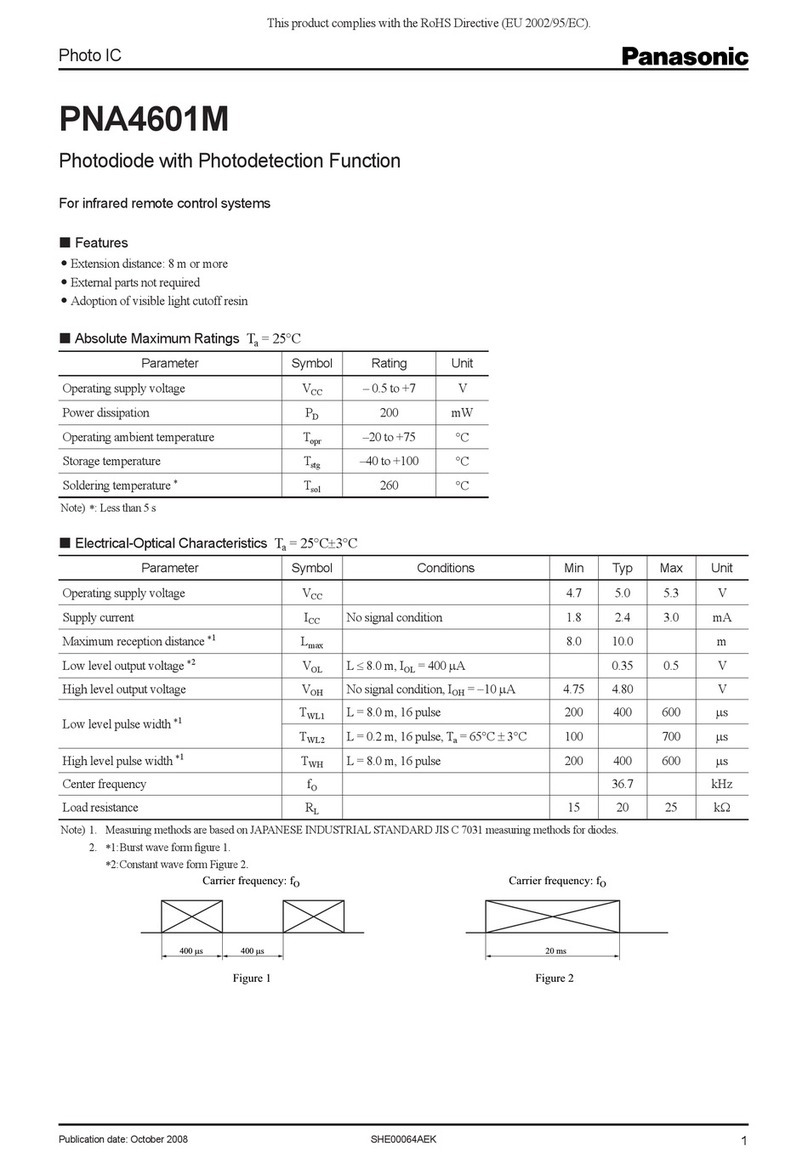
Infoblox NT-1400 User manual

Infoblox Installation Guide for Network Automation
1400 Appliance

1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.1 Product Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2 Hardware Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.3 System, Environmental, and Power Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2. Installing the NT-1400 Appliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 Rack Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 Powering the Appliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.3 Cabling the Appliance to a Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3. Initial Network Automation Appliance Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.1 Configuring the Management System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.2 Configuring a Network Automation Appliance for IPv4 and IPv6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.3 Infoblox Network Automation CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4. Replacing Appliance Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.1 Changing AC Power Supplies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.2 Network Automation NT-1400 FRUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
Introduction
This guide provides an overview of the Network Automation NT-1400 network appliance that ships with the Infoblox Network Automation software
platform. This document explains how to install and configure the system.
Product Overview
The Network Automation NT-1400 is a network appliance designed for smaller enterprise deployments and for use as a Collector for Operations
Center deployments. The NT-1400 supports the Network Automation application suites, including the Automation Change Manager (ACM) for
automating responses to network changes; Switch Port Manager (SPM) for managing and controlling switched Ethernet networks; Security
Device Controller for managing and controlling firewalls and packet-filtering routers; and the full NetMRI package.
You configure and manage the Network Automation NT-1400 through an easy-to-use Infoblox GUI that works efficiently in Windows, Linux, and
Mac environments using standard web browsers. For more information about the Infoblox Network Automation GUI, refer to the Infoblox Network
Automation Administrator Guide for your system.
Key features of the Network Automation NT-1400 appliance include the following:
Optional AC power supply for a redundant hot-swappable 1+1 configuration
Multiple active Ethernet interfaces for network management (LAN1, LAN2 and MGMT)
The Network Automation NT-1400 appliance is a Class A digital appliance per FCC regulations, and is RoHS and WEEE compliant.
Hardware Components
The Network Automation NT-1400 is a 1-U platform that is mounted in a standard two-post or four-post equipment rack using the mounting
brackets and bolts that ship with the appliances. For information about rack mounting, see .Rack Mounting
Front Panel
The Network Automation NT-1400 front panel components include the LCD (liquid crystal display) panel and navigation buttons, communication
ports, and LEDs, as shown in . For explanations of the Ethernet port LEDs, and console and Ethernet port connector pin assignments,Figure 1
