: Configuration and control of the device
The devices have an integrated Web server that allows you to configure and control them remotely from any
Web browser.
This document will focus on the Web server for the E417 model, indicating in each case the features that are
not available in other models.
4.1 Accessing the device
Connect the device to the Ethernet network and the power supply7.
The devices are configured in factory to acquire its IP address by DHCP. If your network has a DCHP server, it
will assign a valid IP to the device about 40 seconds after powering the device.
If there is no DHCP server or isn't accessible for any reason, after 3 minutes approximately, the device will
configure itself with the following access parameters:
IP:
192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask:
255.255.255.0
Gateway:
192.168.1.254
There are three methods to know the IP address of the device:
Connect headphones to the connector and momentarily press the "IP/RD" button . The
device will say its IP address through the headphones.
Using the free "EQUITEL Devices Searcher" application8, for locating Equitel devices in an Ethernet
network.
Using the free application "ENALite"8to access to the device.
Once the IP is known, you can access the web server with a standard web browser following this steps:
Configure the computer's IP in the same subnet as the device and make sure there are no other
devices on the network with the same IP addresses.
Start your browser and type the IP address of the device in the access bar.
A dialog box requesting an username and password will appear. Devices are shipped with the
following credentials by default:
User:
admin
Password
admin
7In PoE models, you can connect the device directly to a PoE switch.
8You can download the applications from our website: www.ena.equitel.es
10
6

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 15
Once the credentials are entered correctly, the initial page is shown:
Figure 10: Web server initial page
At the top of the page are shown the device model, a button to change between control and configuration
mode, and the icons to change the language.
Initially no source is configured. So, the only information shown on this page is the device's MAC, serial
number and firmware version.
The upper button lets you toggle between the two working modes:
Control Mode: When the device is properly configured, this page shows its status and allows its
control (i.e. background music channel selection and volume control). See section 4.3 .
Configuration Mode: To configure the device parameters. See section 4.2.
Mode change
Language change

June 2015 - Ed.2.1
Audio over IP decoders E411, E413, E415 & E417 technical manual Page 16
4.2 Configuration
Once the configuration mode is chosen, the browser will show a page with five tabs to access to all
configurable device parameters:
Figure 11: General settings page
Generic: General information about the device identification and credentials settings.
Audio I/O: Analog audio inputs and outputs related settings. Only applies to E415 and E417.
Channels: Audio channels configuration.
Network: Ethernet interface configuration.
Fw/Reset: Firmware update, initial values recovery and device's reset.
VERY IMPORTANT: After doing changes in the configuration, you must press the "Save" button that appear at
the bottom of the page. If the browser window isn’t high enough to show the button, you must use the
vertical scroll bar to make it visible.
When changes are saved, the device reboots and disconnects for about 30 seconds.
If device is working in DHCP mode, the reboot time is increased to about 60 seconds.
Navigating through the configuration pages doesn’t lose the temporary changes. So, you can save the
changes only after all the configuration is done.
Next sections show the configuration pages.
Other manuals for E411
1
This manual suits for next models
3
Table of contents