HD HD24613 User manual

i
802.11g In-wall WLAN
Access Point
Model No. HD24613
User Guide
HD24613_UG_001

ii
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pur-
suant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiated ra-
dio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will
not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or tel-
evision reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encour-
aged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
zReorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
zIncrease the separation between the equipment and receiver.
zConnect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
zConsult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: To assure continued compliance, (example – use only shielded interface cables when
connecting to computer or peripheral devices). Any changes or modifications not expressly approved
by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or trans-
mitter.
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environ-
ment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20 cm between the ra-
diator & your body.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two condi-
tions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interfe-
rence received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.

iii
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of DIRECTIVE 1999/5/CE OF THE EUROPEAN
PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL OF 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunication
terminal equipment and the mutual recognition of their conformity (R&TTE).
The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC (Telecommunications Termin-
al Equipment and Satellite Earth Station Equipment) as of April 8,2000.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it. Howev-
er, special attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when working
with electrical equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacture must therefore be
allowed at all times to ensure the safe use of the equipment.
EU Countries Intended for Use
The ETSI version of this device is intended for home and office use in Austria, Belgium, Denmark,
Finland, France (with Frequency channel restrictions), Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,
Portugal, Spain, Sweden, The Netherlands, and United Kingdom.
The ETSI version of this device is also authorized for use in EFTA member states Norway and Swit-
zerland.
EU Countries Not Intended for Use
None.

iv
Table of Contents
1. Introduction......................................................................................................................... 1
1.1. Overview................................................................................................................... 1
1.2. Features.................................................................................................................... 1
1.3. LED Definitions.........................................................................................................3
2. First-Time Installation and Configuration............................................................................ 4
2.1. Power........................................................................................................................ 4
2.2. Installing the HD24613 ............................................................................................. 4
2.3. Connecting a Managing Computer........................................................................... 5
2.4. Configuring the AP.................................................................................................... 5
2.4.1. Login............................................................................................................... 6
2.4.2. Selecting Mode............................................................................................... 7
2.4.3. Configuring TCP/IP Settings........................................................................... 8
2.4.4. Configure IEEE 802.11 Settings..................................................................... 9
2.4.5. Review and Apply Settings........................................................................... 10
2.5. Setting up Client Computers................................................................................... 10
2.5.1. Configure IEEE 802.11 Settings................................................................... 10
2.5.2. Configure TCP/IP-Related Settings.............................................................. 11
2.6. Confirm Settings of the HD24613 and Client Computers ....................................... 11
2.6.1. Checking if the IEEE 802.11b-Related Settings Work.................................. 11
2.6.2. Checking if the TCP/IP-Related Settings Work ............................................ 11
3. Advanced Network Management...................................................................................... 12
3.1. Overview................................................................................................................. 12
3.1.1. Menu Structure............................................................................................. 12
3.1.2. Save, Save & Restart, and Cancel Commands............................................ 13
3.1.3. Home and Refresh Commands.................................................................... 14
3.2. Viewing Status........................................................................................................ 15
3.2.1. Associated Wireless Clients ......................................................................... 15
3.2.2. Current DHCP Mappings.............................................................................. 15
3.2.3. System Log................................................................................................... 15
3.2.4. Link Monitor.................................................................................................. 16
3.3. General Operations ................................................................................................ 16
3.3.1. Specifying Operational Mode ....................................................................... 16
3.3.2. Changing Password ..................................................................................... 18
3.3.3. Managing Firmware...................................................................................... 18
3.3.3.1. Upgrading Firmware by HTTP............................................................ 18
3.3.3.2. Backing up and Restoring Configuration Settings by HTTP............... 19
3.3.3.3. Upgrading Firmware by TFTP............................................................ 19
3.3.3.4. Backing up and Restoring Configuration Settings by TFTP............... 21
3.3.3.5. Resetting Configuration to Factory Defaults....................................... 22
3.4. Configuring TCP/IP Related Settings ..................................................................... 22
3.4.1. Addressing.................................................................................................... 22
3.4.2. DHCP Server................................................................................................ 23
3.4.2.1. Basic................................................................................................... 23
3.4.2.2. Static DHCP Mappings....................................................................... 23
3.5. Configuring IEEE 802.11 Related Settings............................................................. 24
3.5.1. Communication............................................................................................. 24
3.5.1.1. Basic................................................................................................... 24
3.5.1.2. Link Integrity....................................................................................... 25
3.5.1.3. Association Control ............................................................................ 25
3.5.1.4. Load Balancing................................................................................... 25
3.5.1.5. Wireless Distribution System.............................................................. 26
3.5.2. Security......................................................................................................... 28
3.5.2.1. Selecting Wireless Security Mode...................................................... 29

