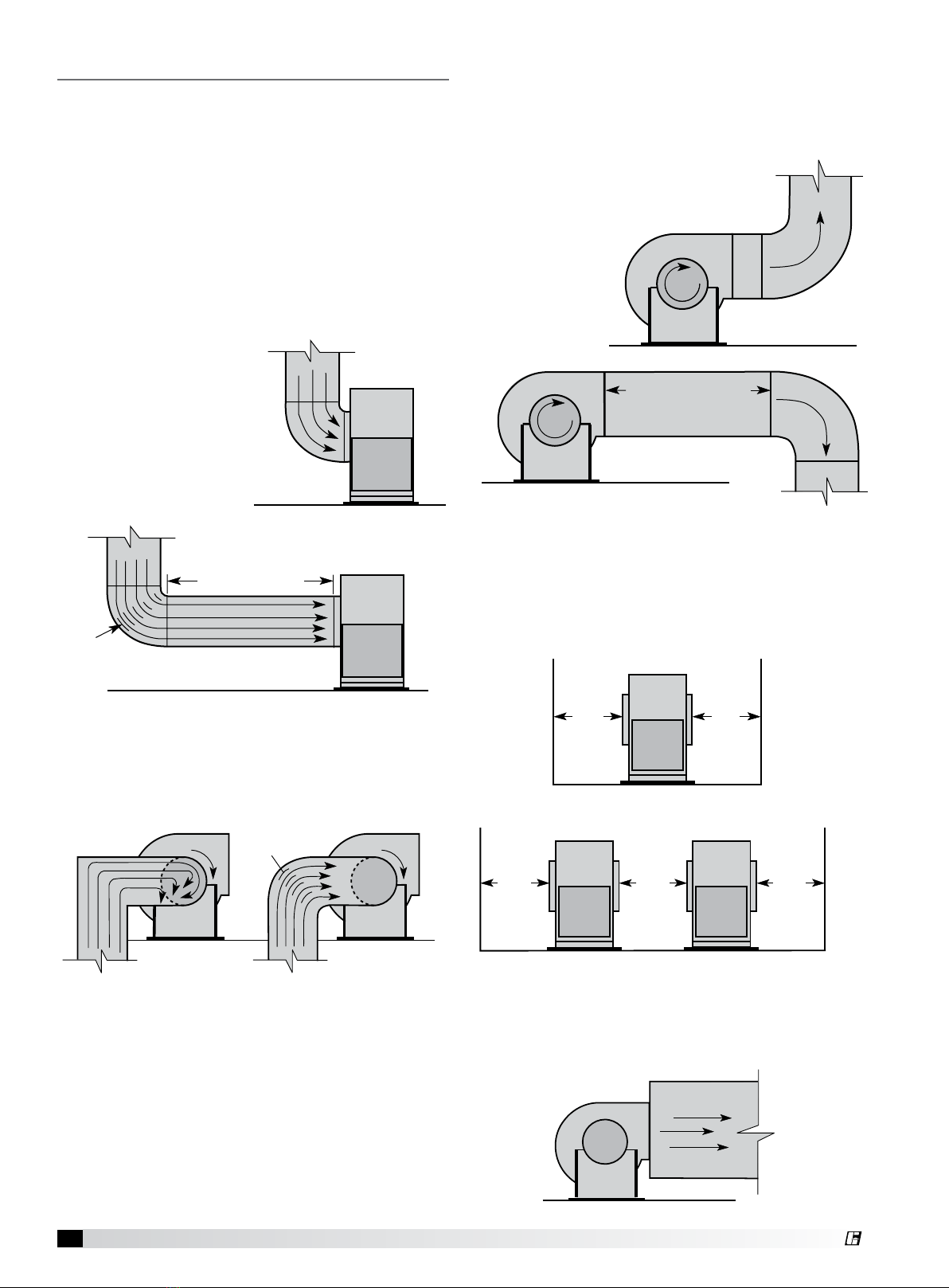
2Centrifugal Single-Width Blower
Receiving
Upon receiving the product, check to ensure all items
are accounted for by referencing the delivery receipt or
packing list. Inspect each crate or carton for shipping
damage before accepting delivery. Alert the carrier
of any damage detected. The customer will make
a notation of damage (or shortage of items) on the
delivery receipt and all copies of the bill of lading which
is countersigned by the delivering carrier. If damaged,
immediately contact your local sales representative.
