Installation Manual 5.1.2
6
1.0 Transportation & Storage
Move and store units in an
upright position. Do not stack
units. Inspect shipment for
shipping damage and check
packing slip for accuracy. Any
equipment or cartons in question should be removed
from the packing and physically inspected. If any
damage is detected, the carrier should make a note on
the delivery slip acknowledging the damage. In some
cases smaller items like thermostat or temperature
sensors will be packed and shipped inside the system.
During freezing conditions special consideration should
be made to prevent unit damage. If a unit is taken to
the job site or put in storage, anti-freeze will need to
be pumped into the water coils to prevent freezing.
Failure to do this will void warranty.
2.0 Electrical Hazard Warnings
THE FOLLOWING IS A GENERAL WARNING
STATEMENT WHICH SHOULD BE READ AND
UNDERSTOOD BEFORE INSTALLING AND OR
OPERATING YOUR NEW HYDRO-TEMP UNIT
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL!!
•Always protect yourself and others. Always turn off
system power before removing panels. Some units
may have more than one or two power supplies.
•Keep all covers and panels in place at all times. When
removed for install or service purposes never leave
the cover off when left un-attended.
•Do not stick hands into return or any other opening.
•All repairs, electrical or mechanical, should be
attempted only by trained Hydro-Temp technicians.
In the event of a unit problem, do not reset the
equipment before correcting the problem.
Equipment failure due to resetting without first
correcting the problem will not be covered by the
warranty.
•The presence of water around the base of the unit
constitutes an electrical hazard. Turn off the power
to the unit as soon as water leakage is discovered and
call a service technician immediately.
•STRIP HEAT WARNING: On systems with
auxiliary/emergency heat strips, be aware that the
heat strip contactor may be wired on a separate
circuit. Therefore an additional breaker must be shut
off before removing panels and servicing unit.
•All breakers/fuses supplying power to this equipment
should be clearly labeled at time of installation.
•All wiring and plumbing should be done in strict
accordance with local and national codes and
ordinances.
2.1 Electrical Connections
Power to the Hydro-Temp System and back-up
electric heater may be two or sometimes three
circuits (Some large dual compressor systems will
require a circuit per compressor). A standard system
requiring one circuit for compressor and one circuit
for strip heat can be wired with 2 breakers in the
main breaker panel or one circuit feeding a sub
breaker panel near the system. All circuits must have
its own power disconnect near the system. The
electrical installation must be performed by a licensed
electrician, except for the low voltage wiring (Class 2)
(i.e. T-Stat) which can be done by the heat pump
contractor. Note: In most areas high voltage can be
taken from disconnect to the unit by the mechanical
contractor if allowed by local codes. All wiring and
plumbing should be done in strict accordance with
local and national codes and ordinances.
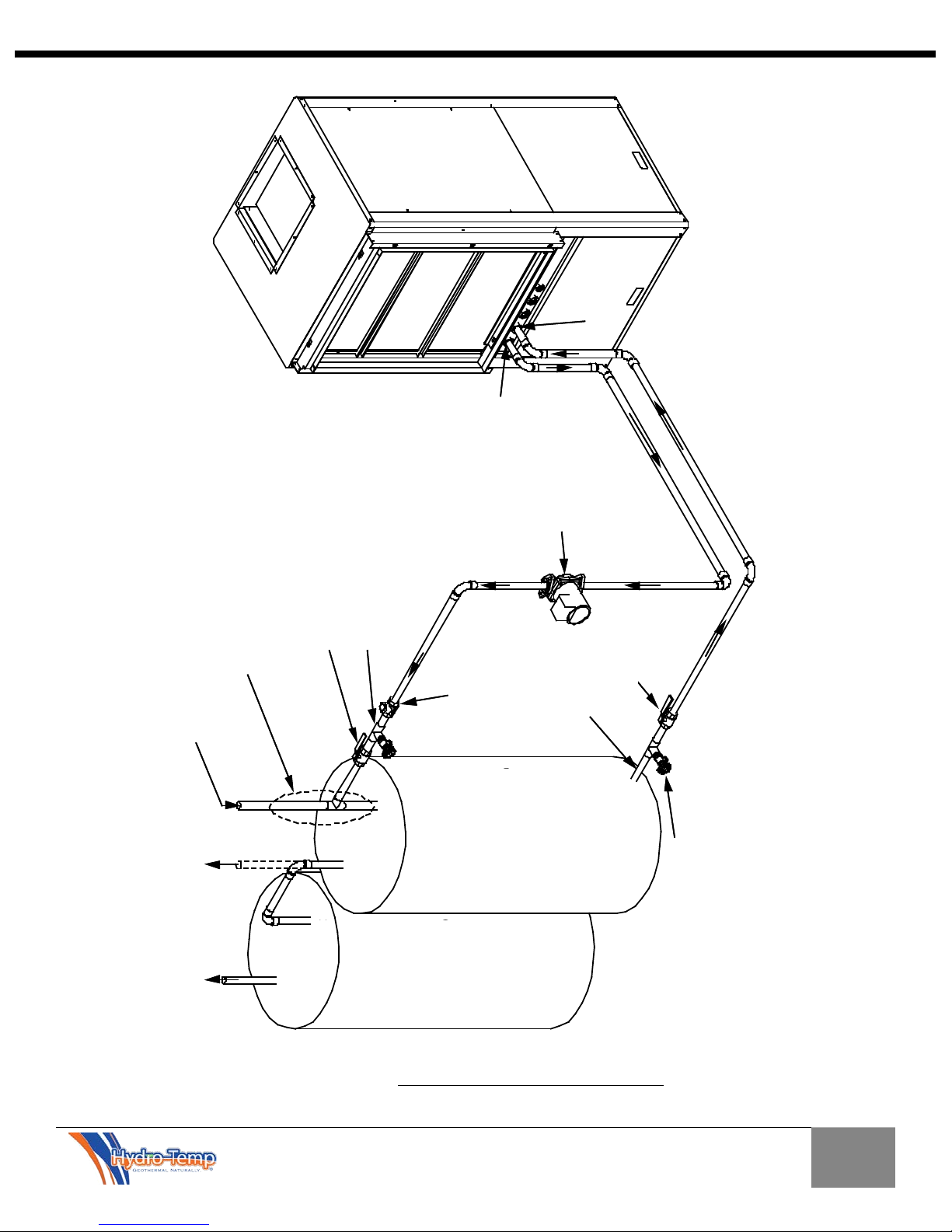
3.0 Hydro-Temp System Installation
Locate the unit in a conditioned, indoor area that allows
for easy servicing. Make sure that the air filter access
and unit access panels are easily accessible. Provide
sufficient room to make all ground loop, well water,
DHW, condensate, electrical, and if applicable
refrigeration connections.
If the unit is placed in a closet, make provision for
adequate return air flow to the unit.
Some installations may require a condensate pump to
take the condensate to a suitable drain location. Do not
locate the unit in an area that is subject to
freezing. The minimum recommended room
temperature for equipment location is 60°F. Provide a
heated, insulated enclosure for the unit where
necessary.