see and .Ethernet Port LEDs Connector Pin Assignments
Network Automation NT-1400Figure 1 , Front View
The front panel components are described in .Table 1
Table 1 Front Panel Components
Component Description
LCD Panel An LCD screen that displays the installed software version and the IP address of the appliance. The LCD panel does not
support data entry, and shows only basic information about the appliance.

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
On/Off
Switch A power switch to turn the power supply of the appliance on and off. The switch is hidden. Use a small blunt object, such as a
paper clip, to gently push the switch.
USB Port Reserved for future use.
Console Port A male DB-9 serial port for a console connection to change basic configuration settings and view system functions through the
CLI (command line interface).
:Caution Should you need to use a USB-to-Serial adapter to carry a serial connection over a USB port in a computer that lacks
a 9-pin serial interface, use a properly grounded USB-to-Serial dongle to connect to the serial console port. If the dongle
connects to a laptop, the laptop must be grounded properly as well. Failure to do so may result in damage to the serial console
port of the Infoblox appliance. Infoblox is not responsible for such damage.
MGMT Port A 10/100/1000-Mbps gigabit Ethernet port used for appliance management. You must use the MGMT port for initial appliance
setup and for primary system operation. The MGMT port may also be used for scan interface connections to managed
networks.
Infoblox recommends retaining the MGMT port exclusively for appliance management traffic.
LAN1 Port A 10/100/1000-Mbps gigabit Ethernet port that is used for scan interface connections to managed networks. You can enable
the LAN1 port and define its use through the GUI after the initial setup. For related information, see Configuring Scan Interfaces
of the .Network Automation Administrator's Guide, Release 6.9
LAN2 Port A 10/100/1000-Mbps gigabit Ethernet port that is used for scan interface connections to managed networks. You can enable
the LAN2 port and define its use through the GUI after the initial setup. For related information, see Configuring Scan Interfaces
of the .Network Automation Administrator's Guide, Release 6.9
UID Button The unit identification button. When you press the UID button, the LCD panel on the front panel blinks and the UID LED on the
rear panel glows blue. In a rack environment, the UID feature enables easier location of the device when moving between the
front and rear of the rack.
Status LED Reserved for future use.
Power LED An LED that glows blue when there is power to the appliance. When it is dark, the appliance is not receiving power, even if the
power cable is plugged in. Ensure that you power on the appliance through the On/Off switch using a small blunt object, such
as a paper clip.
Alarm LED Reserved for future use.
Ethernet Port LEDs
To see the link activity and connection speed of an Ethernet port, you can look at its Activity and Link LEDs. shows the status the LEDsFigure 2
convey through their color and illumination (steady glow or blinking).
Figure 2 LEDs
Connector Pin Assignments
An Infoblox appliance has three types of ports on its front panel:
USB port (reserved for future use)

