IMOVILLI D Series Instruction manual

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 1/11
WORKSHOP MANUAL
DIAPHRAGM PUMPS
1.0
A-M VALVE ZONE CONTROL on pumps with internal manifolds
(M25 – M29 – M30 – M35 – M 50 – M60 – M73 – M104S – M135S)
1.1 Remove the valve covers and remove the A-M valves
from the cylinder head
NOTE: The suffix A-M means "Suction / Delivery"; in
fact, the pump valves can be used indifferently in
suction and delivery
1.2 Break down the valves into the individual elements and
proceed with their inspection; if a component is
particularly worn or damaged they will need to be
replaced.
1.3 Check the inside of the valve covers: if they show signs
of wear in the contact areas with the valve caps or
damage in the plasticization, they must be replaced.

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 2/11
2.0
Tested control in the A-M valve zone
2.1 Check that the support surfaces of the A-M valves on
the head do not show any sag due to the "floating" of
the valves themselves.
2.2 Check that the diameters where the O-rings work
do not present abrasions or grooves due to the
passage of the liquid caused by leaks of the O-
Rings or the valve seat gaskets.
2.3 In case the problems indicated in points 1.3 - 2.1 - 2.2 are found, the head and / or the
covers must be replaced.
3.0
Reassembly
3.1 Replace all O-Rings gaskets which must first be
thoroughly lubricated with grease with the
exception of the pumps with surface treatment of
cataphoresis or lamination.

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 3/11
3.2 Reposition the A-M valves in the head following
the original scheme. We remind you that for the
M25-29-35-60 pumps, the Intake valves must be
placed (with the real cap towards the diaphragm)
in the deepest seat; the opposite for those of
Delivery. The covers must be positioned
accordingly. Make sure that the tooth on the lid is
to be placed in its housing compartment in the
head. For M30-50 the intake valves must be
inserted with the cap towards the diaphragm in the
head housing on the shaft side, those on the
reverse side. For M73, follow the indication on
manifold cover A (intake) M (delivery). For
M104S-135S, follow the indication on the IN
pump casing (OUT).
3.3 Tighten the screws of the covers in a crisscrossed
and homogeneous way, respecting the tightening
torques (see tightening torques tab)

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 4/11
4.0
A-M VALVE ZONE CONTROL on pumps with external manifolds
(MINI – M155 – D series – IP series)
4.1 Remove the intake and delivery manifolds and
extract the valves
4.2 Proceed as in points 1.2 and 1.3
5.0 Reassembly
5.1 Replace all O-Rings gaskets which must have
been abundantly lubricated with grease, with the
exception of pumps with a cataphoresis surface
treatment or plastification.
5.2 Reposition the A-M valves in the heads following
the original scheme. Remember that: for MINI is
the same as for M30 and M50, while for D82 -
D113 - D123 follow the indications given on the
fittings (IN - OUT). All other models have a
mandatory mounting position.

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 5/11
6.0 Diaphragm control and replacement
6.1 For the diaphragm replacement operation,
position the pump as shown, unscrew the diaphragm
locking pin and remove the diaphragms.
After having thoroughly cleaned them, proceed to
check:
a) If they are swollen even without cuts or
tears, they must be replaced because they are
affected by the pumped products;
b) If in the upper part (the one in contact with
the product) there is a clear cut (a "U") in
correspondence with the intake valve or an
incision that coincides with the diameter of
the return washer, it is a symptom that the
pump has operated in conditions of
excessive depression (dirty or insufficient
filter, suction from more than 3 m depth,
obstructions in the suction line) that must be
checked;
c) If in the part in contact with the oil there are
cuts or circular erosions corresponding
approximately to the diameter of the piston,
it is a symptom of contact with the piston
itself and the causes can be:
- Stop and start the pump without having canceled
the pressure
- Oil leaks from segments (because they are faulty
and / or worn)
- Cylindrical scratches in the area from the supply
holes (PMI) to the edge of the cylinder, due to
debris and impurities caused by the operation of the
pump without oil
- Pump operation (at maximum pressure) with
rotation less than the minimum indicated on the
nameplate and instruction booklet.
d) IN CASE OF swelling of the membranes
even without breakages, it is advised, after
removing the cylinders, to empty the oil and
to wash with diesel or kerosene inside the
pump.
e) e) IN CASE OF breaking even one
membrane, it is necessary to completely
disassemble all the crank mechanism for an
accurate control of its components.
b
)
c)