Any physical damage to the unit after acceptance is
not the responsibility of manufacturer.
Unpacking
Verify that all required parts and the correct quantity
of each item have been received. If any items are
missing, report shortages to your local representative
to arrange for obtaining missing parts. Sometimes it
is not possible that all items for the unit be shipped
together due to availability of transportation and truck
space. Confirmation of shipment(s) must be limited to
only items on the bill of lading.
Handling
Fans are to be rigged and moved by the lifting brackets
provided or by the skid when a forklift is used. Location
of brackets varies by model and size. Handle in such
a manner as to keep from scratching or chipping the
coating. Damaged finish may reduce the ability of the
fan to resist corrosion. Fans should never be lifted by
the shaft, fan housing, motor, belt guard, windband
or accessories.
Storage
• Rotate fan wheel monthly and purge bearings once
every three months
• Energize fan motor once every three months
• Store belts flat to keep them from warping
and stretching
• Store unit in a location which does not
have vibration
• After storage period, purge grease before putting
fan into service.
If storage of fan is in a humid, dusty or corrosive
atmosphere, rotate the fan and purge the bearings
once a month. Improper storage which results in
damage to the fan will void the warranty.
Fans are protected against damage during shipment. If
the unit cannot be installed and operated immediately,
precautions need to be taken to prevent deterioration
of the unit during storage. The user assumes
responsibility of the fan and accessories while in
storage. The manufacturer will not be responsible
for damage during storage. These suggestions are
provided solely as a convenience to the user.
INDOOR -
The ideal environment for the storage of
fans and accessories is indoors, above grade, in a
low humidity atmosphere which is sealed to prevent
the entry of blowing dust, rain or snow. Temperatures
should be evenly maintained between 30° to 110°F
(-1° to 43°C), wide temperature swings may cause
condensation and “sweating” of metal parts. All
accessories must be stored indoors in a clean, dry
atmosphere.
Remove any accumulations of dirt, water, ice, or snow
and wipe dry before moving to indoor storage. To avoid
“sweating” of metal parts allow cold parts to reach room
temperature. To dry parts and packages, use a portable
electric heater to remove any moisture build up. Leave
coverings loose to permit air circulation and to allow for
periodic inspection.
The unit should be stored at least 3½ inches
(89 mm)
off the floor on wooden blocks covered with moisture
proof paper or polyethylene sheathing. Aisles between
parts and along all walls should be provided to permit
air circulation and space for inspection.
OUTDOOR - Fans designed for outdoor applications
may be stored outdoors, if absolutely necessary. Roads
or aisles for portable cranes and hauling equipment
are needed.
The fan should be placed on a level surface to prevent
water from leaking into the fan. The fan should be
elevated on an adequate number of wooden blocks
so it is above water and snow levels and has enough
blocking to prevent it from settling into soft ground.
Locate parts far enough apart to permit air circulation,
sunlight and space for periodic inspection. To minimize
water accumulation, place all fan parts on blocking
supports so rain water will run off.
Do not cover parts with plastic film or tarps as these
cause condensation of moisture from the air passing
through heating and cooling cycles.
Fan wheels should be blocked to prevent spinning
caused by strong winds.
Inspection and Maintenance During
Storage
While in storage, inspect fans once per month. Keep a
record of inspection and maintenance performed.
If moisture or dirt accumulations are found on parts,
the source should be located and eliminated. At
each inspection, rotate the wheel by hand ten to
fifteen revolutions to distribute lubricant in motor and
bearings. If paint deterioration begins, consideration
should be given to touch-up or repainting. Fans with
special coatings may require special techniques for
touch-up or repair.
Machined parts coated with rust preventive should be
restored to good condition promptly if signs of rust
occur. Immediately remove the original rust preventive
coating with petroleum solvent and clean with lint-
free cloths. Polish any remaining rust from surface
with crocus cloth or fine emery paper and oil. Do not
destroy the continuity of the surfaces. Thoroughly wipe
clean with Tectyl®506 (Ashland Inc.) or the equivalent.
For hard to reach internal surfaces or for occasional
use, consider using Tectyl®511M Rust Preventive,
WD-40®or the equivalent.