Installation
Receipt of Equipment
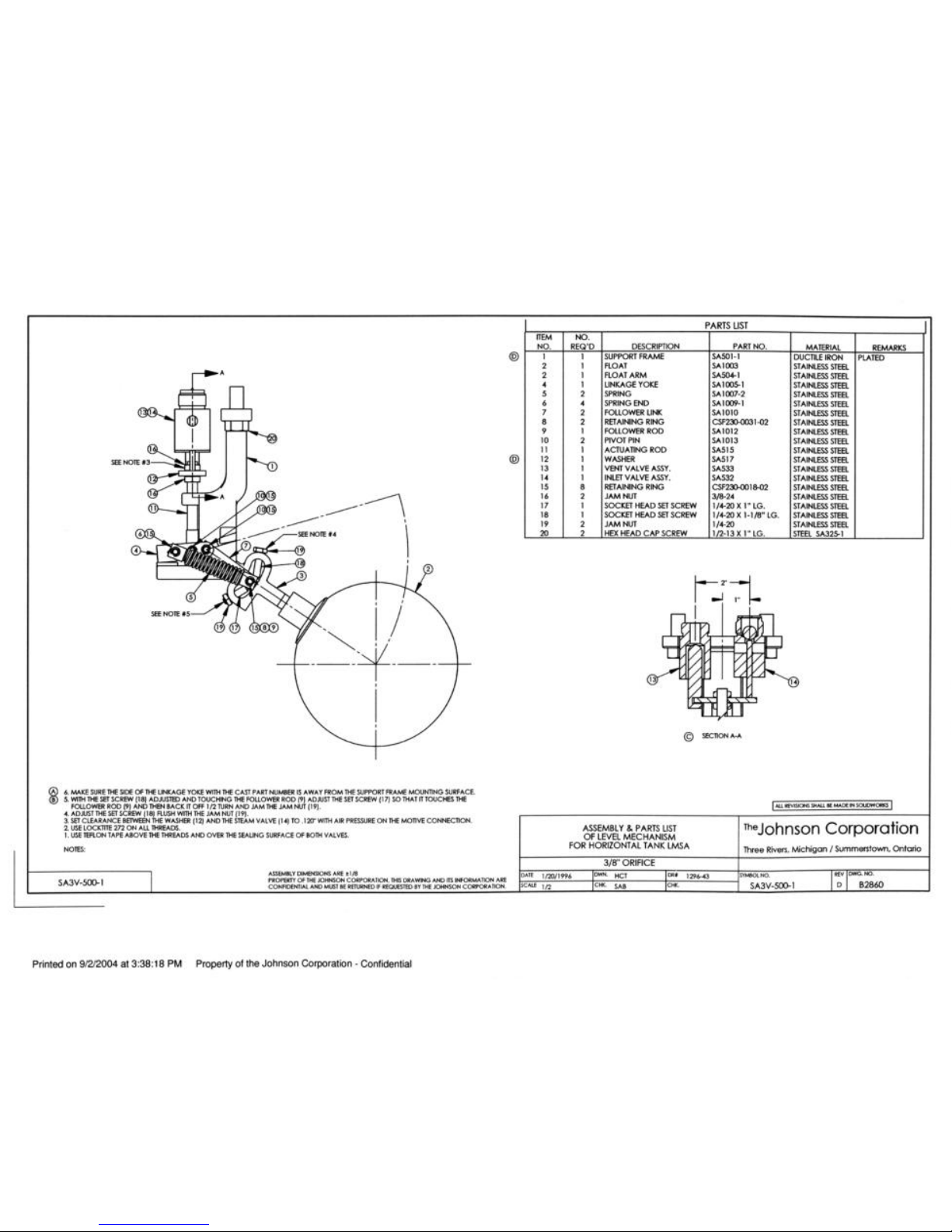
The float assembly has been adjusted and tested at the factory. Additional items such as the inlet baffle (if
supplied), check valves, level gauge glass, cycle counter, and insulation jacket will be packaged separately
in a carton shipped with the unit.
Setting the Unit
On LOOO models, the pump tank may be anchored to the floor using the holes in the mounting feet.
