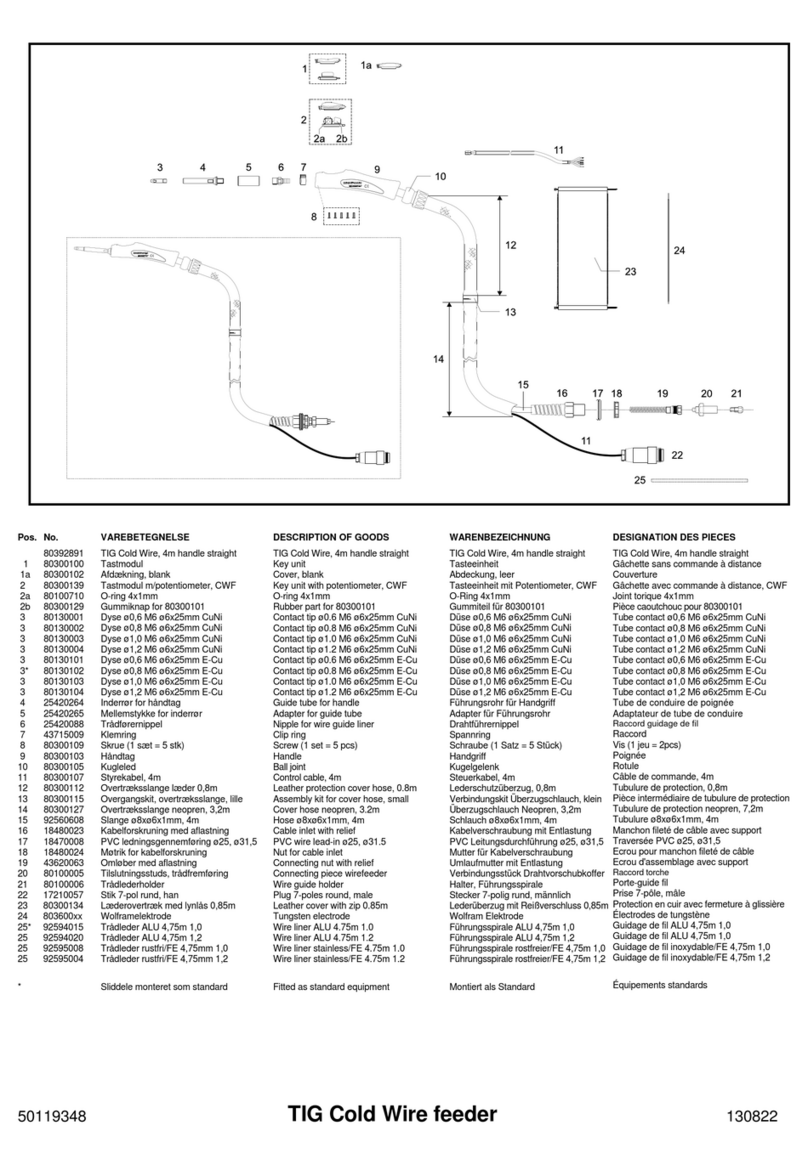
CWF-50 Cold Wire Feeder
- 4 -
“.... there is now a very large volume of scientic
ndings based on experiments at the cellular
level and from studies with animals and people
which clearly establish that low frequency
magnetic elds can interact with, and produce
changes in, biological systems. While most of
this work is of very high quality, the results are
complex. Current scientic understanding does
not yet allow us to interpret the evidence in a
single coherent framework. Even more frustrat-
ing, it does not yet allow us to draw denite
conclusions abut questions of possible risk or to
offer clear science-based advice on strategies to
minimize or avoid potential risks.”
To reduce magnetic elds in the work place, use
the following procedures:
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or
taping them.
2. Arrange cables to one side and away from
the operator.
3 .Do not coil or drape cables around the
body.
4. Keep welding power source and cables
as far away as practical.
5. Connect work clamp to workpiece as
close to the weld as possible.
About Pacemakers:
The above procedures are among those also
normally recommended for pacemaker wearers.
Consult your doctor for complete information.
I. Principal Safety Standards
Reference as applicable
Safety in Welding and Cutting, ANSI Standard
Z49.1, from American Welding Society, 550
N.W. LeJeune Rd, Miami, FL 33126
Safety and Health Standards, OSHA 29 CFR
1910, from Superintendent of Documents, U.S.
Government Printing Ofce, Washington, D.C.
20402
National Electric Code, NFPA Standard 70 from
National Fire Protection Association, Battery-
march Park, Quincy, MA 02269
Recommended Safe Practices for the Prepara-
tion for Welding and Cutting of Containers That
Have Held Hazardous Substances, American
Welding Society Standard AWS F4.1, from
American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune
Rd, Miami, FL 33126
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylin-
ders, CGA Pamphlet P-1, from Compressed Gas
Association, 1235 Jefferson Davis Highway,
Suite 501, Arlington, VA 22202
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, CSA
Standard W117.2, from Canadian Standards
Association, Standards Sales, 178 Rexdale Bou-
levard, Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3
Sales Practices for Occupation and Educational
Eye and Face Protection, ANSI Standard Z87.1,
from American National Standards Institute,
1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018
Cutting and Welding Processes, NFPA Standard
51B, from National Fire Protection Association,
Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269