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 6/11
ATTENTION: The exhausted oil is toxic and polluting.
In particular, oil, especially if used, can cause skin cancer if repeatedly left in contact with the
skin for prolonged periods. Although this is unlikely unless you are using daily oil, it is
recommended to wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water as soon as possible after
handling used oil.
Also being polluting it is mandatory to dispose of it at the collection centers taking care not to
disperse it in the environment.
7.0
Cylinder control
7.1 Verify that the cylinders do not show particularly
deep scratches. In this case they must be replaced.

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 7/11
Disassembly and control of shaft and bearings
8.1 After removing the cylinders, remove the bearing
support and then the shaft. (The tool for removing
the shaft shown in the figure is available on
request)
ATTENTION: for M25 - M30 - M50 pumps the
shaft can only exit in the middle position of its
stroke. Position the keyway, present on the shaft
cone, in a vertical position (or upwards or
downwards), otherwise the piston will be damaged
and the shaft can’t be extracted.

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 8/11
8.2 For pumps with a through shaft
- Protect the oil seal with bush (available on request, see
photo point 8.1)
- - Tap with a plastic hammer on the shaft of the
opposite side until the shaft is removed, remembering
the assembly direction.
- - Disconnect the connecting rings of the connecting
rods making sure that there are any spacers or
shoulder rings (remember the position) and extract
connecting rods + pistons.
- Disassemble the bearings and proceed with a more
blowing and blowing of the components, proceeding
to check them.
- The pistons, the segments, the connecting rods, if
grooved in the part in contact with the shaft, the
bearings, the connecting rod connecting rings, if worn
or scored, must be replaced.
8.3 Pump shaft control
Check the condition of the surface where the
connecting rods work, which must not have any
grooves or metal (of connecting rods) incorporated.
Before replacing it, try to clean it with a very fine
abrasive paper (800). If the result is not positive,
replace it. Also check that there are no deep
grooves in the area where the oil seals works due to
the dust deposited outside the oil seals during
operation.
In this case the shaft must be replaced.

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 9/11
8.4 Reassembly
Perform the operations exactly in the reverse order, replacing all the O-Rings and
gaskets. When reassembling the cylinders, position the feed holes in the direction of the
transverse axis of the pump.
To replace the oil seals, use the protection sleeves that are available on request.
Add SAE 40 oil from the tank.
For screw tightening torques, see table torques tab.
8.5 Air bleeding
When the oil is full and the tank is open, tilt the pump according to its transverse axis,
slowly rotating the shaft. You will notice air bubbles coming out of the pump casing.
Keep topped up and continue the maneuver until no more air comes out. At this point
the pump is ready. Run it for a few minutes without pressure and top up with oil if
necessary.
(See Annex A)
Screw in the oil cap (with diaphragm where provided).

