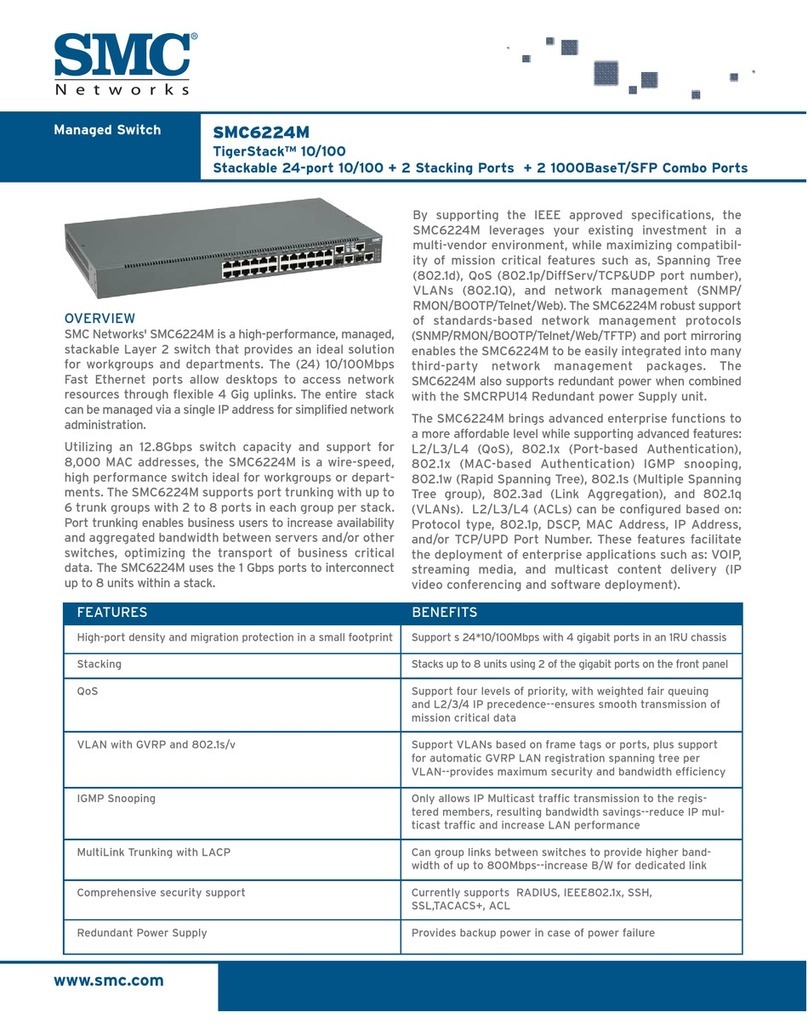
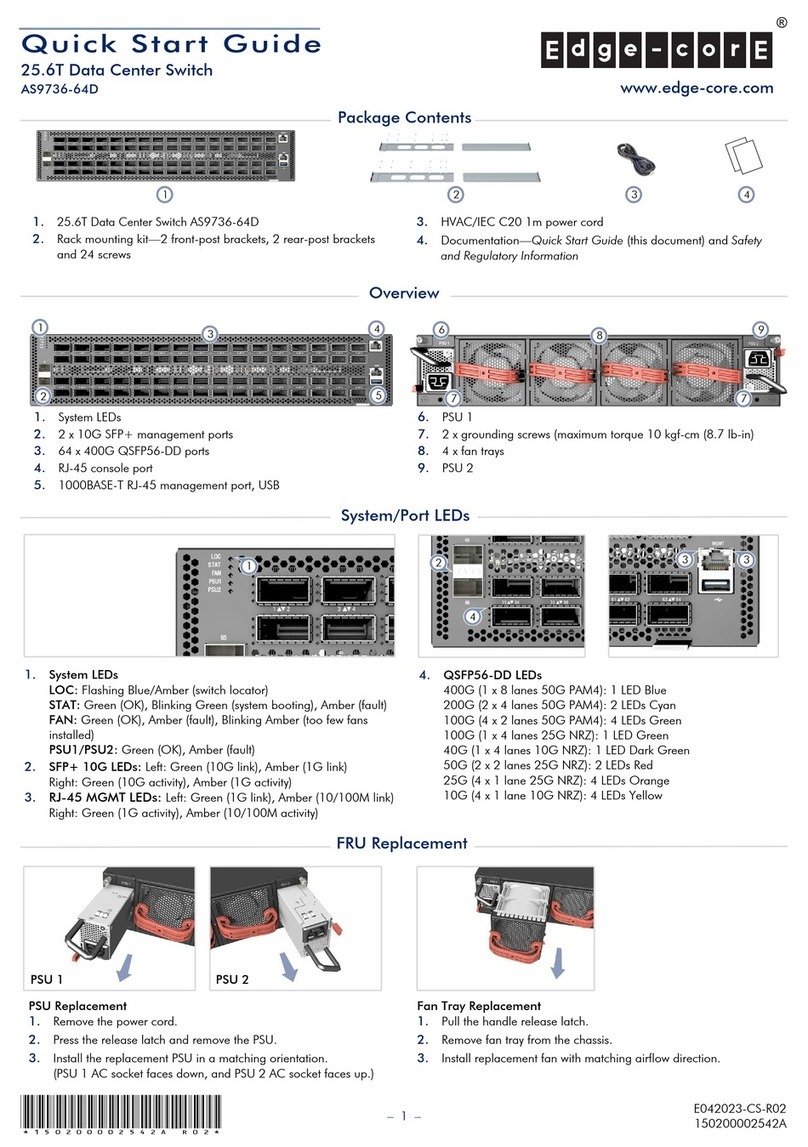
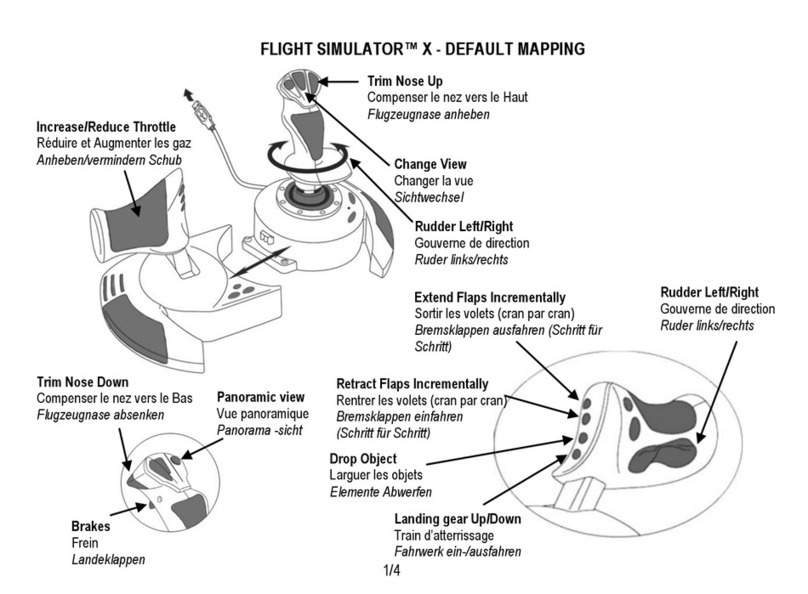
10106094 Rev. 001 Page 4 of 7
In enhanced mode, the /STROBE line is used to signal the SKB to read data from or write
data to the data lines. A change on the data lines has no effect until there is a high-to-low
transition on the /STROBE line. The /STROBE line is driven by the master for both
transmit and receive operations.
R/W Input Line
The R/W line is only used in enhanced mode. The R/W line is driven by the master as a
bus direction control. If the R/W line is driven LOW, /D0-/D7, /SOP and /STROBE line
transitions are interpreted as output operations from the master to the slave. If R/W is
driven high, operations are interpreted as output from the slave to the master.
In SK emulation mode the R/W line must be low to write data to the SKB. Note that this
line is pulled low by default within the SKB.
/HOME Input Line
This line is used in emulation mode. The /HOME line overrides the data lines. A low on
this line forces the SK switch to go to the HOME position and verify the previous
channel position. After this has occurred the SK common stays in the home position.
Note the /HOME must be strobed-in using the /STROBE line. Changes on the /HOME
line have no effect until a high-to-low transition occurs on the /STROBE line.
This line is called RESET on the SK product.
/RESET Input Line
Reset resets the MCU. This is a “hard” reset of the SKB module. All communication
interfaces will be reset.
BUSY Output Line
In SK emulation mode, the BUSY line provides an indication of the switching
mechanism state. The line is LOW when the switch is idle and HIGH while the switching
mechanism is moving to an output channel.
In enhanced mode, the BUSY line provides a flow control mechanism. The slave drives
the BUSY line high after each byte is strobed in. The master will not toggle any lines
until a high-to-low transition of the BUSY line is detected.
ERROR Output Line
In SK emulation mode the ERROR line reports the result of the self-test operation that
occurs whenever the SK switch is reset. If the test fails, the ERROR line goes high and
stays high until a self-test operation is invoked again (assuming the self-test passes on the
next attempt). The error most often indicates a mechanical fault. If an invalid channel
(out of range channel) is strobed in the error line will go high and stay high until a valid
channel is strobed-in.
In the SKB enhanced mode the ERROR line is used to flag the master if the slave detects
an error. When the error line is high this indicates that there is an error in the error