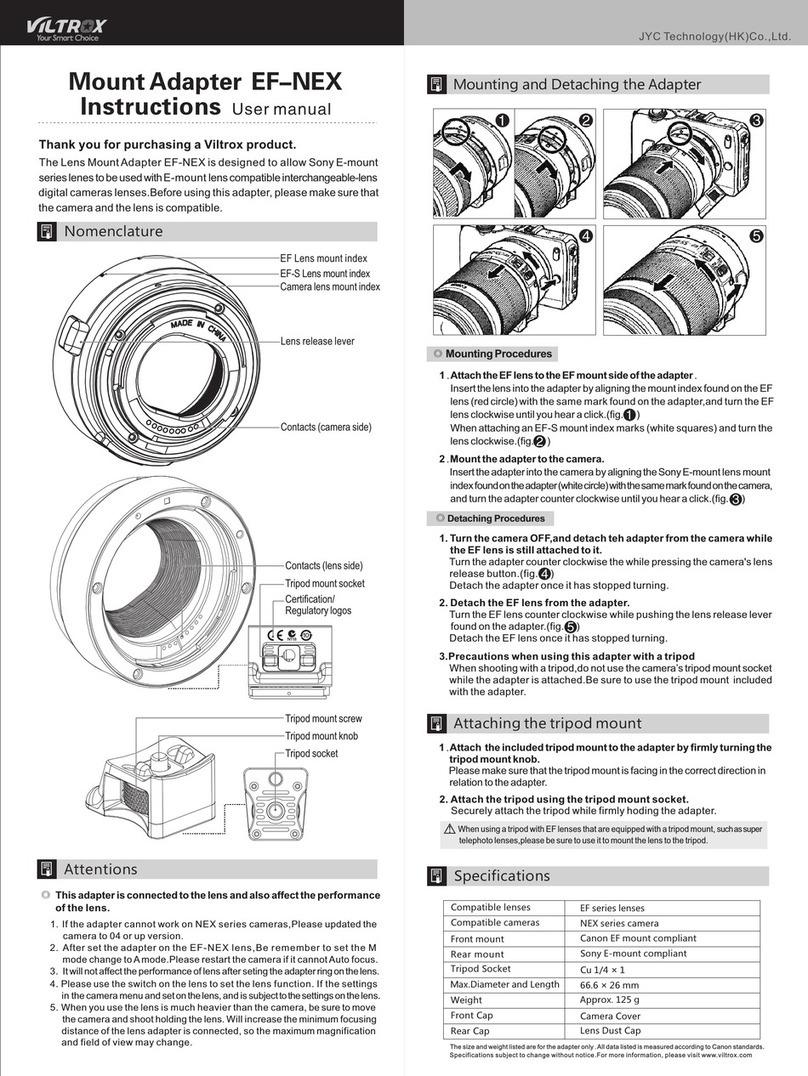
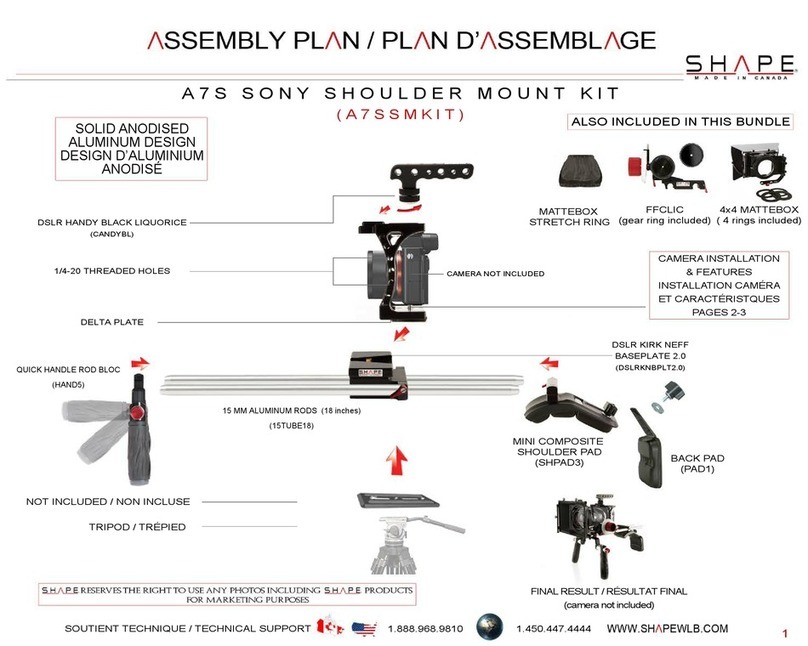
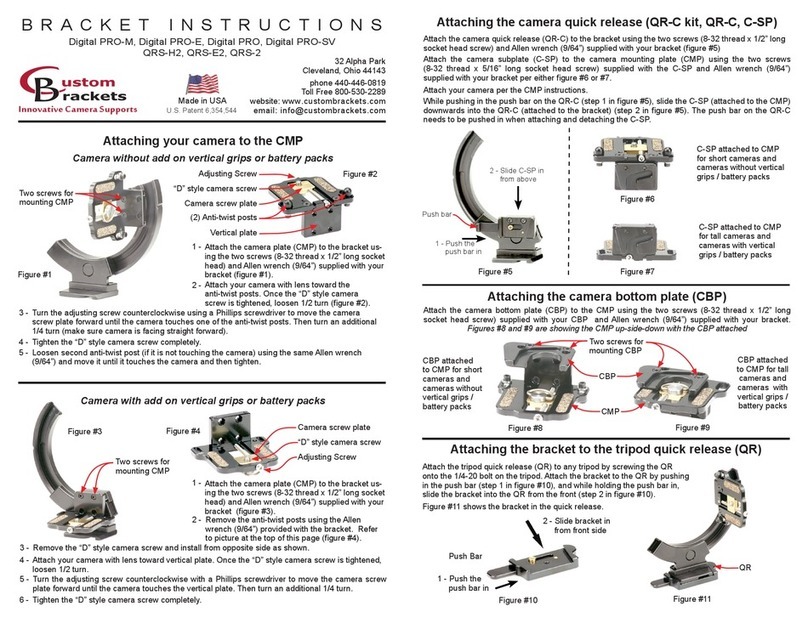
Freedom Lite Installation Manual Revision 12
P a g e 2 | 30
Table 2.1 provides an overview of the 52V Freedom Lite Home and Business range. There
are eight Freedom Lite models in the Home and Business range, as included in the table,
classified in terms of energy capacity.
An image with numbered labels pertaining to the following paragraphs is provided in Figure
2.1. The model number denotes with the first number [1] the total energy storage capacity
in kWh of each model. The second number [2] denotes the average amount of energy in
kWh that should be withdrawn per cycle (on average) in order to optimise the life of the
lithium cells. This equates to 80% of the total for each model i.e. 80% depth of discharge
(DoD). Note that all Freedom Lite batteries offer a maximum of 90% DoD as standard.
The range is designed with a tall and slim profile with the “Home” models intended to be
wall mounted (floor mounting is also possible – all models are supplied standard with plastic
feet). The larger “Business” range is floor standing with aluminium feet with plastic pads on
the underside.
The Ah capacity is also provided in the tables for each model for easy reference.
The maximum current for each model is governed by the rating of the built-in circuit breaker
[3], which has been sized below the maximum current capability of the lithium cells. There is
no noticeable cell temperature rise during operation and no active cooling of the cells is
required. The time limit for operation at the maximum current is 5 minutes in a 30 minute
cycle. To ensure that the circuit breaker does not trip in normal operation it is advised that
the design of the system aims to remain at or below the continuous current value.
For the 52V models the absolute maximum allowable voltage when fully charged is 56V,
however a more typical inverter charge setting range is 55.5V to 55.8V, depending on the
inverter voltage tracking accuracy in preventing a voltage overshoot above 56V. The voltage
normally used as the minimum cut off is 48V, however this will not typically be reached if
operating down to 90% Depth of Discharge (DoD). The BMS will command the connected
inverter with CAN Bus interface to stop discharging the battery at 10% SoC (90% DoD),
which roughly equates to 49,0V). Under high load the voltage may drop to 48V whilst still
above 10% SoC. A voltage of 48V or even lower can be observed in systems without a CAN
Bus interface or where the standby current draw on the inverter has caused the battery to
be discharged below 10% SoC. The battery breaker will eventually trip the battery at around
47V to protect the cells from undervoltage.