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
Male DB-9 console port
RJ-45 10Base-T/100Base-T/1000Base-T auto-sensing gigabit Ethernet ports (2 active)
The DB-9 and RJ-45 Ethernet connector pin assignments are illustrated in . DB-9 pin assignments follow the EIA232 standard. RJ-45Figure 3
Ethernet pin assignments follow IEEE 802.3 specifications. All Infoblox Ethernet ports are auto-sensing and automatically adjust to standard
straight-through and cross-over Ethernet cables.
Note: Contact your Infoblox sales representative to obtain Infoblox-specific serial console cables.
10Base-T Ethernet and 100Base-T fast Ethernet use the same two pairs of wires. The twisted pair of wires connecting to pins 1 and 2 transmit
data, and the twisted pair connecting to pins 3 and 6 receive data. For 1000Base-T connections, all four twisted-pair wires are used for
bidirectional traffic.
Figure 3 Connector Pin Assignments

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
Rear Panel
The rear panel components include the power connectors, hard disk drive, fans, air vent, and the UID LED, as shown in .Figure 4
Network Automation NT-1400Figure 4 , Rear View

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
Table 2 Rear Panel Components
Component Description
Hard Disk
Drive One (1) Infoblox data storage device.
Drive
Indicators LEDs that flash green to indicate the hard drive is processing data.
Fans A fan system (5 fans total) to help maintain optimum operating temperature. Do not obstruct.
UID LED Blue = UID is activated through pressing the UID button on the appliance Blinking Blue = UID is activated through the Infoblox
GUI or CLI command Dark = UID is deactivated
Note: When UID is activated, the LCD on the front panel blinks at the same time.
Power
Supply Each power supply has a power outlet for connecting the appliance to a standard AC power source.
Power LED The power indicator is green if the power supply has power and is dark if it does not have power.
Air Vent An air vent that allows warm air to flow out of the appliance. Do not obstruct.
System, Environmental, and Power Specifications
System specifications describe the physical characteristics of the appliance. Environmental specifications describe the temperature and moisture
limits it can withstand. Power specifications describe the electrical range within which the appliance circuitry can operate.
System Specifications
Form Factor: 1-U rack-mountable appliance
Dimensions: 1.73" H x 17.36" W x 17.2" D (4.4 cm H x 44.1 cm W x 43.7 cm D)
Weight: Approximately 24 to 28 pounds (10.9 to 12.7 kg)
Ethernet Ports: MGMT, HA, LAN1, LAN2 – auto-sensing 10Base-T/100Base-T/1000Base-T
Serial Port: DB-9 (9600/8n1, Xon/Xoff)
USB Port: USB2.0/1.1 compliant
LCD Panel: LCD (liquid crystal display) with input buttons
Environmental Specifications
Operating Temperature: 41 to 95 degrees F (5 to 35 degrees C)
Storage Temperature: -13 to 158 degrees F (-25 to 70 degrees C)
Operating Relative Humidity: 10% to 90% (non-condensing)
Airflow CFM (Cubic Feet/Minute): 31 CFM
Airflow Direction: Front-to-Back

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
1.
2.
Electrical Power Specifications
AC Power Supply: Dual input, 450 Watts
Input Voltage.: 100 – 240VAC
Input Frequency: 50 – 60 HZ
Input Current: 4A max at 230V
Inrush Current: 20A max at 230V
Power Factor: > 0.94/230V 50 Hz
Maximum Power Consumption: 186W
Heat Output (BTU/hour): 636 Maximum
Optional DC Power Supply: 450 Watts
Input Voltage.: -36 - 72DC
Input Current: 20A/ -36VDC, 10A/ -72VDC
Inrush Current: 100A 2u sec max
Maximum Power Consumption: 186W
Heat Output (BTU/hour): 636 Maximum
Installing the NT-1400 Appliance
Follow these instructions to rack mount the Network Automation NT-1400, connect it to a power source, and cable it to a network. Before
proceeding, review the and follow the necessary precautions.Infoblox Safety Guide
Note: Ensure that you install the appliance in an environment that allows open air to the front and back of the appliance. Do not obstruct the
appliance or block air flow going from the front to the back of the appliance.
Rack Mounting
The Network Automation NT-1400 appliances mount into a standard 19" (48 cm) equipment rack. The appliances ship with accessory kits that
contain the following: a pair of rack slide brackets and chassis slide rails, a pair of rack ears, eight (8) 10-32 screws, and eight (8) 8-32 screws.
Infoblox offers a second four-post rack-mounting kit that you can order separately. This chapter includes instructions for use of both types of
rack-mounting kits.
To mount the appliances to an equipment rack, you also need a #2 screwdriver with a cross-headed tip. There are two ways to rack mount the
Network Automation NT-1400:
Two-post rack mount (kit included with purchase)
Four-post rack mount (aftermarket kit available from Infoblox)
Infoblox offers a second four-post rack-mounting kit that you can separately order. This chapter includes instructions for use of both types of
rack-mounting kits.
Two-Post Rack Mount
To mount the appliance to an equipment rack and secure it at the rear rack posts:
Align the mounting holes on the rack ears with the rear-most mounting holes on each side of the chassis.
Attach each rack ear on each side of the chassis with two (2) 8-32 screws, as shown in .Figure 5
Figure 5 Rack Ears in Two-Post Rack Mount