v
3.5.2.2. MAC-Address-Based Access Control ................................................ 31
3.5.3. IEEE 802.1x/RADIUS................................................................................... 33
3.6. Advanced Settings.................................................................................................. 35
3.6.1. Packet Filters................................................................................................ 35
3.6.1.1. Ethernet Type Filters.......................................................................... 35
3.6.1.2. IP Protocol Filters............................................................................... 35
3.6.1.3. TCP/UDP Port Filters......................................................................... 36
3.6.2. Management................................................................................................. 36
3.6.2.1. UPnP.................................................................................................. 36
3.6.2.2. System Log ........................................................................................ 37
3.6.2.3. SNMP................................................................................................. 37
Appendix A: Default Settings................................................................................................ 39
Appendix B: Troubleshooting................................................................................................ 40
B-1: Wireless Settings Problems................................................................................... 40
B-2: TCP/IP Settings Problems ..................................................................................... 41

1
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview
The HD24613 modular WLAN access point (AP) enables 802.11g or 802.11b client computers to
access the resources on an Ethernet network wirelessly or wired. It conveniently fits into standard
wall outlets and only takes a few minutes to install and configure for use. The HD24613 has a
built-in browser-based management application offering an easy to follow setup-wizard for novice
wireless users as well as comprehensive settings for more advanced users and/or network administra-
tors.
1.2. Features
zHD24613 Firmware Features
Operational Modes
AP/Bridge. This mode provides both Access Point and Static LAN-to-LAN Bridg-
ing functionality. The static LAN-to-LAN bridging function is supported through
Wireless Distribution System (WDS).
AP Client. This mode is for Dynamic LAN-to-LAN Bridging. The AP Client auto-
matically establishes bridge links with APs from any vendor.
RF Type Selection. The RF type of the WLAN interface can be configured to work in
IEEE 802.11b only, IEEE 802.11g only, or mixed mode (802.11g and 802.11b simulta-
neously).
64-bit and 128-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). For authentication and data
encryption.
Enabling/Disabling SSID Broadcasts. When the HD24613 is in AP/Bridge mode, the
administrator can enable or disable the SSID broadcasts functionality for security reasons.
When the SSID broadcast functionality is disabled, a client computer cannot connect to the
HD24613 with “blank” network name (SSID, Service Set ID); the correct SSID has to be
specified on client computers.
MAC-address-based Access Control. When the HD24613 is in AP/Bridge mode, it
can be configured to block unauthorized wireless client computers based on MAC (Media
Access Control) addresses. Additionally, an ACL (Access Control List) can be downloaded
from a TFTP server.
IEEE 802.1x/RADIUS. When the HD24613 is in AP/Bridge mode, it can be configured
to authenticate wireless users and distribute encryption keys dynamically by IEEE 802.1x
Port-Based Network Access Control and RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User
Service).
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access). The HD24613 supports the WPA standard proposed
by the Wi-Fi Alliance (http://www.wi-fi.org). Both WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) mode and
full WPA mode are supported. WPA is composed of TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Pro-
tocol) and IEEE 802.1x and serves as a successor to WEP for better WLAN security.

