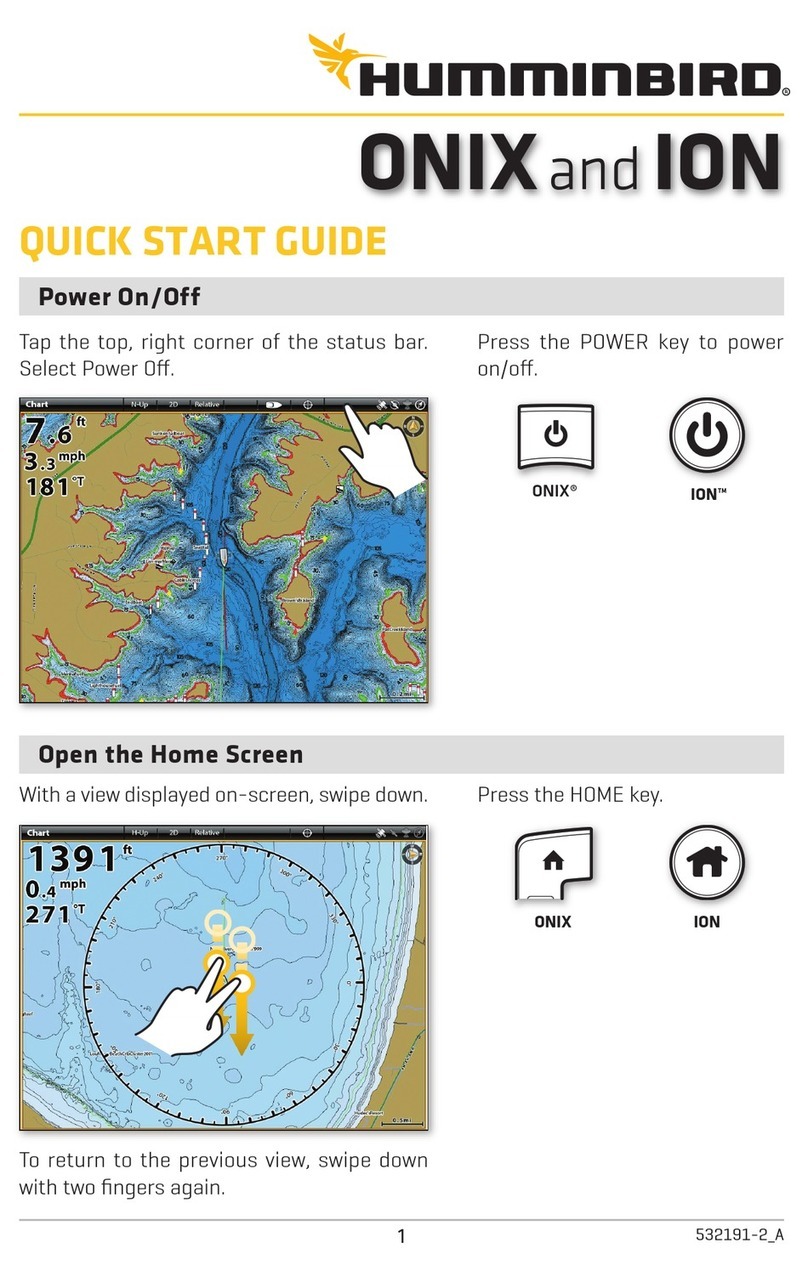
Hiprom Technologies 1756HP-GPS User manual

1756HP-GPS
USER MANUAL
Rev 2.8 – March 2009

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 2 of 39
Table of Contents
Chapter 1
Introduction ......................................................................................................3
Chapter 2
Module Accessories.........................................................................................4
Chapter 3
Module Operation.............................................................................................5
Chapter 4
Installing the Module ........................................................................................7
Chapter 5
Configuring the Module....................................................................................8
Chapter 6
I/O Address Map ............................................................................................12
Chapter 7
Module Specific Commands ..........................................................................17
Chapter 8
Module Status ................................................................................................23
Appendix A
PLC Ladder Example.....................................................................................26
Appendix B
Recommended PLC Data Types ...................................................................27
Appendix C
Specifications .................................................................................................31
Appendix D
GPS Operation...............................................................................................32
Appendix E
Time standards ..............................................................................................36
Appendix F
Glossary .........................................................................................................38

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 3 of 39
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
The 1756HP-GPS module provides accurate time and position information and services
for the Allen-Bradley ControlLogix PLC system.
The module makes use of Global Positioning System (GPS) technology to derive accurate
time which is synchronized with the atomic clocks located on the GPS satellites.
This document serves to describe the functionality, installation, configuration and use of
the module.