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
1.
2.
3.
3. Lift the appliance and position it in the equipment rack.
4. Attach each rack ear to the equipment rack with two (2) 10-32 screws on each side.
Four-Post Rack Mount
To mount the appliance to an equipment rack and secure it at the front and rear rack posts:
Align the mounting holes on the rack ears with the front-most mounting holes on each side of the chassis.
Attach the rack ears to each side of the chassis with two (2) 8-32 screws, as shown in .Figure 6
Slide the inner chassis slide rails out of the rack slide brackets, as shown in .Figure 7
Figure 6 Rack Ears and Chassis Slide Rails in Four-Post Rack Mount
Figure 7 Chassis Slide Rail and Rack Slide Bracket
4. Align the mounting holes on the chassis slide rails with the rear-most mounting holes on each side of the chassis. Ensure that you place
the chassis slide rails in the correct orientation. Otherwise, the mounting holes do not align properly.
5. Attach the chassis slide rails to each side of the chassis with two (2) 8-32 screws, as shown in .Figure 6
6. Select a desired location and secure the rack slide brackets to the rear posts of the equipment rack with two (2) 10-32 screws on each
side of the rack, as shown in .Figure 8
Figure 8 Rack Slide Bracket Attached to the Rear Post of the Rack

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
1.
a.
b.
c.
7. Lift the appliance and position it in front of the equipment rack.
8. Align the chassis slide rails on the appliance with the rack slide brackets on the posts of the equipment rack.
9. Slide the appliance into the rack slide brackets.
10. Secure the rack ears to the rack with two (2) 10-32 screws on each side of the rack.
Powering the Appliance
The Network Automation NT-1400 ships with one (1) AC power supply module. You can order an additional AC power supply to set up a
hot-swappable redundant 1+1 configuration. In the 1+1 configuration, Infoblox recommends using the power cables shipped with the appliance to
connect each power supply to separate power circuits. In the event of a power failure on one circuit, the appliance can then operate on the other
circuit.
Note: If your appliance comes with one power supply and an empty module, ensure that the power supply is in the PSU #1 slot and the empty
module in the #2 slot. You cannot switch them.
Network Automation appliances with a single power supply will go dark if the single power supply stops working for any reason. Infoblox
recommends ordering an additional Power Supply for a redundant 1+1 configuration.
To power the appliance:
Connect a power cable between the power connector on the back of the appliance and a properly grounded and rated power circuit that
meets the provisions of the current edition of the National Electrical Code, or other wiring rules that apply to your location. Make sure that
the outlet is near the appliance and is easily accessible.
Cabling the Appliance to a Network
Use straight-through Category 5/6 Ethernet cables to connect the Network Automation NT-1400 to the network.
The Network Automation NT-1400 appliance does not require a monitor, keyboard, or mouse for normal operation. It requires only an Ethernet
connection. Follow these steps to connect the NT-1400 appliance to the network:
Configure the appliance to use one port (same port for both system administration and network analysis): Connect from the MGMT
Ethernet connector on the appliance front panel to an available Ethernet connection on the network.
or
Configure the appliance to use two or three ports (the MGMT port for Network Automation administration and the LAN1 and LAN2 port for
network analysis):
Connect from the MGMT Ethernet connector on the appliance front panel to the network supporting your management systems.
Connect from the LAN1 Ethernet connector on the appliance front panel to an available Ethernet connection on the network that
Network Automation will be analyzing.
Optionally, connect from the LAN2 Ethernet connector on the appliance front panel to an available Ethernet connection on the
network that Network Automation will be analyzing.
Note: The Network Automation NT-1400 appliance supports 10/100/1000Mbps network connections.