2
Repeater. When the HD24613 is in AP/Bridge mode, it can communicate with other APs
or wireless bridges via WDS (Wireless Distribution System). Therefore, a HD24613 can
wirelessly forward packets from wireless clients to another HD24613. Then the second
HD24613 forwards the packets to the Ethernet network.
Wireless Client Isolation. When the HD24613 is in AP/Bridge mode, wire-
less-to-wireless traffic can be blocked so that the wireless clients cannot see each other.
This capability can be used in hotspots applications to prevent wireless hackers from at-
tacking other wireless users’ computers.
AP Load Balancing. Several HD24613’s can form a load-balancing group. Within a
group, wireless client associations and traffic load can be shared among the devices. This
function is available when the HD24613 is in AP/Bridge mode.
Transmit Power Control. Transmit power of the HD24613’s RF module can be ad-
justed to desired RF coverage.
Link Integrity. When the HD24613 is in AP/Bridge mode and its Ethernet LAN interface
is detected to be disconnected from the wired network, all currently associated wireless
clients are disassociated by the HD24613 and no wireless client can associate with it.
Association Control. When the HD24613 is in AP/Bridge mode, it can be configured to
deny association requests when it has served too many wireless clients or traffic load is too
heavy.
Associated Wireless Clients Status. When the HD24613 is in AP/Bridge mode, it
can show the status of all wireless clients that are currently associated or ‘connected’.
Auto Channel Selection. The auto channel selection feature allows the device to auto-
matically select the channel that will provide optimum performance on powering up the
HD24613.
zDHCP client. The HD24613 can automatically obtain an IP address from a DHCP server.
zDHCP server. The HD24613 can automatically assign IP addresses to computers or other de-
vices by DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
Static DHCP Mappings. The administrator can specify static IP address to MAC ad-
dress mappings so that IP addresses are always assigned to the hosts with the specified
MAC addresses.
Showing Current DHCP Mappings. Displays which IP address is assigned to which
host identified by an MAC address.
zPacket Filtering. The HD24613 provides Layer 2, Layer 3, and Layer 4 filtering capabilities.
zFirmware Management Tools
Firmware Upgrade. The firmware of the HD24613 can be upgraded in the following
methods:
TFTP-based. Upgrading firmware by TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol).
HTTP-based. Upgrading firmware by HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol).

3
Configuration Backup. The configuration settings of the HD24613 can be backed up to
a file via TFTP or HTTP for later restoring.
Configuration Reset. Clears current configuration settings and restores to facto-
ry-default values.
zManagement
Browser-based Network Manager for configuring and monitoring the HD24613 via a
Web browser. The management protocol is HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol)-based.
SNMP. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) MIB I, MIB II, IEEE 802.1d,
IEEE 802.1x, and Private Enterprise MIB are supported.
UPnP. The HD24613 responds to UPnP discovery messages so that a Windows XP user
can locate the HD24613 in My Network Places and use a Web browser to configure it.
System Log. For system operational status monitoring.
Local log. System events are logged to the on-board RAM of the HD24613 and can
be viewed using a Web browser.
Remote log by SNMP trap. Systems events are sent in the form of SNMP traps to
a remote SNMP management server.
zPower over Ethernet. Power is supplied to the HD24613 via an Ethernet cable using an
802.3af compliant power injector.
zHardware Watchdog Timer. If the firmware “hangs” in an invalid state, the hardware
watchdog timer will detect this situation and restart the HD24613. This way, the HD24613 can
provide continuous services.
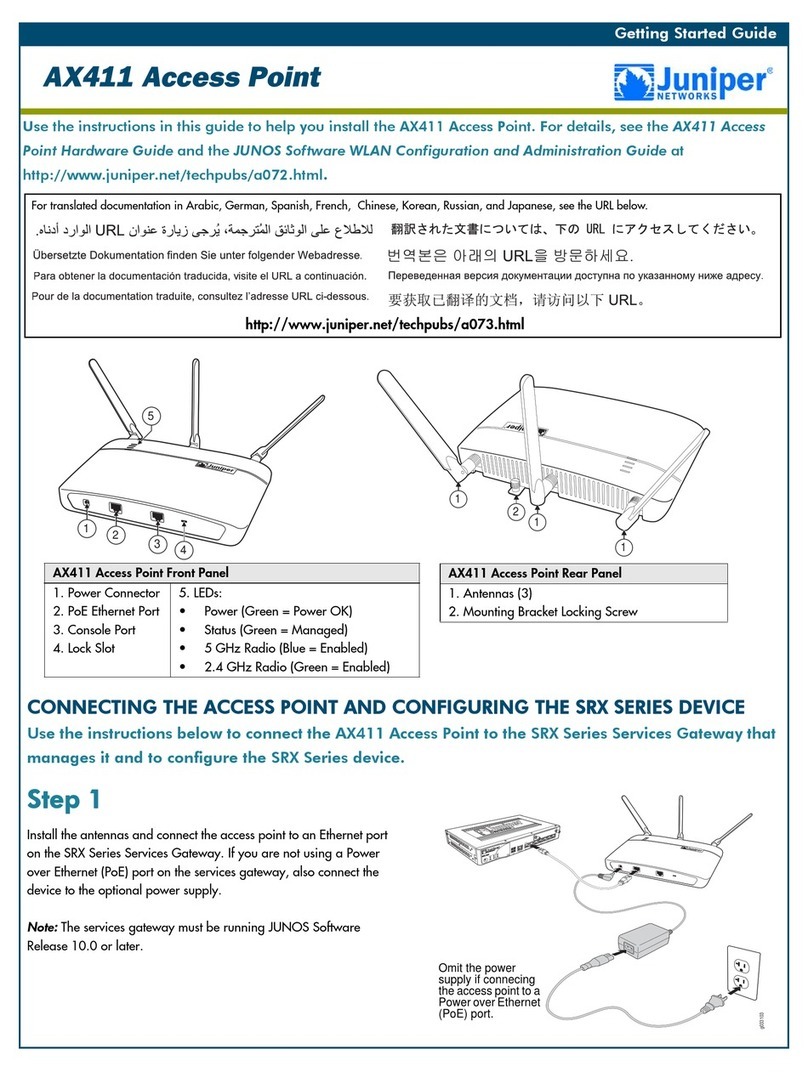
1.3. LED Definitions
There are several LED indicators on the front of the HD24613. Please refer to the definitions below:
A. Power: Green, solid when receiving power
B. WAN: Green, solid when connected, flashing when data activity
C. Wireless: Green, solid when on, flashing when wireless data activity

