1
Precautions
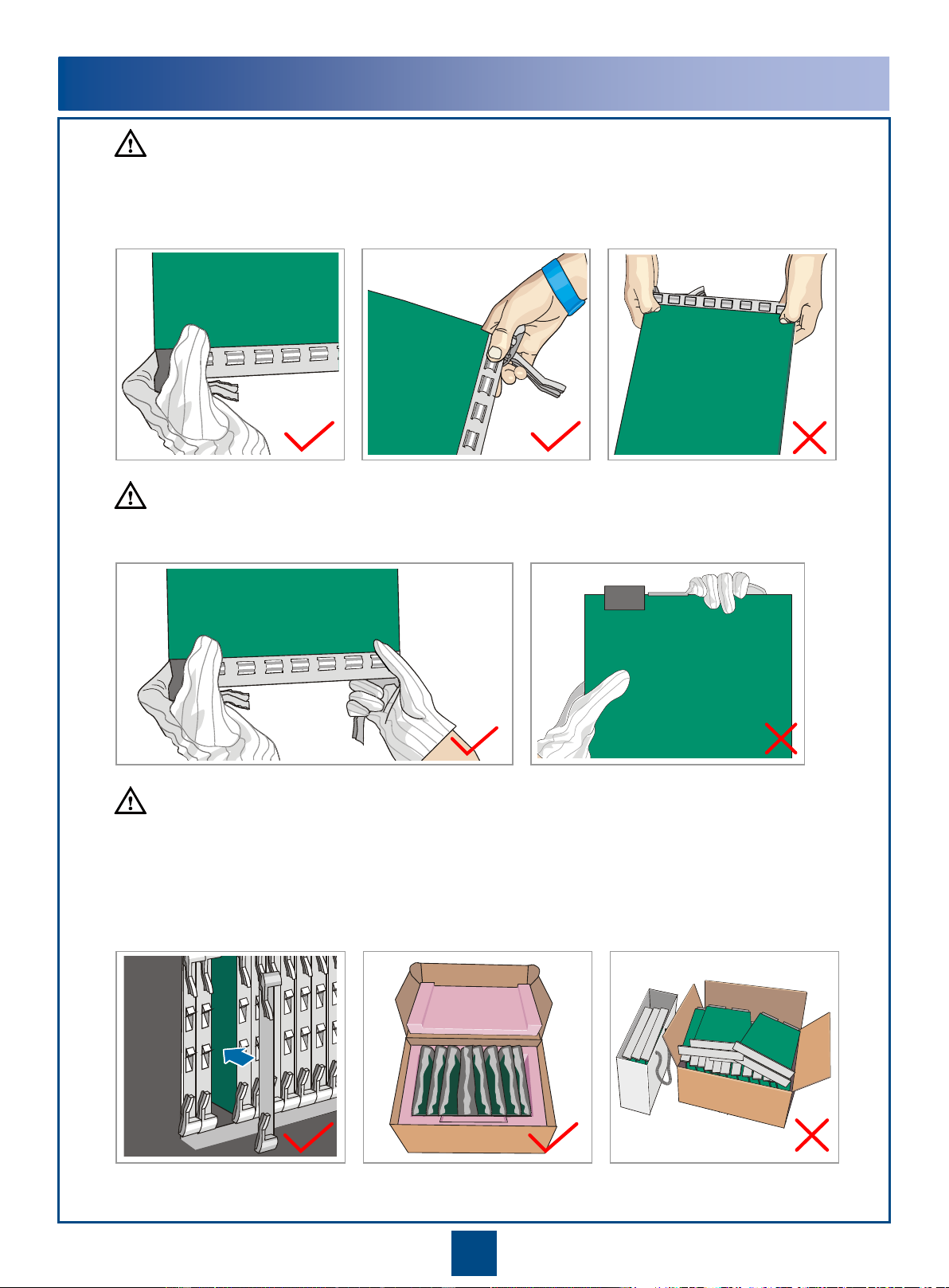
Electrostatic Discharge
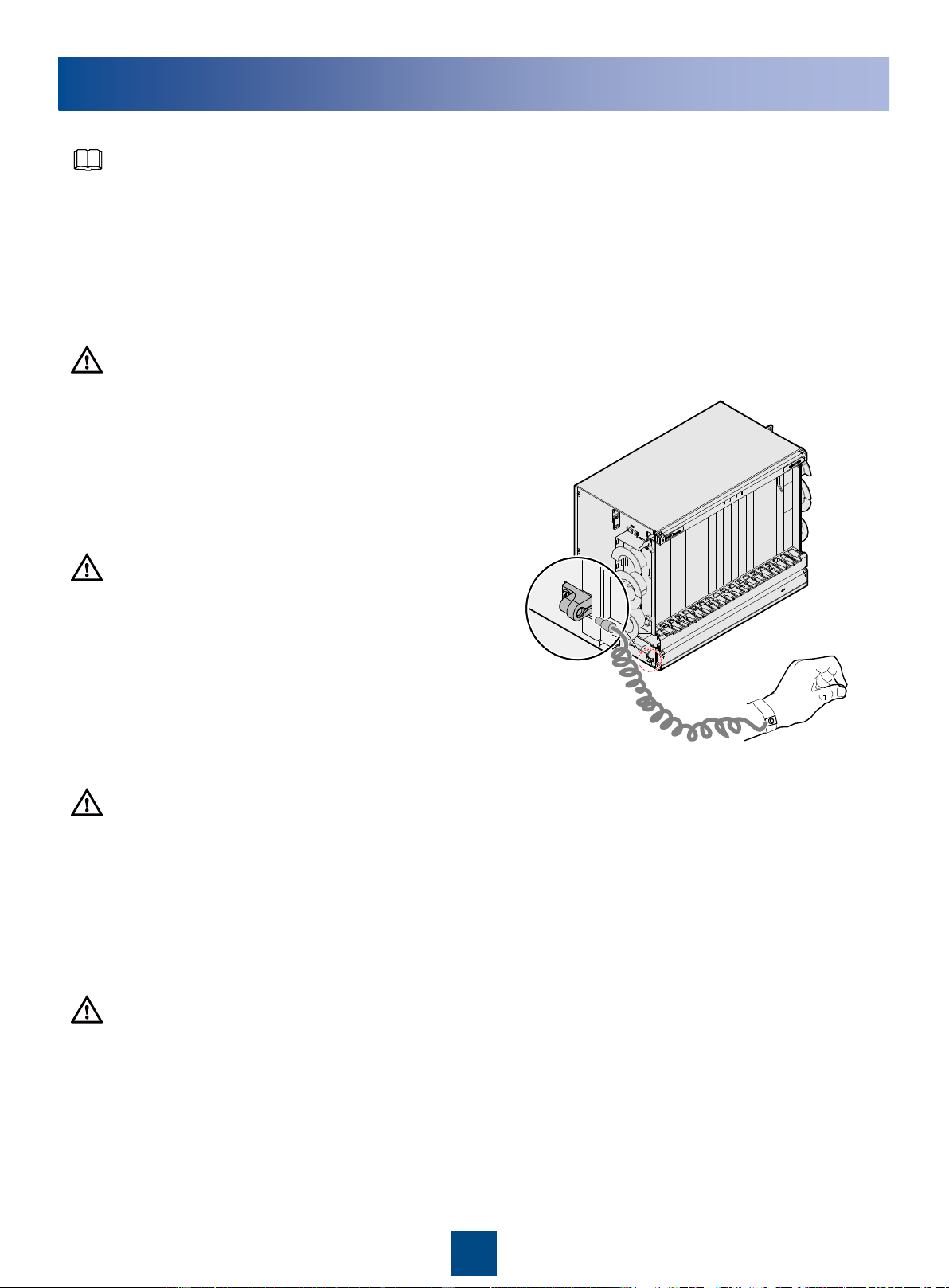
Before touching the device, or holding the boards and IC
chips, wear the anti-static gloves or the anti-static wrist
strap to prevent the electrostatic discharge of the human
body from damaging the sensitive components. Ensure
that the other end of the anti-static wrist strap is well
grounded.