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
1.
2.
3.
4.
2. After connecting the network cables, plug the NT-1400 appliance into an AC power source.
3. Verify that the Link LED is steady amber or steady green on the RJ45 port, indicating a good connection to the network. If possible, verify
that the link indicator is lit on the switch port to which the appliance is connected.
Figure 9 Cabling the NT-1400 Appliance to the Network
Note: By default, the Infoblox appliance automatically negotiates the optimal connection speed and transmission type (full or half duplex) on the
physical links between its LAN1, LAN2 and MGMT ports and the Ethernet ports on neighboring devices.
4. Use the Infoblox GUI to access the Infoblox appliance from a management system. Through the GUI, you can set up and administer the
appliance. For management system requirements and access instructions, see Initial .Network Automation Appliance Configuration
Initial Network Automation Appliance Configuration
The management system is the computer from which you configure and monitor the Infoblox Network Automation appliance. You can access the
appliance from the management system remotely across an Ethernet network or directly through a serial cable.
Note: The computer used as the management system must support a minimum screen resolution of 1280x800.
After completing the steps in , you can make an HTTPS connection to the appliance and access the InfobloxCabling the Appliance to a Network
Network Automation GUI using one of the supported Internet Web browsers listed in the Release Notes for the software release installed in your
system.
For command-line operation, you can make a terminal console connection through an SSHv2 client. You can also access the CLI by connecting a
serial cable directly from the console port of a management system to the console port on the appliance, and then using a terminal emulation
program.
Note: If you wish to configure the Network Automation appliance for IPv6 connectivity, see the later section, Configuring a Network Automation
.Appliance for IPv4 and IPv6
Network Automation equally supports IPv4 and IPv6 networks, and reports and manages all devices running IPv4 and/or IPv6 protocols.
Configuring the Management System
The Network Automation appliance listens on the private IP address 169.254.1.1/24, which can be used at any time to configure the system. The
easiest way to access the appliance on that address is to temporarily configure your workstation to use an address on the same subnet, such as
169.254.1.5/24 (or any other address on the same subnet not occupied by another device).
Depending on the operating system, the procedure to configure your workstation can be slightly different. The following procedure is for systems
running Windows 7:
From the menu, select .Start Control Panel
In the dialog box, click .Control Panel Network and Sharing Center
In the dialog box, click .Network Connections Change Adapter Settings
Right-click the icon for the Ethernet interface you wish to change (Local Area Connection, for example), and choose from theProperties