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 4 of 39
HIPROM GPS
PPS LOC OK
LOCK
CHAPTER 2
MODULE ACCESSORIES
Each 1756HP-GPS package includes the following components:
•1756HP-GPS module
•5m RG58 patch lead with a SMA male and TNC male connector on either end
•3.3V active 50Ωhard mount antenna
•1756HP-GPS user manual
Figure 2.1 : 1756HP-GPS module with antenna and patch-lead

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 5 of 39
CHAPTER 3
MODULE OPERATION
The 1756HP-GPS module is designed to operate within the Allen-Bradley ControlLogix
PLC system. All power required for the module’s operation is derived from the 1756
backplane.
Figure 3.1 : 1756HP-GPS Layout
The on-board GPS receiver is connected via the external SMA antenna port and external
antenna patch-lead to the active GPS antenna. As soon as the module is powered-up it
will begin searching for available GPS satellites. Soon after lock on at least 4 satellites has
been achieved the module’s internal time will become valid.
Alphanumeric Display
Status LEDs
Reserved External Interface Port
SMA Antenna Port

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 6 of 39
The current status of the module is conveyed to the user by means of the 3 bi-color Status
LED’s and the alphanumeric LED display.
The following information is available to the user directly across the backplane by means
of a scheduled connection:
•Date and Time in Gregorian Format (year, month, day, hour, minute etc.)
•Universal Coordinate Time (UTC)
•GPS Receiver Status
•Number of satellites being tracking
•Position in Polar Coordinates (latitude, longitude and altitude)
•Position in Cartesian Coordinates ( Earth-centered-earth-fixed X,Y,Z axis)
•Velocity in Polar Coordinates (Northerly, Easterly and Upward)
•Velocity in Cartesian Coordinates ( Earth-centered-earth-fixed X,Y,Z axis)
The module requires regular updates of the ControlLogix Controller’s CST (Coordinate
System Time) value to enable accurate CST conversion and wall-clock offset functions.
All time and date information can be adjusted to the local time-zone by configuring the
Time-Zone offset, in the scheduled output image.
Detailed GPS satellite information can also be requested by means of an unconnected
message, responding with the following for each of the 8 GPS receiver channels :
•Satellite Identifier (PRN)
•Current Satellite Azimuth
•Current Satellite Elevation
•Signal Strength
The 1756HP-GPS module supports two unconnected time conversion services, namely:
•CST ÆUTC and Gregorian
•UTC ÆGregorian
This allows the user by means of a custom message service to convert between different
time formats. The conversion is valid only for time data that is less than 1 hour old.

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 7 of 39
CHAPTER 4
INSTALLING THE MODULE
GPS utilizes a spread spectrum signal in the 1.5GHz range, and thus cannot penetrate
conductive or opaque surfaces. Thus the antenna should be mounted in a horizontal
position with an unobstructed view of the sky.
Attach the antenna patch lead to the antenna. It is recommended that waterproofing tape
be used to seal the connection.
NOTE: Should a longer patch lead be required it is recommended that a GPS signal
booster is used. Contact your local Hiprom distributor for assistance.
The module is equipped with a RIUP (Removal and Insertion Under Power) circuitry
enabling the module to be installed or removed from the chassis while power is applied.
Attach the patch lead SMA (male) to the module’s SMA (female) connector. It is not
recommended that the antenna patch lead exceed a total loss of 10dB at 1.5GHz, as this
may increase the time to GPS lock, or in extreme cases, prevent GPS lock from being
achieved at all.
Once the module has been powered up for the first time, it will search for satellites from a
cold start (i.e. no almanac). The module will take approximately 5 minutes to acquire Lock.
Once a complete almanac has been downloaded, the time to achieve fix will be reduced to
around 45 seconds.

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 8 of 39
CHAPTER 5
CONFIGURING THE MODULE
A direct connection between the controller and the 1756HP-GPS module is required to
transfer I/O data to and from the module. In addition the module supports various
unconnected messages that can be used to retrieve particular information.
5.1. Establishing the Direct Connection
This section describes the procedures necessary to configure the 1756HP-GPS module
within the ControlLogix system. Each 1756HP-GPS module must be owned by a single
ControlLogix controller.
The 1756 Generic Module is used in RSLogix5000 to configure the module. The
configuration of the module is detailed in the table below.
Data Format
CommFormat Data – DINT
Connection parameters
Description Instance Size
Input 1 29
Output 2 3
Configuration 4 2
RPI
Min 1.0 msec Max 750.0 msec
Table 5.1 : 1756HP-GPS connection parameters.
The steps required to add a new 1756HP-GPS module are detailed below.
Figure 5.1 : Right-click on I/O Configuration and select New Module