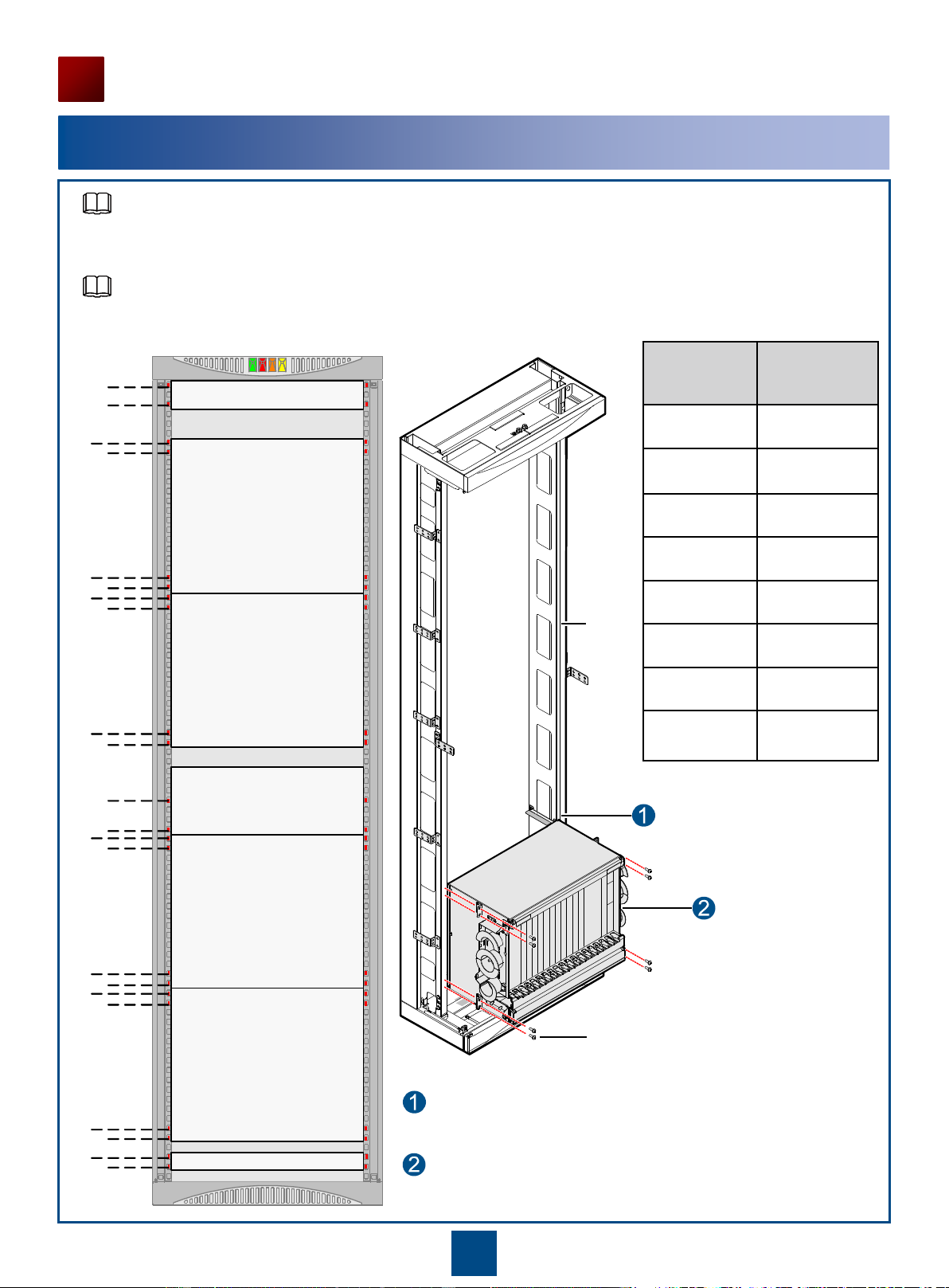
Checking Before Installation
Before starting installation, you should make the equipment room, power supply, ground cable, optical cables, and
other facilities in the equipment ready. When these installation conditions are confirmed, the installation may begin
according to the pre-designed layouts. For detailed requirements and related index, refer to Installation Reference.
Safety Information
When moving the cabinet, wear protective gloves to protect your
hands.
When moving the cabinet, take self-protection measures if the cabinet
inclines.
This document aims to provide simple and distinctive guidelines for hardware installation.
This document does not describe operations for the pre-delivery installation. Instead, this document describers only the
operations for on-site installation.
Bundling cables
The distance between cable ties or fiber holders inside the cabinet should be within 250 mm. (For subscriber cable, the
distance is 200 mm.)
The distance between cable ties for all cables and corrugated pipes outside the cabinet is determined according to the
distance between two horizontal beams. For the cable trough without beams, bundle the cables with the distance not
exceeding 250 mm between cable ties.
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
NOTE