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 10/11
ANNEX "A"
CHECKING AND REPLACING THE OIL
In diaphragm pumps, the oil contained in the crankcase performs two functions:
1. Lubrication of mechanical parts.
2. Diaohragm support during the pressure pumping phase.
Therefore the verification of the level and quality of it is to be considered of vital importance for the
functionality and duration of the pump and must be done at each start-up.
Level verification.
The oil level is visible from the cap and the control must be done with the pump stopped; if the oil
is lower than the minimum level imprinted on the tank or even not visible inside it, it will need to be
topped up using quality oil and the same gradation as the original (SAE 40) but not exceeding the
recommended maximum level.
Oil change
The replacement of the lubricant is advisable in the following cases:
a) Rupture of the diaphragms: the white-yellow coloring of the oil contained in the tank or the non-
visibility of the level inside the tank even after a small refilling indicates that the diaphragm (s) has
failed.
It will therefore be necessary to examine the pump and promptly repair it; in these cases the pump
must not be used and it is advisable to empty the pump completely from the liquid contained therein
by removing a head and the related cylinder; then insert diesel into the crankcase with the intention
of preserving the mechanical parts from oxidation. Then contact an authorized center.
b) Scheduled periodic maintenance: the periodic maintenance tables according to the type of use
DO NOT provide for the replacement of the lubricant as an end in itself; the replacement of the
lubricant is done in concomitance with the programmed replacement of the diaphragms.
Starting the pump after replacing diaphragms and / or lubricating oil
After an intervention to replace the diaphragms and / or lubricating oil or simply after inspecting the
crank mechanism of the pump, pay particular attention to the first start of the pump and you must
observe some rules listed below in order to allow the complete "purging" air contained within it and
in fact guarantee the pump to achieve maximum efficiency and functionality.
a) When the oil is full and the oil tank is open, tilt the pump according to its transverse axis and
slowly rotate the shaft by hand or using a crank. With this operation you will notice a substantial
leak of air bubbles from the pump casing and the oil level will drop.

Imovilli Pompe S.r.l.
Reggio Emilia – Italy
www.imovillipompe.it
Manuale d’officina – Pompe a membrana 11/11
Keeping the maneuver with the top up until more air is seen.
At this point the pump is ready to start
b) The first start-up must always take place with the pressure canceled, the suction line connected to
a tank of adequate capacity and containing water and possibly with a rotation speed lower than the
maximum.
c) After about 15 - 20 seconds of operation at this speed and with the pressure canceled, switch off
the pump; then restart and keep running for at least as many seconds and repeat this operation a
couple of times. With this maneuver, air escapes from the pump casing, with consequent
conspicuous lowering of the level of the lubricant inside the tank; reset therefore at each power off
to the original level
d) Start the pump again and increase the rotation speed equal to the maximum; progressively
increase the delivery pressure up to a value between 40 - 50% of the maximum and then switch off
the pump without removing the pressure. Once the stop has been completed, remove the pressure
and then start again and repeat this operation a couple of times. Even during these operations you
will notice a lowering of the oil level in the tank which must always be restored to the original level.
e) Start the pump again and increase the delivery pressure up to the maximum expected and, acting
on the pressure canceling device placed on the control, cancel and reset the repeating pressure while
remaining in the two conditions (pressure canceled & maximum pressure) at least 5 - 10 s. This
maneuver must be repeated at least 5 to 6 times and then switch off the pump (having canceled the
pressure before this last operation). Also in this case you will notice a certain lowering of the oil
level in the tank and that it will have to be restored.
f) Repeat the procedure d) at least another 2/3 times; at the end of these repeated cycles of shutdown
and start-up, a gradual regularization of the pumping can be noticed, which can be noticed by the
lower oscillations of the pressure gauge indicator and by the more contained vibrations of the pump
and the pipes and by a more regular and homogeneous noise.
NOTE: If the quality of the pump in terms of regularity of pressure or vibration of the pump and of
the pipes is unsatisfactory, repeat steps c) d) & e) several times.
The escape of air bubbles from the pump casing during pressure operation are synonymous with an
incomplete "purge" operation carried out; during the operation of the pump in the expected working
conditions this phenomenon tends to progressively decrease until the total disappearance; in this
case the complete and effective purge operation is considered.
NOTE: If the pump remains stationary for a long time, due to the residues of the water or the
products used, the valves may stick and the pump may not be able to effectively unlock the
passages during the loading phase. In this case it is sufficient, with the pump stopped, to blow with
a compressor inside the intake manifold without the need to disassemble any component of the
pump.
This manual suits for next models
12
Table of contents
Popular Water Pump manuals by other brands

