Construcciones Mecánicas Iriondo S.A.
-Do not remove or modify the electropump plates.
The arrow showing turning direction must be kept
clearly legible at all times.
-Electrical equipment must only be installed and
maintained by a qualified electrician.
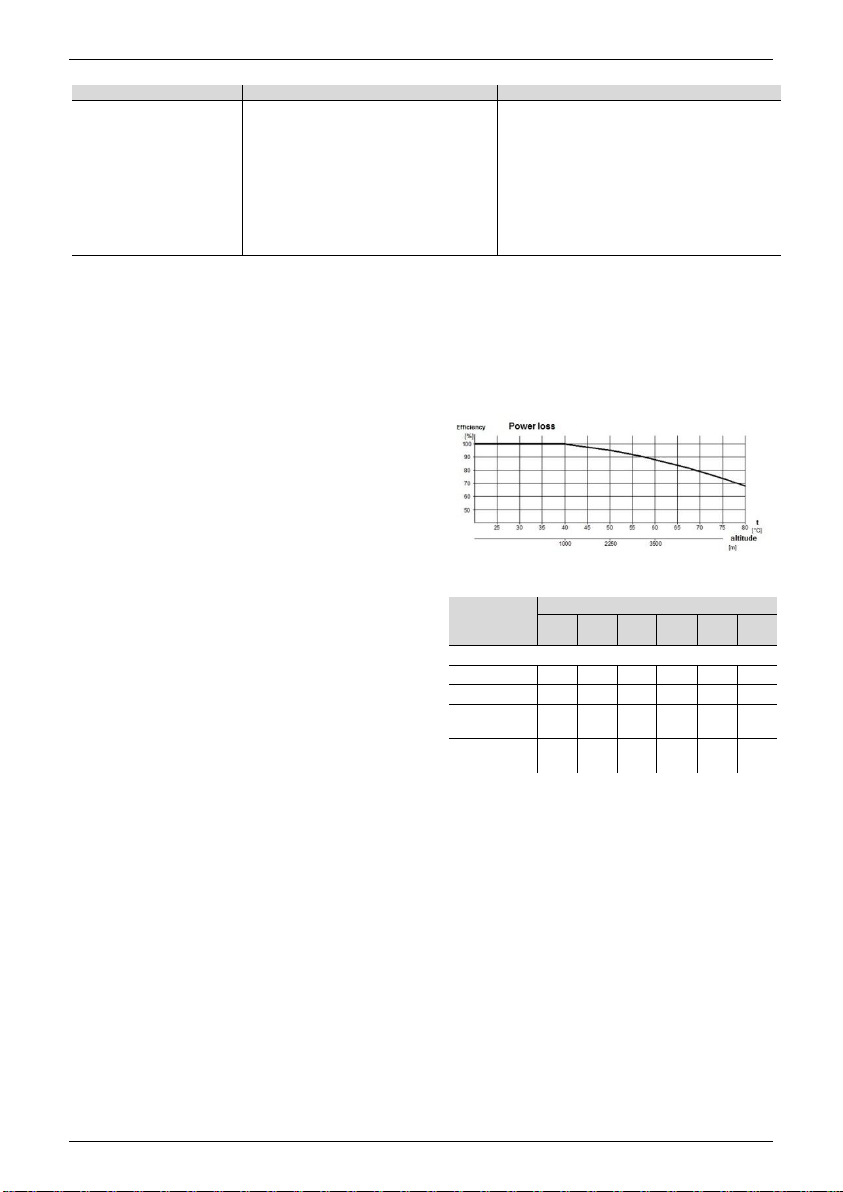
-The electropump is designed to work in
ventilated places protected from the weather,
remembering that the maximum ambient
temperature without loss of power in the electric
motor is 40 °C.
4. Transport, storage and installation
The electropumps are packaged in specially made
boxes to guarantee optimal shipping conditions. The
heaviest, bulkiest electropumps are mounted on a
pallet for easier transport.
Check that the packaging has not been
damaged during shipping.
Loading other goods on top is not allowed.
4.1. Transport
The motor eyebolts are designed to carry only the
weight of the motor. Only lift the electropump with
lifting and loading equipment that is in a perfect
condition and can withstand the load.
4.2. Storage
The electropump must be stored in an environment
which is dry, with constant temperature, is well
ventilated and free of vibrations, even during short
storage periods.
The bearings must be relubricated or replaced after
long periods of storage (over 2 years).
4.3. Installation
The customer must ensure that the electropump's
installation site is suitable. The environment where it
is installed must comply with the requirements set out
in section 3.1. General information.
Installing and commissioning in areas with a
potentially explosive atmosphere is strictly forbidden
unless the electropump is ATEX certified.
4.3.1 Installing pipes
Perfect operation of the electropump depends directly
and largely on proper assembly, both in terms of
suction and delivery.
It is essential to ensure the pump's suction inlet is
completely clean and free when installing.
-Suction
In immersion pumps, the pump vacates the liquid from
the submerged part. It is therefore necessary to
ensure that the impeller (or the lowest one, if several
are fitted) is completely covered when starting up the
pump. Once the pump has started up, this generates
a suction capacity corresponding to the NPSH level in
each case.
The models with a threaded lower cover include the
option to fix a pipe in order to extend suction beyond
the pump's physical limit, reaching the bottom of the
tank whenever necessary. The pump can be started
up beyond its impeller limit position if a foot valve is
applied to the bottom of this pipe.
If the aim is for the pump to completely empty the
tank, a pipe can be added in order to reach the end.
-Delivery
It is very important for the delivery pipe's diameter to
match the diameter of the pump's outlet. Shut-off
should be as close as possible to the end of the circuit
if we want to keep the pump's pressure and flow
characteristics as stable as possible.
Apart from installing a pressure gauge, fitting a shut-
off valve is recommended in order to regulate flow and
pressure.
4.3.2 Installation in the tank
Always respect the maximum and
minimum liquid levels.
Leaving a minimum distance of 20-50 mm between
the bottom of the tank and the suction inlet is
recommended, depending on the volume of flow that
the pump can decant.
A proportional filtering system should be fitted if the
liquid to be pumped contains a lot of solid particles or
these particles are large in size.
4.3.3 Electrical installation
The electrical connection must be completed by a
qualified company or person, always following local
regulations.
Good electrical installation is vital to electropump
operation, making it essential to check that the line
section from the machine’s electrical equipment
through to the pump motor is enough to maintain the
voltage required by the motor without any oscillations.
The electropump must also be installed with suitable
thermal protection and a magnetothermic switch to
ensure it stops in the event of overload or phase
failure.
There must be no foreign bodies, dirt or
moisture in the junction box. Hermetically
seal the junction box to prevent the ingress of
water and dust, but without blocking the
unused cable inputs.
The connection must comply with the following layout
in both triangle and star configuration, depending on
whether the motor pump connection is three-phase
type:
-Checking turning direction
The motor's turning direction must match the arrow
direction on the motor hood. To check, turn on and off
quickly (not exceeding 10 seconds).
If turning direction is incorrect, change either of the
two phases L1, L2 or L3 in the motor's terminal box.