4
D. RJ-45 LAN port
Amber, solid when LAN connection
Green, solid when LAN connection, flashing when activity
2. First-Time Installation and Configuration
2.1. Power
The HD24613 is powered using PoE (Power over Ethernet). The HD24613 automatically selects the
suitable power supply.
To power the AP by PoE:
1. Plug one connector of an Ethernet cable to an available port of a PoE injector or switch.
2. Plug the other connector of the Ethernet cable to the WAN port on the rear of the HD24613.
NOTE: The HD24613 is 802.3af compatible.
2.2. Installing the HD24613
The HD24613 has two options for installation: desktop/flat surface or into a standard Ethernet wall
jack.
Desktop or flat surface:
1. Remove the HD24613 from the box and snap apart the two pieces of the screw less faceplate
that are affixed to the HD24613.
2. Place the HD24613 in desired location upon the desk or flat surface.
3. Using the single-port PoE Injector, connect one end of an Ethernet LAN cable from a LAN port
on the network router or switch and the opposite end to the port marked “Data In”. Use another
Ethernet LAN cable to connect the port marked “Data Out” to the WAN port (on rear) of the
HD24613.
4. Plug the single-port PoE power cord into an electrical outlet.
5. Check the LED indication lights. All three (Power, WAN, Wireless) should be properly lit.
Ethernet Wall Jack:
1. Remove the Ethernet wall jack faceplate and measure the depth of wall box.
2. Adjust the top and bottom brackets of the HD24613 accordingly.
3. Separate the cover (top) of the HD24613 faceplate from the frame (bottom).
4. With the HD24613 still in the faceplate frame, plug the wall jack LAN cable to the WAN port of
the HD24613. All three green LEDs on the HD24613 should be lit if properly connected to a
router/switch and PoE power supply. If “yes”, proceed to step 5.

5
5. Slowly insert the HD24613 into the wall box until the faceplate frame is flush to the wall.
6. Fasten both the HD24613 and the faceplate frame to the wall box with screws provided.
7. Line-up and push the faceplate cover onto the frame until it snaps securely into place.
2.3. Connecting a Managing Computer
To configure the HD24613 using the Advanced option, a managing computer with a Web browser is
needed.
NOTE: If you are using the browser, Opera, to configure the HD24613, click the menu item File,
click Preferences..., click File types, and edit the MIME type, text/html, to add a file extension
“.sht” so that Opera can work properly with the Web management pages of the AP.
Since the configuration/management protocol is HTTP-based, make sure that the IP address of the
managing computer and the IP address of the managed AP are in the same IP subnet (the default
IP address of the HD24613 is 192.168.100.1 and the default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.)
To connect the Ethernet managing computer and the managed HD24613 for first-time configuration,
you have two choices as illustrated in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Connecting a managing computer and the HD24613 via Ethernet
You can use either a standard Ethernet cable (included in the package) or a switch/hub with two nor-
mal Ethernet cables.
NOTE: One connector of the Ethernet cable must be plugged into the HD24613 WAN port for con-
figuration.
2.4. Configuring the AP
After the IP addressing issue is resolved, launch a Web browser on the managing computer. Then, go
to “http://192.168.100.1” to access the Web-based Network Manager login page.