On LROO models, you will also need to install a Johnson supplied receiver. The receiver is held in saddles
with ‘U’ bolts supported by (4) pipes on floor flanges. The floor flanges have mounting holes for attachment
to the floor.
On LRSM models, the entire skid should be supported. Mounting holes may be drilled through the skid for
attachment to the floor.
All tanks should be installed level.
Piping
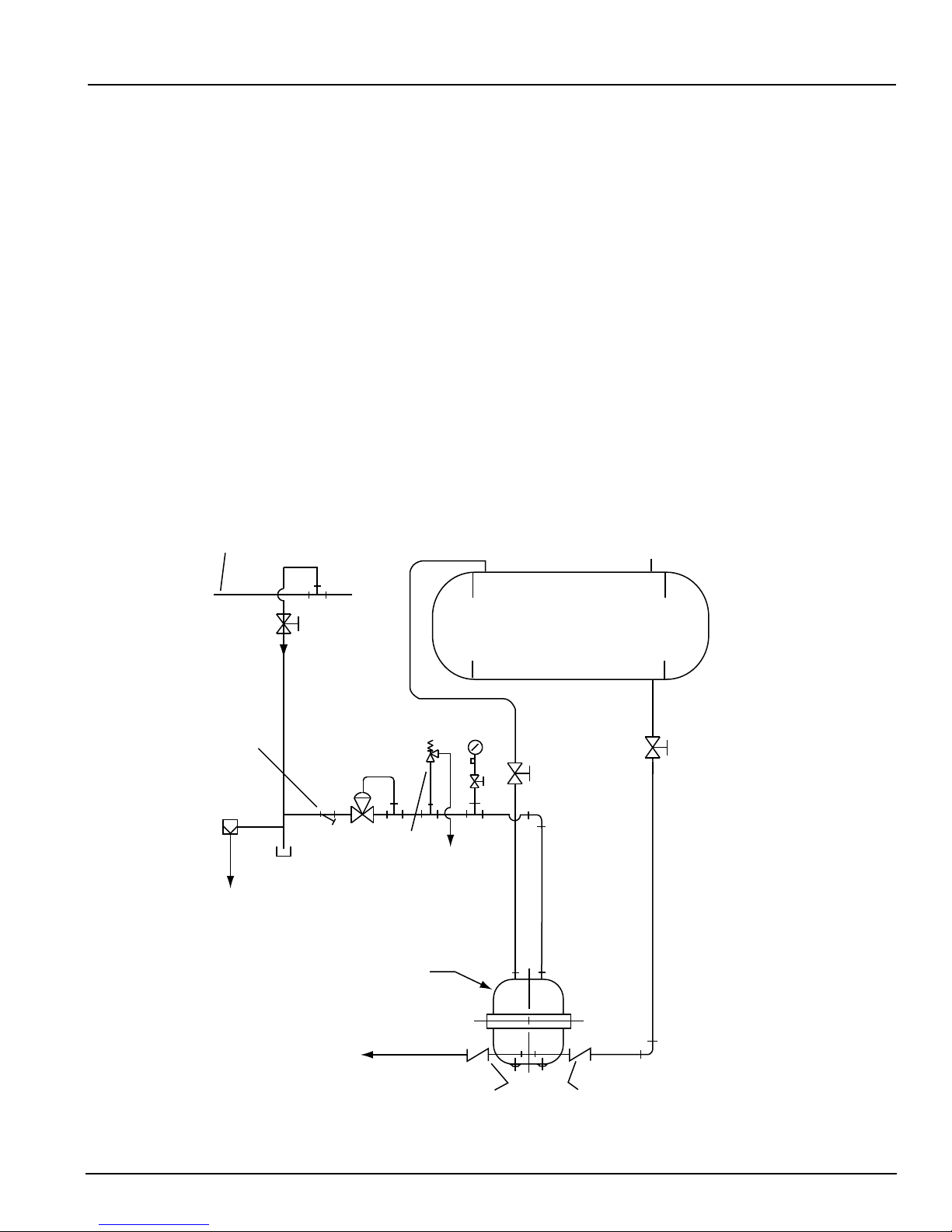
On LROO and LRSM models, the Johnson supplied receiver will normally have (3) top connections for: con-
densate inlet, atmospheric vent, and pressure gauge. For ‘closed systems’ (no atmospheric vent), an air
eliminator and safety relief valve will need to be installed. On LOOO models, the condensate is piped direct-
ly to the inlet check valve from an existing receiver or pipe accumulator.
