Part 1: Building the PCB
Soldering notes
Take the PCB out of your kit and you’ll notice that one side of the PCB has white silkscreen
printed on it with the other side being completely blank. All components, apart from the male
to female sockets, will be soldered to the silkscreen side of the PCB.
Soldering tips:
When soldering components to a circuit board it is always best to start with the smallest
components first. This helps keep the board flat and stops access to pads from being
restricted by larger components. We have deliberately ordered the steps within the guide so
that components are soldered in order of height.
The first step is to start by soldering the resistors. In your kit these will be marked
appropriately. The orientation of most of the components doesn’t matter but we will point out
any components where the orientation does matter. In these cases it is important to make
sure you have them inserted correctly.
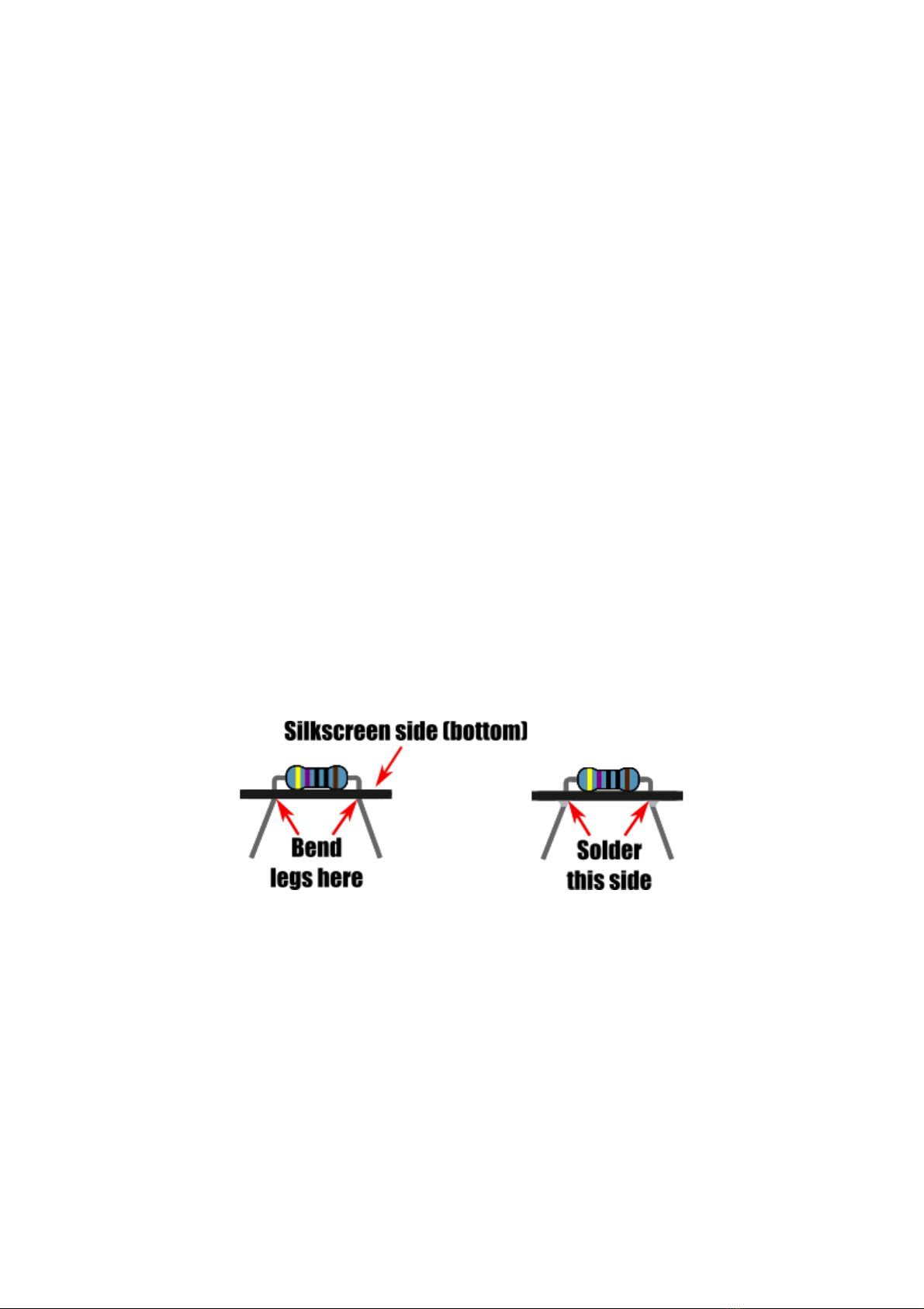
Unless otherwise stated, solder components to the PCB by inserting their legs through the
appropriate pad holes on the silkscreen side of the PCB, then flip the PCB and solder the
component legs to the PCB pads on the opposite side (non-silkscreen side).
For components with flexible legs like resistors and capacitors you can keep them held in
place by splaying the legs outwards slightly. Once soldered any excess leg can be trimmed
using a pair of snips or side cutters.