6
TIP: The HD24613 can be reached by its host name using a Web browser. For example, if the
HD24613 is named “AP”, you can use the URL “http://AP” to access.
2.4.1. Login
Before the Home page is shown, you will be prompted to enter the user name and password to gain
the right to access the Web-based Network Manager. For first-time configuration, use the default user
name “root” and default password “root”, respectively.
Fig. 2. The Login page
NOTE: It is strongly recommended that the password be changed for security reasons. On the start
page, click the General, Password link to change the value of the password (see Section 3.3.1 for
more information).

7
Once you have successfully logged in, the Home page opens. Click the Setup Wizard option to
quickly setup the HD24613 for use in 4 steps. Alternately, click Advanced Setup to manually setup.
Fig. 3. The Home page
2.4.2. Selecting Mode
The HD24613 supports two operational modes:
AP/Bridge. This mode provides both Access Point and Static LAN-to-LAN Bridging
functionality. The static LAN-to-LAN bridging function is supported through Wireless
Distribution System (WDS).
AP Client. This mode is for Dynamic LAN-to-LAN Bridging. The AP Client automati-
cally establishes bridge links with APs from any vendors.
Fig. 4. Operational mode settings
1. Click on General from the side menu, and then select Operational Mode.
2. Select an operational mode and click Save to apply the setting.
In either mode, the HD24613 forwards packets between its Ethernet interface and wireless interface
for wired hosts on the Ethernet side and wireless host(s) on the wireless side.
There are two types of wireless links as specified by the IEEE 802.11 standard.

8
STA-AP. This type of wireless link is established between an IEEE 802.11 Station (STA)
and an IEEE 802.11 Access Point (AP). An STA is usually a client computer (PC or PDA)
with a WLAN network interface card (NIC). The AP Client mode is actually an STA.
WDS. This type of wireless link is established between two IEEE 802.11 HD24613’s.
Wireless packets transmitted along the WDS link comply with the IEEE 802.11 WDS
(Wireless Distribution System) format at the link layer.
The relationships among the operational modes and the wireless link types are shown in the following
table:
AP/Bridge AP Client
AP/Bridge WDS STA-AP
AP Client STA-AP
Table 1. Operational modes vs. wireless link types.
To establish a static bridge link based on WDS, the AP/bridges at both end of the WDS link must be
manually configured with each other’s MAC addresses (see Section 3.5.1.5 for more information). To
establish a dynamic bridge link between an HD24613 and an AP Client, both devices have to be con-
figured with the same SSID and WEP settings. The AP Client automatically scans for any HD24613
that is using the matched SSID and establishes a bridge link with the scanned HD24613.
NOTE: Although it’s more convenient to use dynamic bridging, it has a limitation—the AP Client
only can forward TCP/IP packets between its wireless interface and Ethernet interface; other type of
traffic (such as IPX and AppleTalk) is not forwarded.
TIP: When the HD24613 is configured to be in AP Client, it can be used as an Ethernet-to-wireless
network adapter. For example, a notebook computer equipped with an Ethernet adapter can be con-
nected to this device with a crossover Ethernet cable for wireless connectivity to another access point.
2.4.3. Configuring TCP/IP Settings
The IP address can be manually set or automatically assigned by a DHCP server on the LAN. If you
are manually setting the IP address, Subnet mask, and Default gateway settings, set them appro-
priately, so that they comply with your LAN environment. In addition, you can specify the Host name
and Domain (DNS suffix) of the AP.