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
4.
5.
6.
7.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
shortcut menu.
In the dialog box, select in the Network Components list, andLocal Area Connection Properties Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
then click .Properties
In the dialog box, select Use the following IP address, and then fill in the andInternet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties IP address Subnet m
fields using the IP address and subnet mask .ask 169.254.1.5 255.255.255.0
Click in the and dialog boxes. (Depending on your operatingOK Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Local Area Connection Properties
system, you might need to reboot your computer.)
Note: This address change is necessary only for the initial setup of Network Automation. Once the setup is complete, return your workstation to
its prior configuration.
8. Click Close in the dialog box.Local Area Connections Status
9. Temporarily disconnect the Network Automation appliance from the network by unplugging the Ethernet cable from the MGMT port of the
appliance.
10. Obtain an Ethernet cross-over cable and connect your computer to the MGMT port using the cross-over cable.
11. Use an SSH client to access Network Automation at the IP address 169.254.1.1.
12. Log in with user name and password .admin admin
13. Continue the configuration by following the instructions described in Configuring a Network Automation .Appliance for IPv4 and IPv6
Notes on Windows IPv6 Configuration
Of course, users can manage Network Automation on an IPv6 network. The Network Automation Management port has its own factory default
link-local IPv6 address that is unique on its connected subnet. The default IPv6 address derives from the Ethernet MAC address of the
Management interface (MGMT).
You must use a Windows 7 system to configure Network Automation to run on an IPv6 network, because Windows 7 natively supports IPv6.
To configure a new Infoblox Network Automation appliance to be managed through IPv6, do the following:
Reboot Windows 7, ensure that it is enabled for IPv6 networking, and connect it to the management (MGMT) port of the Network
Automation appliance, using a standard Ethernet cable.
On the Windows 7 system, open a DOS command line window and run .ipconfig
Check the listing in the Local Area Connection section of the ipconfig listing, and make a note of the interface number associated with the
PC's IPv6 Link Local address. The IPv6 value will have an fe80: prefix and end with a %* designator, such as fe80:505:ac3b:49b7:d
. The value 15 in this example is the interface number, which will vary with each client.c38%15
In a Windows command line, run the following command:
netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor
Find the Interface *: Local Area Connection section (the * corresponds to the interface number for your PC system's IPv6 address). No
entry should be present in this category for any address starting with the fe80: prefix.
In the Windows PC's command line, run a multicast IPv6 ping to all nodes on the subnet where the Management port is running. This
executes a multicast IPv6 ping to the Network Automation management port connected to the PC.
In the Windows command prompt, run the following command:
ping -6 -n 5 ff02::1
Allow the command to complete whether or not responses occur.
In the Windows PC's command line, run the following command a second time:
netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor
The MGMT port IPv6 link-local address should now appear in the neighbor table under the Interface xx: Local Area Connection section,
similar to the following:
fe80::230:48ff:febc:97da 00-30-48-bc-97-da Reachable
This is the link-local address of the Network Automation appliance management port (MGMT).
Open an SSH client session to the Network Automation CLI at the IPv6 address shown in Step 6 along with the interface number. Log in
with the factory default username/password admin/admin.
Next, you assign a globally routable static IPv6 address on the management port.
Proceed with appliance configuration as described in .Configuring a Network Automation Appliance for IPv4 and IPv6
Configuring a Network Automation Appliance for IPv4 and IPv6
If Network Automation uses DHCP, make a note of the IP address assigned to Network Automation, and then use the Setup Wizard as described
in in the .Configuring Network Automation Using the Setup Wizard Network Automation Administrator's Guide
Note: The Network Automation appliance supports dual-stack connectivity for reachability on both IPv4 and IPv6 networks. You can use either or
both.
Otherwise, configure IP addresses as follows:

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
1.
2. At the CLI (command line interface) command prompt, enter , and specify the following:configure server
Enter the new Database Name and press Enter.
Database Name is a descriptive name for this deployment. It is used in reports titles, headers, etc.
Recommended: Begin name with uppercase letter.
Database Name []: Corp100_west
3. For the first-time installation, you can choose to generate a new HTTPS certificate.
Do you want to generate a new HTTPS Certificate? (y/n) [n]: y
4. Enter the local domain name in which the controller resides. This value is used for truncating device names in Network Automation data
sets throughout the system.
Domain Name 1 (e.g., example.com) []: corp100.com
Domain Name 2 (optional) []:
5. Enter the time server IP address if one is available or is necessary:
Time Server [us.pool.ntp.org]:
6. Enter the time zone region by typing in the suggested numeric value from the list.
Enter choice (0-47) [0]: 45
7. Enter the time zone location by typing in the suggested numeric value from the list:
Choose a location within your time zone.
0. Alaska 1. Aleutian 2. Arizona 3. Central
4. East-Indiana 5. Eastern 6. Hawaii 7. Indiana-Starke
8. Michigan 9. Mountain 10. Pacific 11. Samoa
Enter choice (0-11) [0]: 10
8. Follow the steps for configuring the management port IP settings:
+++ Configuring Management Port Settings
You must configure an IPv4 or IPv6 address/mask on the management port.
Network Automation can perform analysis from the management port or a separate
scan port.
IP Address (optional) []: 10.120.25.212
Subnet Mask (optional) []: 255.255.255.0
IPv6 Address (optional) []:
IPv6 Prefix (optional):
You must provide either an IPv4 gateway, an IPv6 gateway, or both.
IPv4 Default Gateway (optional) []: 10.120.25.1
IPv6 Default Gateway (optional) []:
Note: You must provide either an IPv4 or IPv6 gateway address, or both, depending on the Network Automation IP address.
The configure server command then requests configuration of the Scan port if you are running two-port configuration:
Do you want to configure the Scan Port? <y/n> [n]:
Entering instructs the configure server command to skip IP configuration for the Scan port.N
Note: The Network Automation appliance uses active Ethernet ports labeled MGMT, LAN1 and LAN2. The LAN1 port corresponds to the Scan
port referred to in the configure server command. When you define the Scan port settings in configure server, it is the LAN1 port IP connectivity
you are defining for the appliance. In two-port configurations, this interface is used to connect to the networks being scanned and managed by
Network Automation. You can also configure the LAN2 port as a another scan interface through the Network Automation UI.

