Preface
The H8S/2646 Series is a series of high-performance microcontrollers with a 32-bit H8S/2600
CPU core, and a set of on-chip supporting functions required for system configuration.
This LSI is equipped with a 16-bit timer pulse unit (TPU), programmable pulse generator (PPG),
watchdog timer (WDT), serial communication interface (SCI), A/D con erter, motor control
PWM timer (PWM), LCD controller/dri er (LCDC) and I/O ports as on-chip supporting modules.
In addition, data transfer controller (DTC) is pro ided, enabling high-speed data transfer without
CPU inter ention. This LSI is suitable for use as an embedded processor for high-le el control
systems. Its on-chip ROM are flash memory (F-ZTAT™*) that pro ides flexibility as it can be
reprogrammed in no time to cope with all situations from the early stages of mass production to
full-scale mass production. This is particularly applicable to application de ices with
specifications that will most probably change.
Note: * F-ZTAT™ is a trademark of Hitachi, Ltd.
Target Users: This manual was written for users who will be using the H8S/2646 Series in the
design of application systems. Members of this audience are expected to understand
the fundamentals of electrical circuits, logical circuits, and microcomputers.
Objecti e: This manual was written to explain the hardware functions and electrical
characteristics of the H8S/2646 Series to the abo e audience. Refer to the
H8S/2600 Series, H8S/2000 Series Programming Manual for a detailed description
of the instruction set.
Notes on reading this manual:
• In order to understand the o erall functions of the chip
Read the manual according to the contents. This manual can be roughly categorized into parts
on the CPU, system control functions, peripheral functions and electrical characteristics.
• In order to understand the details of the CPU's functions
Read the H8S/2600 Series, H8S/2000 Series Programming Manual.
• In order to understand the details of a register when its name is known
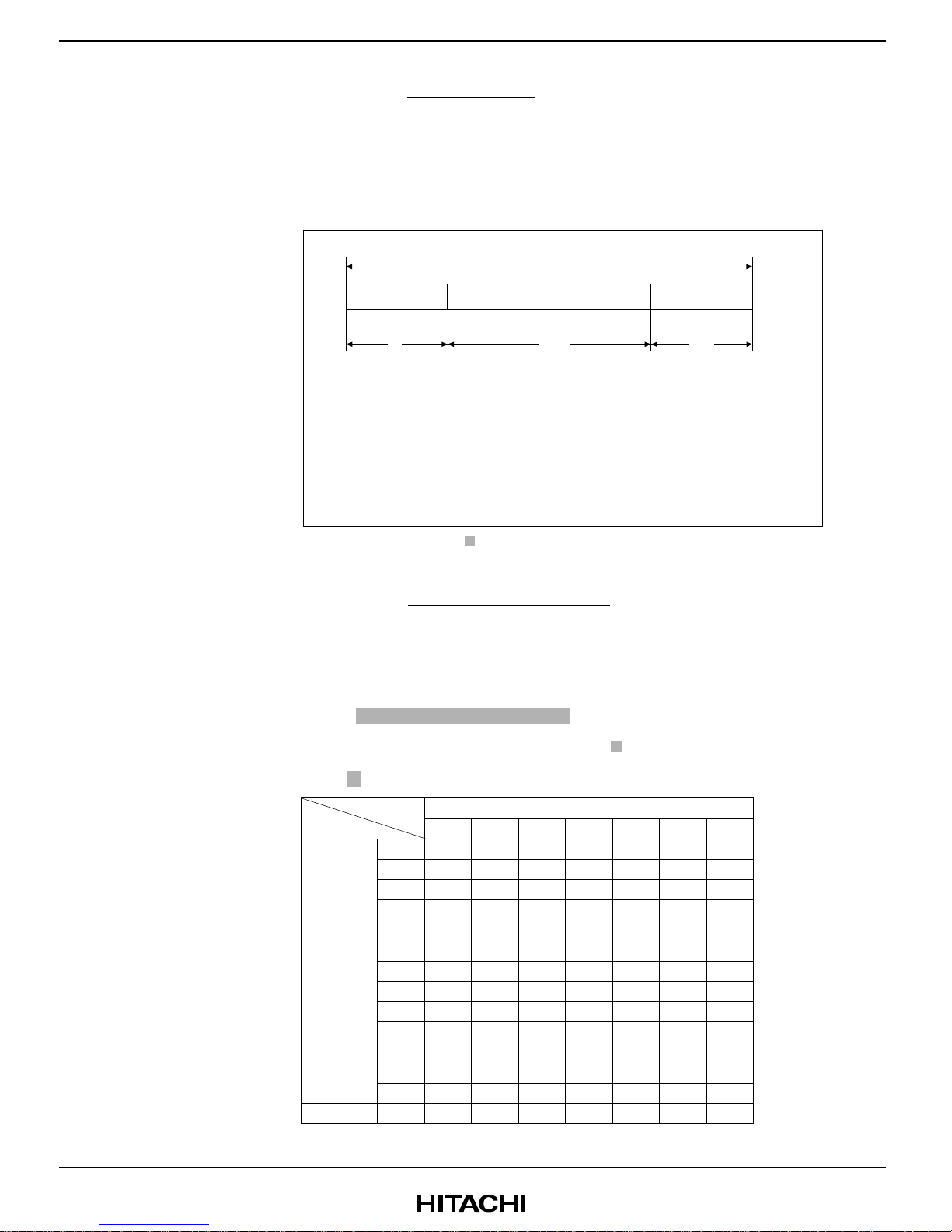
The addresses, bits, and initial alues of the registers are summarized in Appendix B, Internal
I/O Registers.
Example: Bit order: The MSB is on the left and the LSB is on the right.
Related Manuals: The latest ersions of all related manuals are a ailable from our web site.
Please ensure you ha e the latest ersions of all documents you require.
http://www.hitachisemiconductor.com/