9
Fig. 5. TCP/IP settings
1. Click on TCP/IP from the side menu and select Addressing.
2. When you have finished making changes, click Save or Save & Restart.
2.4.4. Configure IEEE 802.11 Settings
The Network Manager utility allows the user to configure IEEE 802.11b-related communication set-
tings, including Regulatory domain, Channel number, and Network name (SSID) of the HD24613.
The number of available RF channels depends on local regulations; therefore you have to choose an
appropriate regulatory domain to comply with local regulations. The SSID of a wireless client com-
puter and the SSID of the HD24613 must be identical for them to communicate with each other.
NOTE: Put a check in the Auto Channel Selection checkbox to allow the Frequency Channel of
the HD24613 to be automatically set.
Fig. 6. IEEE 802.11 communication settings
1. Click on IEEE 802.11 from the side menu, and then select Communication.
2. When you have finished, scroll to the bottom of the screen and click either Save or Save &

10
Restart.
2.4.5. Review and Apply Settings
On the Summary page, you can review all the settings you have made. Changes are highlighted in red.
If they are OK, click Restart to restart the HD24613 for the new settings to take effect.
Fig. 7. Settings changes are highlighted in red.
TIP: Since the Home page shows the current settings and status of the AP, it can be saved or printed
within the Web browser for future reference.
NOTE: Allow 7 seconds for the HD24613 to complete its restart process.
2.5. Setting up Client Computers
The TCP/IP and IEEE 802.11b-related settings of wireless client computers must match those of the
HD24613 in order for a wireless link to be established.
2.5.1. Configure IEEE 802.11 Settings
Before the TCP/IP networking system of a wireless client computer can communicate with other hosts,
the underlying wireless link must be established between a wireless-enabled computer and the
HD24613.
To establish a wireless link:
Launch the configuration/monitoring utility provided by the vendor of the installed wireless adapter
OR
Use the automatic wireless network connection feature in Windows XP.
NOTE: A wireless client computer must be in infrastructure mode before it can associate with an AP.

11
NOTE: The SSID of the wireless client computer and the SSID of the HD24613 must be identical.
Or, in case the SSID broadcasts capability of the HD24613 is enabled (by default), the SSID of the
wireless client computer could be set to “any”.
NOTE: Both the wireless client computer and the HD24613 must have the same WEP settings for
them to communicate with each other.
NOTE: For better wireless security, IEEE 802.1x capability of the HD24613 must be enabled so that
only authenticated wireless users can access the wireless network.
2.5.2. Configure TCP/IP-Related Settings
Use Windows Network Control Panel Applet to change the TCP/IP settings of the client computers,
so that the IP addresses of the client computers and the IP address of the HD24613 are in the same IP
subnet.
If a client computer is originally set a static IP address, you can either change its IP address to match
the IP address of the AP, or select an automatically-obtain-an-IP-address option if there is a DHCP
server on the network.
NOTE: For some versions of Windows, the computer needs to be restarted for the changes of TCP/IP
settings to take effect.
2.6. Confirm Settings of the HD24613 and Client
Computers
After configuring the HD24613 and setting up client computers, it is recommended that all settings
are checked and confirmed.
2.6.1. Checking if the IEEE 802.11b-Related Settings Work
To check if a wireless client computer can associate with the AP:
1. Launch the configuration/monitoring utility provided by the vendor of the installed WLAN NIC.
2. Check if the client computer is associated to an access point, and the access point is the
HD24613.
If the check fails, see Appendix B-1, “Wireless Settings Problems” for troubleshooting.
2.6.2. Checking if the TCP/IP-Related Settings Work
To check if a client computer can access the Internet:
1. Open a Windows Command Prompt window on the client computer.
2. Type “ping advap”, where advap is a placeholder for the IP address of the AP. Replace it with
your real IP address—for example, 192.168.0.1. Then press Enter.
If the HD24613 responds, go to the next step; else, see Appendix B-2, “TCP/IP Settings Prob-
lems” for troubleshooting.

12
3. Type “ping default_gateway”, where default_gateway is a placeholder for the IP address of the
default gateway of the wireless client computer. Then press Enter.
If the gateway responds, go to the next step; else, see Appendix B-2, “TCP/IP Settings Prob-
lems” for troubleshooting.
4. Type “ping 1st_dns_server”, where 1st_dns_server is a placeholder for the IP address of the
primary DNS server of the wireless client computer. Then press Enter.
If this DNS server responds, go to the next step; else, see Appendix B-2, “TCP/IP Settings
Problems” for troubleshooting.
5. Type “ping 2nd_dns_server”, where 2nd_dns_server is a placeholder for the IP address of the
secondary DNS server of the wireless client computer. Then press Enter.
If this DNS server responds the client should have no problem with TCP/IP networking; else,
see Appendix B-2, “TCP/IP Settings Problems” for troubleshooting.
3. Advanced Network Management
This section covers the options and settings available in the ‘Advanced’ mode of the Web-based
Network Manager utility.
3.1. Overview
To enter, simply click on the “Advanced” option on the Home page after login.
Fig. 8. The Summary page
3.1.1. Menu Structure
The left side of the screen contains a menu for you to carry out commands. Here is a brief description
of the menu options:

13
zHome. Click this tab to return to the Home page.
zSummary. Click this tab to view a screen with at-a-glance status information.
zStatus. Click this tab to access the following settings:
Wireless Clients. The status of the wireless clients currently associated with the AP.
DHCP Mappings. Current IP-MAC address mappings of the built-in DHCP server.
System Log. System events log.
Link Monitor. When the HD24613 is in AP Client mode, this page shows the signal
strength and link quality of the wireless link to its associated access point.
zGeneral. Click this tab to access the following settings:
Operational Mode. Operational mode of the HD24613 —AP/Bridge or AP Client.
Password. Modify the login settings.
Firmware Tools. For upgrading the firmware of the HD24613, backing up and restoring
configuration, and configuration reset settings of the HD24613.
zTCP/IP. Click this tab to access the following settings:
Addressing. Modify IP address settings of the HD24613.
DHCP Server. Modify settings for the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
server.
zIEEE 802.11. Click this tab to access the following settings:
Communication. Modify basic IEEE 802.11b/g settings of the HD24613 to work prop-
erly with wireless clients.
Security. Modify security settings for authenticating wireless users and encrypting wire-
less data.
IEEE 802.1x/RADIUS. Modify IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Network Access Control and
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) security settings.
zAdvanced. Advanced settings of the HD24613.
Packet Filters. Ethernet Type Filters, IP Protocol Filters, and TCP/UDP Port Filters set-
tings.
Management. Modify UPnP, System Log, and SNMP settings.
3.1.2. Save, Save & Restart, and Cancel Commands
At the bottom of each page that contains settings you can configure, there are up to three but-
tons—Save, Save & Restart, and Cancel. Clicking Save stores the settings changes to the memory of
the HD24613 and brings you back to the Summary page. Clicking Save & Restart stores the settings
changes to the memory of the HD24613 and restarts the HD24613 immediately for the settings

14
changes to take effect. Clicking Cancel discards any settings changes and brings you back to the start
page.
Fig. 9. Save, Save & Restart, and Cancel.
If you click Save, the start page will reflect the fact that the configuration settings have been changed
by showing two buttons—Restart and Cancel. In addition, changes are highlighted in red. Clicking
Cancel discards all the changes. Clicking Restart restarts the HD24613 for the settings changes to
take effect.
Fig. 10. Settings have been changed
3.1.3. Home and Refresh Commands
At the bottom of a status page, there are two buttons—Home and Refresh. Clicking Home brings you
back to the Summary page. Clicking Refresh updates the shown status information.
Fig. 11. Home and Refresh buttons

15
3.2. Viewing Status
3.2.1. Associated Wireless Clients
On this page, the status information of each associated client, including its MAC address, IP address,
user name (if the client has been IEEE 802.1x authenticated), number of bytes it has sent, number of
bytes it has received, and the time of its last activity, is shown.
Fig. 12. Status of associated wireless clients
3.2.2. Current DHCP Mappings
On this screen, all the current static or dynamic DHCP mappings are shown. A DHCP mapping is a
correspondence relationship between an IP address assigned by the DHCP server and a computer or
device that obtains the IP address. A computer or device that acts as a DHCP client is identified by its
MAC address.
Fig. 13. Current DHCP mappings
A static mapping indicates that the DHCP client always obtains the specified IP address from the
DHCP server. You can set static DHCP mappings in the Static DHCP Mappings section of the
DHCP Server configuration page (see Section 3.4.2). A dynamic mapping indicates that the DHCP
server chooses an IP address from the IP address pool specified by the First allocateable IP address
and Allocateable IP address count settings on the DHCP Server configuration page.
3.2.3. System Log
System events are recorded in the memory of the HD24613. The logged information is useful for
troubleshooting purposes. See Section 3.6.2.2 for more information.
Table of contents