2.4GHz Self-powered Wireless Doorbell
WAS-2271EN V1.00 4 / 12 December 12, 2022
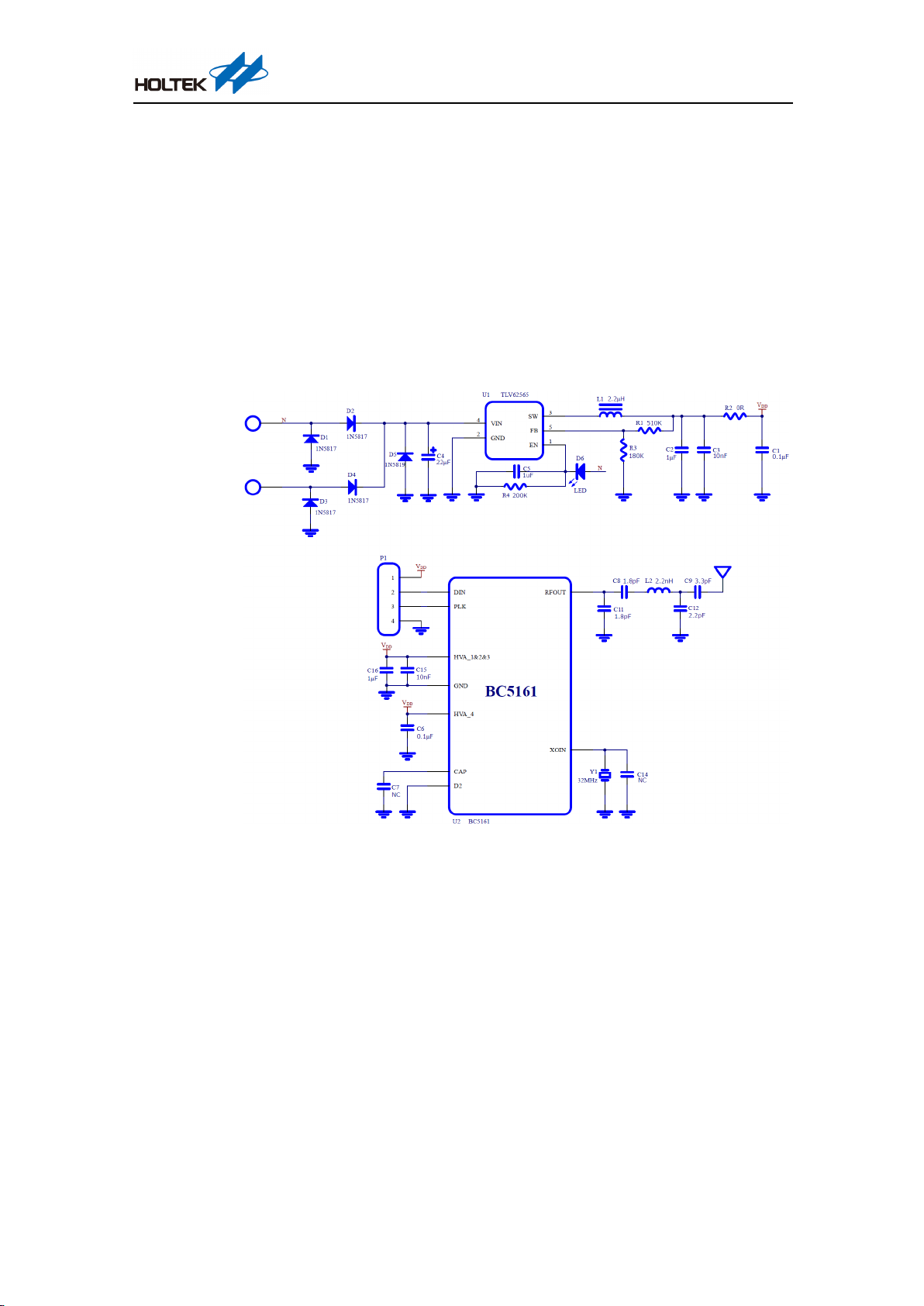
Receiver Module
BM5602-60-1
Master MCU
HT66FV140
Mains
Interface
Fuse
Indicator
Indicator
Audio Output
Interface
Volume+
Swit ch
Stop
Volume-
Figure 4. Transponder Main Components
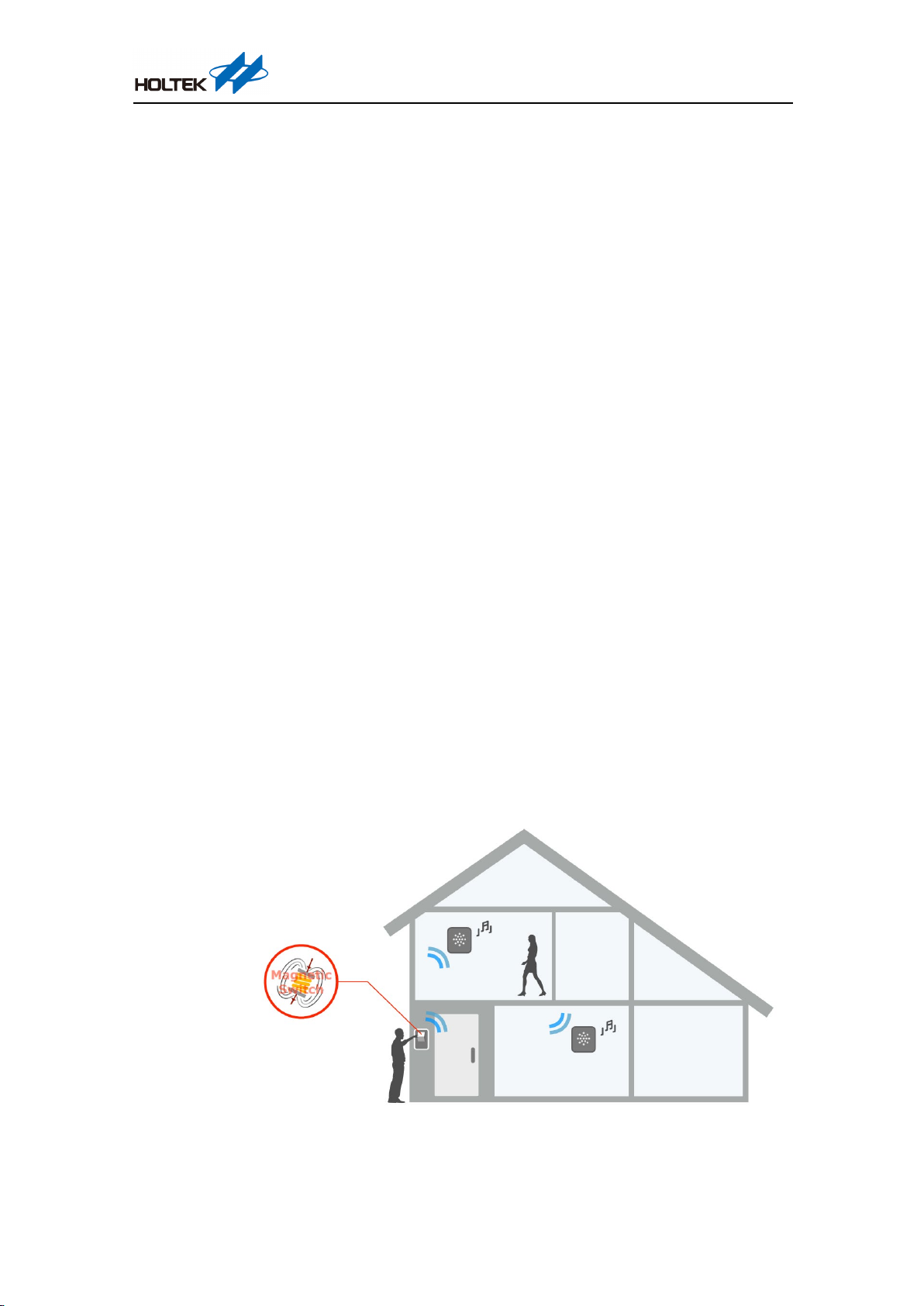
Before use, ensure that the doorbells and transponder have been paired with each other. Each
transponder can pair with a maximum of four doorbells. Therefore, if the fifth doorbell has been
successfully paired to the transponder, the first paired doorbell will be then unavailable. The
transponder only responds to doorbells that have already been paired. Each transmitter has a unique
24-bit ID. Pairings are required to enable the receiver to save the transmitter IDs for identification.
After the transponder has been powered on by the mains supply, if the doorbell is pressed and then
released, it will generate an RF signal. After the transponder receives the RF signal, it will generate
an audio output using the audio amplifier and can also implement other related operations using the
corresponding control keys.
1. Learning the address code
After power-on, press the Volume+ and Vo l u m e - keys simultaneously and then release them,
the LED indicator remains on, which indicates that the receiver has entered the learning address
code mode. Then press the doorbell and the receiver should ring along with a flashing LED to
indicate that the address code has been successfully learned. If no data has been received within
10 seconds, the receiver will exit the learning address code mode. Repeat the above operation
to learn another address code. A single receiver can pair up to four transmitters. When a fifth
address code has been learned, the first paired address code will be discarded and so on.
2. Clear the address code
After power-on, if the learned addresses are required to be cleared, press the Switch and Stop
keys on the receiver simultaneously and then release them. When the LED indicator flashes
three times quickly, this indicates that all the stored address codes have been cleared and that
the address code of the doorbell to be connected should be learned again.
3. Switch the ringtone
On the transponder, press the Switch key and release it to select the next ringtone, or to the first
ringtone if it is the last one.
4. Stop playing the ringtone
Press the Stop key and release it, the transponder will stop playing the ringtone.
5. Volume adjustment
On the transponder, press the Vo l u m e + key and release it to increase the volume by one level.
Press the Volume- key and release it to decrease the volume by one level. In this way it will
switch among five different volume levels.