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 9 of 39
Figure 5.2 : Select Generic 1756 Module ( 1756-MODULE )
Figure 5.3 : Configure module’s parameters

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 10 of 39
Figure 5.4 : Configure module’s RPI (Requested Packet Interval)
Ensure that the first configuration byte of the configuration image is set to 0x00, as
illustrated below. If the user is using RSLogix 5000 v16 the UTC time base is different from
previous versions of RSLogix. To ensure that ControlLogix PLC’s running different
versions can be time synced using the 1756HP-GPS module the user must select if v16 is
used or not. The last bit (least significant bit) of the second byte of the configuration image
configures the module to use or not use v16 UTC time. By setting the bit, the module will
use v16 UTC time. The highest bit (most significant bit) of the second byte of the
configuration image configures the module to be the CST master. By setting this bit, the
module will attempt to become the CST master. If a CST master is present, it will not
become the CST master and indicate that a duplicate master was detected.
Configuration Image
BYTE VALUE
0 0x00
1 0x??
Byte 1 = X000 000Y (binary) where ‘X’ will make the module a CST master if set to 1 and
‘Y’ will make the module use v16 UTC time if set to 1.
Once a modules configuration data has been downloaded to the controller, it will attempt
to establish a connection with the module. A connection will fail if there is inappropriate
configuration data.

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 11 of 39
5.2. Coordinate System Time Master
It is important that at least one controller or 1756HP-GPS module in the ControlLogix rack
be configured as the Coordinate System Time master. This can be configured in
RSLogix5000 by right-clicking on the Controller and selecting Properties. Ensure that the
checkbox as indicated below is checked to make the controller the CST master; otherwise
the procedure in section 5.1 above may be followed to make the 1756HP-GPS module the
CST master.
Figure 5.5 : Configure CST Master

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 12 of 39
CHAPTER 6
I/O ADDRESS MAP
The input and output image of the 1756HP-GPS module is defined in the following
sections. Appendix A and B provide example code and recommended structures that can
be used to extract and view the data.
6.1. Input Image
Figure 6.1 : Connected Input Image

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 13 of 39
6.2. Input Image Description
Field/Value Description Location Type
Module OK
Module Status
0 = Module has faulted
1 = Module is operating properly
Local:s:I.Data[0].16 BIT
GPS Locked
Satellite Lock
0 = Not tracking sufficient satellites to provide
positional fix
1 = Sufficient satellites being tracked to provide
positional fix
Typically, tracking 4 satellites is sufficient to provide
lock.
Local:s:I.Data[0].17
BIT
CST Ok
Valid CST
1 = Module is receiving updates CST
0 = Module has not received updated CST for 1sec or
more
Local:s:I.Data[0].18 BIT
Time Valid
Date / Time Valid
0 = Date Time Not Valid
1 = Date Time synchronized with GPS
Local:s:I.Data[0].19
BIT
PPS
Pulse per Second
This bit transitions from 0 to 1 precisely every second.
The pulse duty cycle is approximately 50%.
Local:s:I.Data[0].20
BIT
BATT Ok
Battery Backup on Boot
0 = No battery backup available on boot-up.
1 = Battery backup available on boot-up.
With battery backup enabled the time taken for the
GPS module to regain satellite lock is greatly
reduced.
It is recommended that if the module is not to be used
for an extended period that the battery backup be
disabled.
Local:s:I.Data[0].21 BIT
ANT Ok
Antenna OK
0 = Antenna Fault
1 = Antenna OK
An Antenna fault will occur if the antenna is not
present or has been damaged.
Local:s:I.Data[0].22 BIT
PDOP Ok
PDOP OK
0 = Position Dilution of Precision is unacceptable
1 = No Position Dilution of Precision present
Position Dilution of Precision occurs when although
there are sufficient satellites in lock, 2 or more of
them appear to occupy similar positions in the sky
and thus the number of effective satellites is
decreased.
Local:s:I.Data[0].23 BIT
West
Current East / West Hemisphere
0 = Current position in East hemisphere
1 = Current position in West hemisphere
Local:s:I.Data[0].24 BIT
South
Current North / South Hemisphere
0 = Current position in North hemisphere
1 = Current position in South hemisphere
Local:s:I.Data[0].25 BIT
Reserved Reserved Local:s:I.Data[0].26..27 BIT