venotec
venotec Abyzz A400 IPU operating manual

Drummond
Drummond 63324 Owner's manual & safety instructions

Pentair
Pentair Aurora 382B CC Series Installation and operation manual

Homa
Homa Saniquick 1A Original instruction manual

Wilo
Wilo Padus PRO Installation and operating instructions

Mobiak
Mobiak 0806293 user manual

Pentair
Pentair ME7 Series Installation, Operation & Parts Manual

DROPSA
DROPSA Sumo User and maintenance manual

Huntleigh
Huntleigh AlphaXcell Electric Service manual

Sensia
Sensia CLIF MOCK LGS-1 Installation, operation & maintenance manual
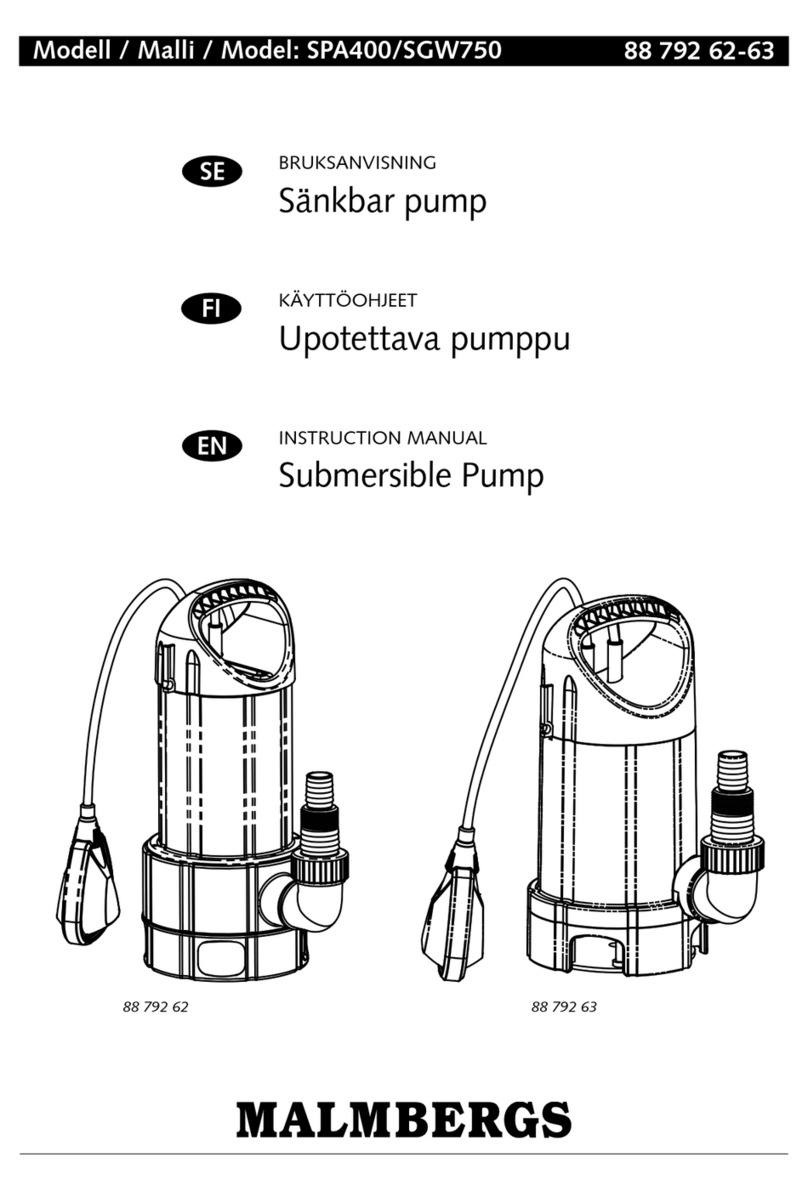
Malmbergs
Malmbergs SPA400 instruction manual

EINHELL
EINHELL GC-GP 1046N Original operating instructions





