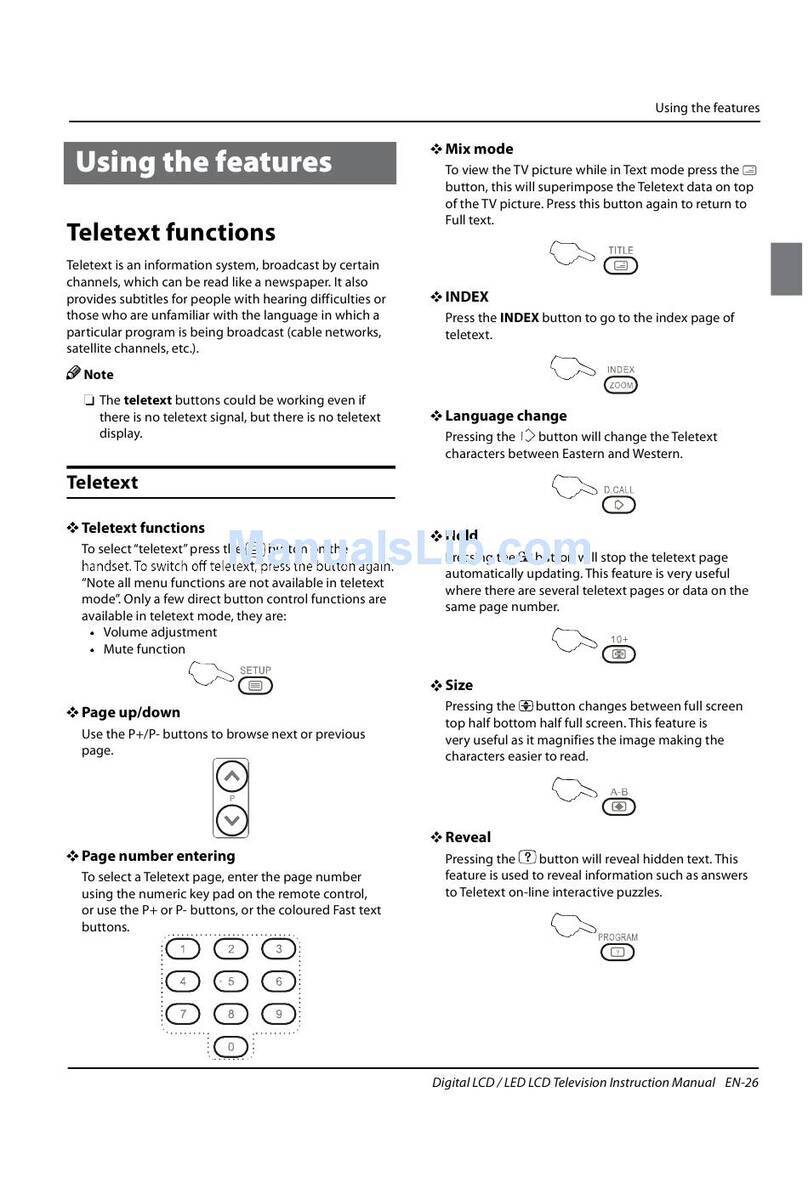
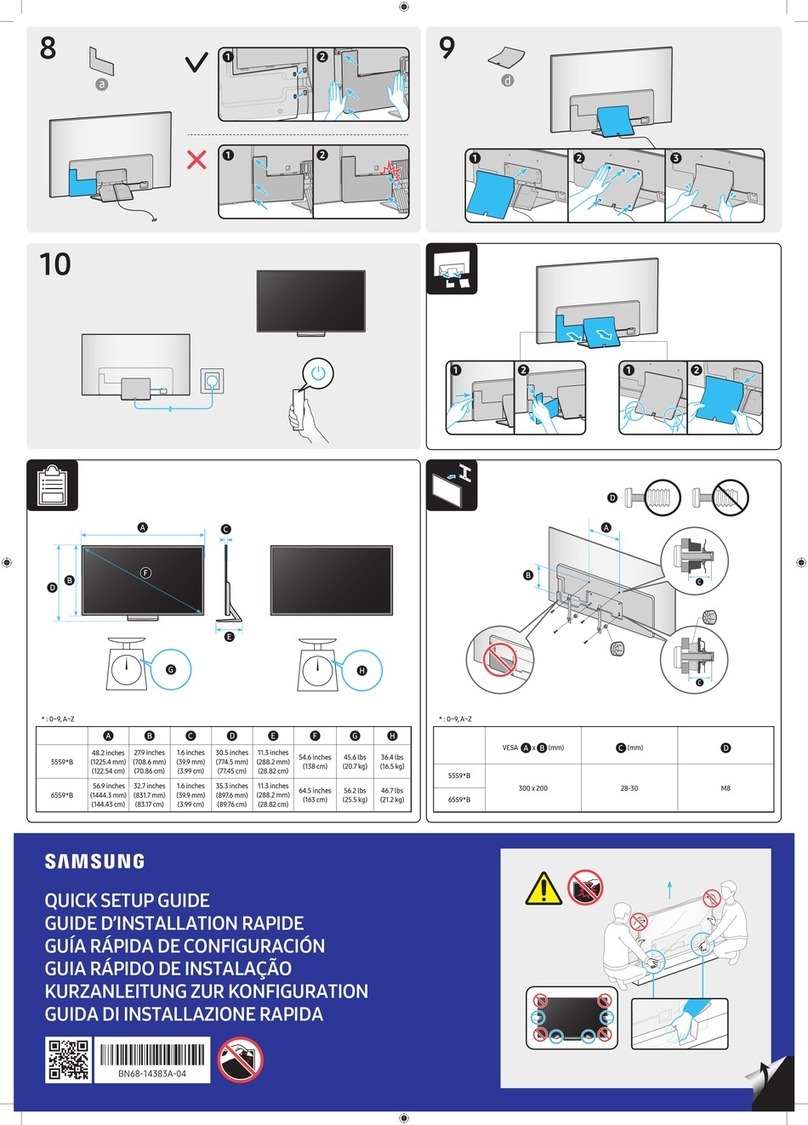
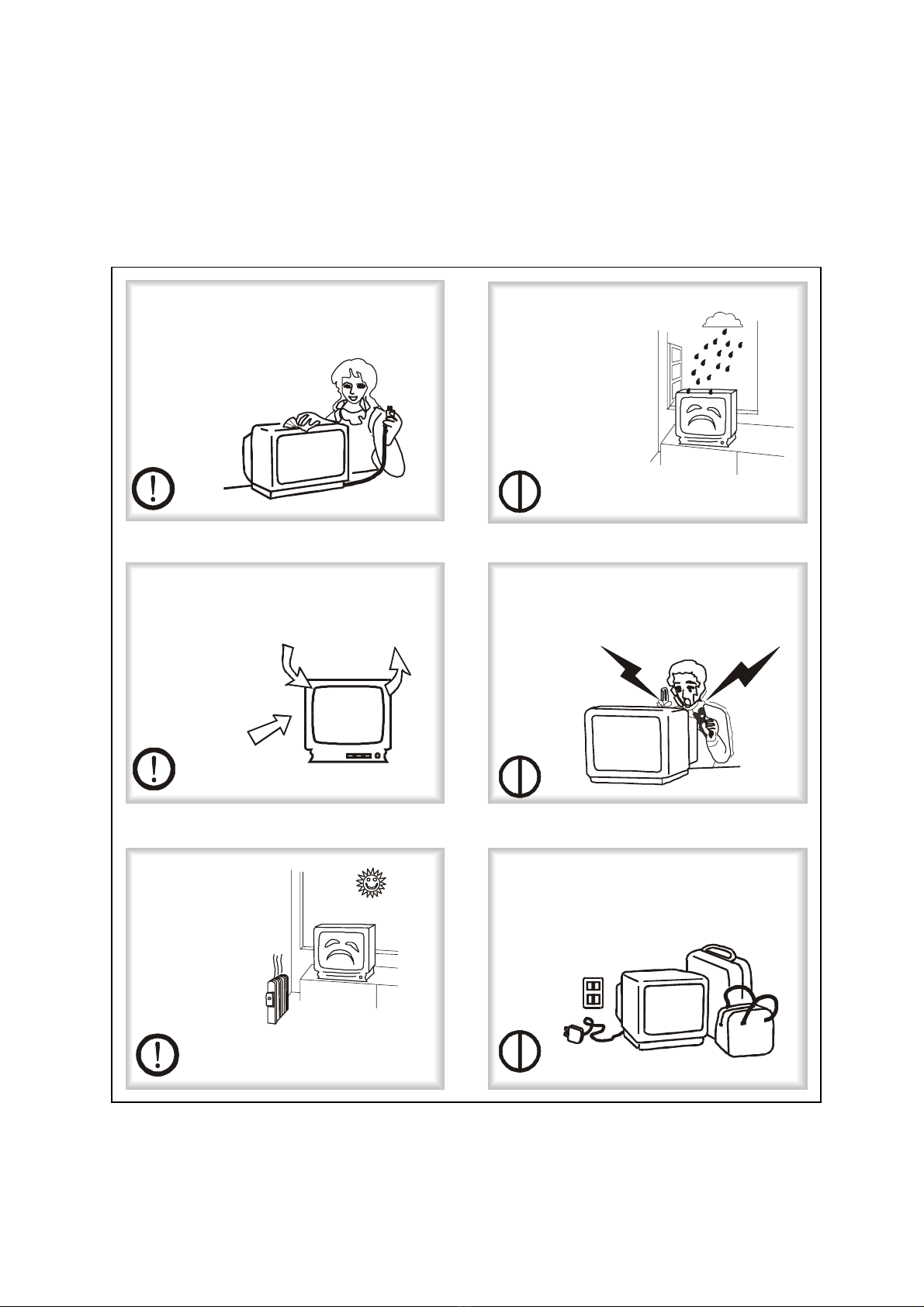
7
8. Always connect the test receiver ground lead to the receiver chassis ground
before connecting the test receiver positive lead.
Always remove the test receiver ground lead last.
9. Use with this receiver only the test fixtures specified in this service manual.
CAUTION: Do not connect the test fixture ground strap to any heat sink in this
receiver.
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity.
Such components are usually called Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices.
Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field effect
transistors and semiconductor “chip” components. The following techniques should
be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage caused by static
electricity.
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-
equipped assembly, drain off any electrostatic charge on your body by touching a
known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available
discharging wrist strap device, which should be removed to prevent potential
shock prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the
assembly on a conductive surface such as aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic
charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static type folder removal device. Some solder removal devices
not classified as “anti-static” can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage
ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges
sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until
immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most replacement ES devices are
packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum
foil or comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a
replacement ES device, touch the protective material to the chassis or circuit
assembly into which the device will be installed.
CAUTION: Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all
other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices.
(Otherwise even some normally harmless motions such as mutual brushing of