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 14 of 39
Dup Master
A duplicate CST master has been detected
0 = No duplicate CST master detected
1 = A duplicate CST master is detected
Local:s:I.Data[0].28 BIT
CST Master
This module is the local rack CST master
0 = This module is not the CST master
1 = This module is the CST master
Local:s:I.Data[0].29 BIT
Reserved Reserved Local:s:I.Data[0].30..31 BIT
SV Count
Satellite count
Number of Satellites currently being tracked
Local:s:I.Data[1] DINT
Year
Calendar Year
Current Local Calendar Year
This is dependent on the configured time zone (O:e.2)
Local:s:I.Data[2] DINT
Month
Calendar Month
Current Local Calendar Month ( 1 - 12 )
This is dependent on the configured time zone (O:e.2)
Local:s:I.Data[3] DINT
Day
Calendar Day of Month
Current Local Calendar Day ( 1 - 31 )
This is dependent on the configured time zone (O:e.2)
Local:s:I.Data[4] DINT
Hours
Real Time Hours
Current Local time Hours ( 0 - 23 )
This is dependent on the configured time zone (O:e.2)
Local:s:I.Data[5] DINT
Minutes
Real Time Minutes
Current Local time Minutes ( 0 - 59 )
This is dependent on the configured time zone (O:e.2)
Local:s:I.Data[6] DINT
Seconds Real Time Seconds
Current real time Seconds ( 0 - 59 ) Local:s:I.Data[7] DINT
Microseconds Real Time Microseconds
Current real time Microseconds ( 0 – 999 999 ) Local:s:I.Data[8] DINT
UTC Current Universal Time Constant (UTC)
Local:s:I.Data[9]
To
Local:s:I.Data[10]
64BIT
CST Current CLX Coordinate System Time (CST)
Local:s:I.Data[11]
To
Local:s:I.Data[12]
64BIT
CST Offset
Current CLX Coordinate System Time (CST) Offset
Current Time = CST + CST Offset
This is dependent on the configured time zone (O:e.2)
Local:s:I.Data[13]
To
Local:s:I.Data[14]
64BIT
Latitude
Degrees Current Position Latitude Degrees Local:s:I.Data[15] Low
16Bit INT
Latitude
Minutes Current Position Latitude Minutes Local:s:I.Data[15] High
16Bit INT
Latitude
Seconds Current Position Latitude Seconds Local:s:I.Data[16] REAL
Longitude
Degrees Current Position Longitude Degrees Local:s:I.Data[17] Low
16 Bit INT
Longitude
Minutes Current Position Longitude Minutes Local:s:I.Data[17]
High 16 Bit INT
Longitude
Seconds Current Position Longitude Seconds Local:s:I.Data[18] REAL
Altitude Current Position Altitude
(Meters above mean sea level) Local:s:I.Data[19] REAL
Velocity –
North
Current Northerly Velocity
(m/s x 10)
A negative value indicates a Southerly direction of
movement.
Local:s:I.Data[20] REAL
Velocity –
East
Current Easterly Velocity
(m/s x 10)
A negative value indicates a Westerly direction of
movement.
Local:s:I.Data[21] REAL
Velocity –
Upward
Current Upward Velocity
(m/s x 10)
A negative value indicates a Downward direction of
movement.
Local:s:I.Data[22] REAL

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 15 of 39
ECEF
Position X
Distance from Earth-centre along the X - axis.
(metres)
Position is calculated with respect to the WGS-84
Earth-Centred Earth-Fixed co-ordinate system.
The X-axis is defined as the vector with origin at the
earth's centre and passing through the intersection of
the equator and Greenwich meridian.
Local:s:I.Data[23] REAL
ECEF
Position Y
Distance from Earth-centre along the Y - axis.
(metres)
Position is calculated with respect to the WGS-84
Earth-Centred Earth-Fixed co-ordinate system.
The Y-axis is defined as the vector with origin at the
earth's centre and passing through the equator 90
degrees east of the Greenwich meridian.
Local:s:I.Data[24] REAL
ECEF
Position Z
Distance from Earth-centre along the Y - axis.
(metres)
Position is calculated with respect to the WGS-84
Earth-Centred Earth-Fixed co-ordinate system.
The Z-axis is defined as the vector with origin at the
earth's centre and passing through the North pole.
Local:s:I.Data[25] REAL
ECEF
Velocity – X
Speed with respect to the X - axis.
(m/s x 10)
The X-axis is defined as the vector with origin at the
earth's centre and passing through the intersection of
the equator and Greenwich meridian.
Local:s:I.Data[26] REAL
ECEF
Velocity – Y
Speed with respect to the Y - axis.
(m/s x 10)
The Y-axis is defined as the vector with origin at the
earth's centre and passing through the equator 90
degrees east of the Greenwich meridian.
Local:s:I.Data[27] REAL
ECEF
Velocity – Z
Speed with respect to the Z - axis.
(m/s x 10)
The Z-axis is defined as the vector with origin at the
earth's centre and passing through the North pole.
Local:s:I.Data[28] REAL