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
9. Enter to continue. This enforces single-port appliance configuration, and displays the appliance DNS Server settings:n
DNS Servers are used to map hostnames to IP addresses.
You may enter up to 2 name servers below.
DNS Server 1 (IP) []: 10.102.3.50
DNS Server 2 (optional) []: 10.102.3.10
DNS server 1 and DNS Server 2:
10. Enter the IP addresses of the DNS servers that Network Automation will use.
In the listing, review your entries.Current settings
Current settings:
Database Name: rgraceDev
Server Name: rgrace-dev
Domain Name 1: inca.infoblox.com
Domain Name 2: inmd.infoblox.com
Time Server: us.pool.ntp.org
Time Region: US
Time Location: Pacific
Mgmt Port IP Address: 10.120.25.212
Mgmt Port Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Mgmt Port IPv6 Address:
Mgmt Port IPv6 Prefix:
Mgmt Port IPv4 Default Gateway: 10.120.25.1
Mgmt Port IPv6 Default Gateway:
Scan Port IP Address:
Scan Port Subnet Mask:
Scan Port IPv6 Address:
Scan Port IPv6 Prefix:
Scan Port IPv4 Default Gateway:
Scan Port IPv6 Default Gateway:
DNS Server 1: 10.102.3.50
DNS Server 2: 10.102.3.10
— Edit these settings? <y/n> [n]:
11. If you accept the settings, enter .n
— Configure the system with these settings? <y/n> [y]:
12. Enter to configure the server with the settings you entered. Wait while Network Automation configures the network and sets the weby
interface to use the new IP address.
13. Network Automation automatically reboots if you change its default time zone. Otherwise, a reboot is not necessary.
14. Enter to log out.exit
15. Shut down the Network Automation unit and physically install it in the global network. The unit is now reachable on its global static IP
address for further CLI configuration and UI access.
16. Configure Network Automation software using the Setup Wizard, as described in Configuring Network Automation Using the Setup Wiz
in the .ard Network Automation Administrator's Guide
Infoblox Network Automation CLI
The Infoblox CLI allows you to configure and monitor the appliance using a small set of Infoblox commands. There are some tasks, such as
resetting the appliance, that you can only do through the CLI. You can access the Infoblox CLI through a direct console connection from your
management system to the Infoblox appliance. You can also enable remote console access — that is, SSHv1/v2 client access — through the
Infoblox GUI, and then access the CLI from a remote location using an SSHv2 client (Settings icon –> Network Automation Settings –>
tab).Security –> SSH Settings