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 16 of 39
6.3. Output Image
6.4. Output Image Description
Field Description Location Type
Reserved Reserved 64Bits
Local:s:O.Data[0]
to
Local:s:O.Data[1] 64BIT
Time zone
Time Zone Configuration
Used to set the module to report in local time standard.
Time zone = UTC Offset where the UTC Offset is the
difference, in hours, between local time and GMT.
E.g. For Pacific Standard Time (GMT - 8) set time zone = -
8
Local:s:O.Data[2] REAL
The Time zone needs to be copied from a tag (of type real) into the output word. Appendix
A and B provide example code and recommended data types.

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 17 of 39
CHAPTER 7
MODULE SPECIFIC COMMANDS
The 1756HP-GPS module offers specific commands that enable the system to retrieve
GPS satellite information, as well as performing time base conversions. These are
accomplished using unconnected messaging via the MSG ladder instruction. This enables
communication to the module without a direct connection.
Appendix A and B provide example code and recommended data structures that can be
used to store the information.
7.1. Retrieving GPS Satellite Data
The module provides tracking data for up to 8 satellites/channels. Information pertaining to
each satellite includes:
PRN,
Each operational GPS satellite has a unique PRN identification number
Elevation
Measure of the elevation of the satellite in degrees from the horizon
Azimuth
Measure of the bearing to the satellite in degrees from true north
SnR
Measure of the satellite signal strength in dBHz calculated during signal
correlation.
The information is requested by setting up a CIP Generic Custom message block. The
configuration of the message instruction is as follows :
Field Value
Message Type CIP Generic
Service Type Custom
Service Code 0x32
Class 0x71
Instance 0x01
Attribute 0x01
Source Length 0
Destination Element Destination tag for reply data
Table 7.1 : Satellite data request configuration.

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 18 of 39
The message instruction will return the information in the following structure :
Field Bytes Type Description
Satellite[n] Prn 1 SINT Satellite number [1..32]
Satellite[n] Ele 1 SINT Elevation [0..90]
Satellite[n] Azm 2 INT Azimuth [0..360]
Satellite[n] SnR 4 DINT Signal – noise ratio
where n indicates the channel number ( 1 … 8)
Table 7.2 : Satellite data information response.
The above data structure is repeated for all 8 satellites, thus giving a total length of 64
bytes for the response.
Refer to Appendix B for a recommended data structure for the satellite data.
Figure 7.1 : Satellite data message structure.

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 19 of 39
7.2. Converting Time Bases
The 1756HP-GPS stores a rolling log of the CST/UTC pairs for the last 1 hour.
Timestamps in a system can either be CST or UTC values. The 1756HP-GPS module
provides functionality for converting between values that are within the last hour.
7.3. Converting CST to UTC and Gregorian
By supplying the full 64 bit CST value, the module will return the corresponding full
Gregorian date and UTC value. Configuration of this message is illustrated below.
Figure 7.2: Configuring the MSG CST->UTC conversion request instruction.
Refer to Appendix A for code examples.
Field Value
Message Type CIP Generic
Service Type Custom
Service Code 0x32
Class 0x70
Instance 0x01
Attribute 0x01
Source Length 0
Destination Element Destination tag for reply data
Table 7.3: CST->UTC conversion request configuration.

1756HP-GPS - User Manual Rev 2.8
.
Page 20 of 39
The structure of the request is as follows :
Field Bytes Type Description
CST 8 DINT[2] CST value
Table 7.4 : CST->UTC conversion request data.
A successful conversion will result in the following response :
Field Bytes Type Description
Year 2 DINT Gregorian year
Month 2 DINT Gregorian month
Day 2 DINT Gregorian day
Hour 2 DINT Gregorian hour
Min 2 DINT Gregorian min
Sec 2 DINT Gregorian sec
µSec 2 DINT Gregorian µSec
UTC 8 DINT[2] Corresponding UTC value
CST 8 DINT[2] Given CST value
Table 7.5: CST->UTC conversion successful response data.
An unsuccessful response will be sent back should the CST not fall within the previous
logged hour. The Table below identifies the error responses
Error Code Value
0x0000 0002 CST sent in request is too far in the future (> 1Sec in
future)
0x0000 0003 CST sent in request is too far in the past (> 1 Hour in past)
0x0000 0005 Module could not convert the request due to conversion
table not initializing fully or module loosing LOCK during
the time.
Table of contents
Other Hiprom Technologies GPS manuals