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
Using Network Automation CLI Help
You can display a list of available Network Automation CLI commands by typing at the command prompt.?
admin64-212.customer.com> ?
Available Commands:
acl ftp md5sum register set
autoupdate grep more remoteCopy setup
cat halt netstat removedsb show
clear help ping removemib snmpwalk
configure installdsb provisiondisk repair ssh-key
debug installhelpfiles quit reset supportbundle
deregister installmib rdtclient restore telnet
diagnostic license reboot rm tftpsync
exit ls recalculate-spm route top
export maintenance refreshgroups sandbox traceroute
To view an in-depth explanation of a CLI command and its syntax, type after the command prompt. For example:command ?
admin64-212.customer.com> show ?
Show Commands:
acl disk io servers updatelog
certificate dsb license settings version
date ethernet load stats virtual
dbprocs id memory tech
diagnosticlog idmethods process tunclient
discovery interfaces route updatehistory
The two main groups of Infoblox CLI commands are set and show. To see the complete list of the set commands, enter after thehelp set
command prompt. Likewise, to see a complete list of the show commands, enter . For information about the CLI commands, refer to theshow ? I
nfoblox Network Automation Administrator Guide.
Replacing Appliance Components
Network Automation NT-1400 appliances provide AC power supplies as a field replaceable unit (FRU) in the system.
All replaceable units must be replaced with parts of the same specifications as described in this section. You can also order an offered part as a
local spare. For information about compatible parts and their part numbers, see .Table 3
Changing AC Power Supplies
Note: Before changing the power supply, make sure it is securely cabled. An apparently failed power supply may simply be improperly connected
to its power source.
:Caution Never remove a correctly functioning power supply in a live system. Removing the power supply from a correctly operating Infoblox
appliance appliance can cause a complete failure of the appliance and require an RMA (Return Material Authorization).
The Network Automation NT-1400 ships with one AC power supply, with the option to add a second power supply for a redundant 1+1
configuration. In a 1+1 configuration, when a power supply fails for any reason, the other assumes the full load automatically and the Infoblox GUI
displays a power supply alarm. The appliance can also be configured through the Network Automation software to send an email notification and
to report an SNMP trap when such events occur in a 1+1 configuration. This configuration minimizes the chance of system failure due to failure of
an individual power supply. illustrates the process of replacing an AC power supply.Figure 10
Each power supply weighs about one pound (0.454 kg). The faceplate of the power supply contains a power LED and a power switch. Each AC
power supply provides a dedicated power outlet.

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Note: If your appliance comes with one power supply and an empty module, ensure that the power supply is in the PSU #1 slot and the empty
module in the #2 slot. A single power supply runs only in #1 slot as shown in .Figure 10
Figure 10 Removing a Network Automation NT-1400 AC Power Supply
To replace a Network Automation NT-1400 AC power supply, do the following:
Turn off the power circuit to the appliance's AC power supply.
Disconnect the AC power cable from the appliance's AC power supply.
Gently press the black catch-release lever toward the handle, grip the power supply handle, and pull the power supply unit out of the
chassis as illustrated in .Figure 10
Place the replacement power supply into the bay and push it forward until it is fully seated in the chassis. The catch-release lever will
gently click into place.
Reconnect the power cable.
Turn on the power supply. If it is fully seated, powered on, and operating, the LED glows steady green.
Network Automation NT-1400Figure 11 with Dual AC Power Supplies
Network Automation NT-1400 FRUs
Table 3 lists field replaceable units and orderable parts for the Network Automation NT-1400 appliance. It specifies compatibility of the units and
their part numbers. Contact your Infoblox field representative or Infoblox Technical Support for more information.
Table 3 Field-Replaceable Units and Orderable Parts
Field-Replaceable Unit Part Number Type NT-1400
Network Automation NT-1400 Series AC PSU IB-1400-R2-PSU-AC FRU and orderable
option Y
1400 Series rack kit for 2-post or 4-post racks up to 600mm deep T-800-1400-RAIL-2-4- 600MM FRU only Y
800, 1400 and 2200 Series rack rail kit for 4-post racks 600-900 mm deep,
adjustable T-800-1400-2200-
RAIL-4-600-900 FRU only Y

Copyright ©2018, Infoblox, Inc.All right reserved.
Infoblox 1400 Series 18AWG AC Power Cord IB-POWER-CORD-US Contact Infoblox Support Y
Table of contents
Other Infoblox Network Hardware manuals

Infoblox
Infoblox Trinzic TE-2205 User manual

Infoblox
Infoblox TE-2210 User manual

Infoblox
Infoblox Trinzic 100 User manual

Infoblox
Infoblox 1405 Series User manual

Infoblox
Infoblox 4005 Series User manual

Infoblox
Infoblox Trinzic 805 Series User manual

Infoblox
Infoblox 2205 Series User manual

Infoblox
Infoblox Infoblox-250-A User manual

Infoblox
Infoblox SoT-1405 Series User manual

Infoblox
Infoblox Trinzic Reporting 1400 User manual