Refer to the Johnson assembly drawing that accompanies this product for typical piping diagrams. The inlet
baffle (if supplied) must be installed into the pump tank prior to installing the inlet check valve.
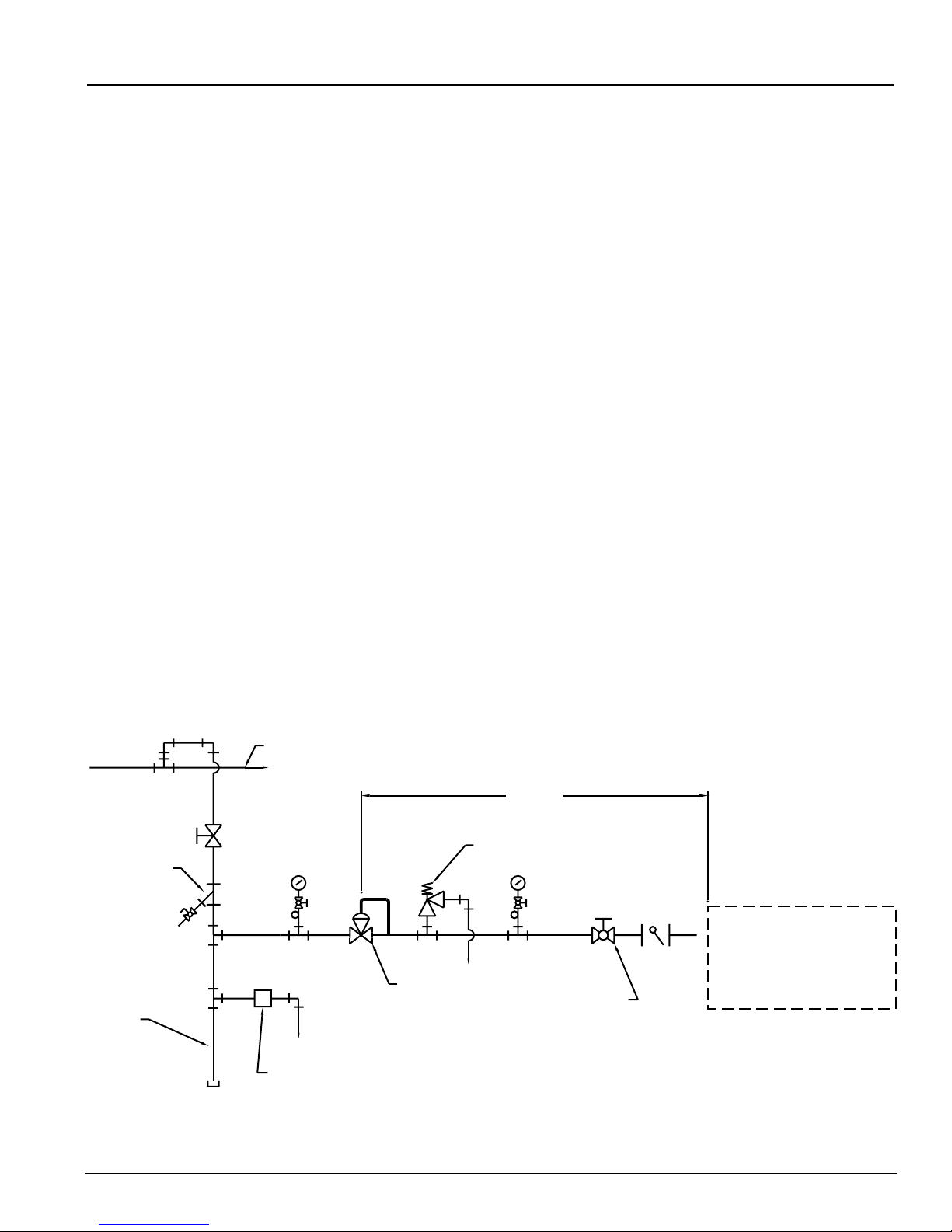
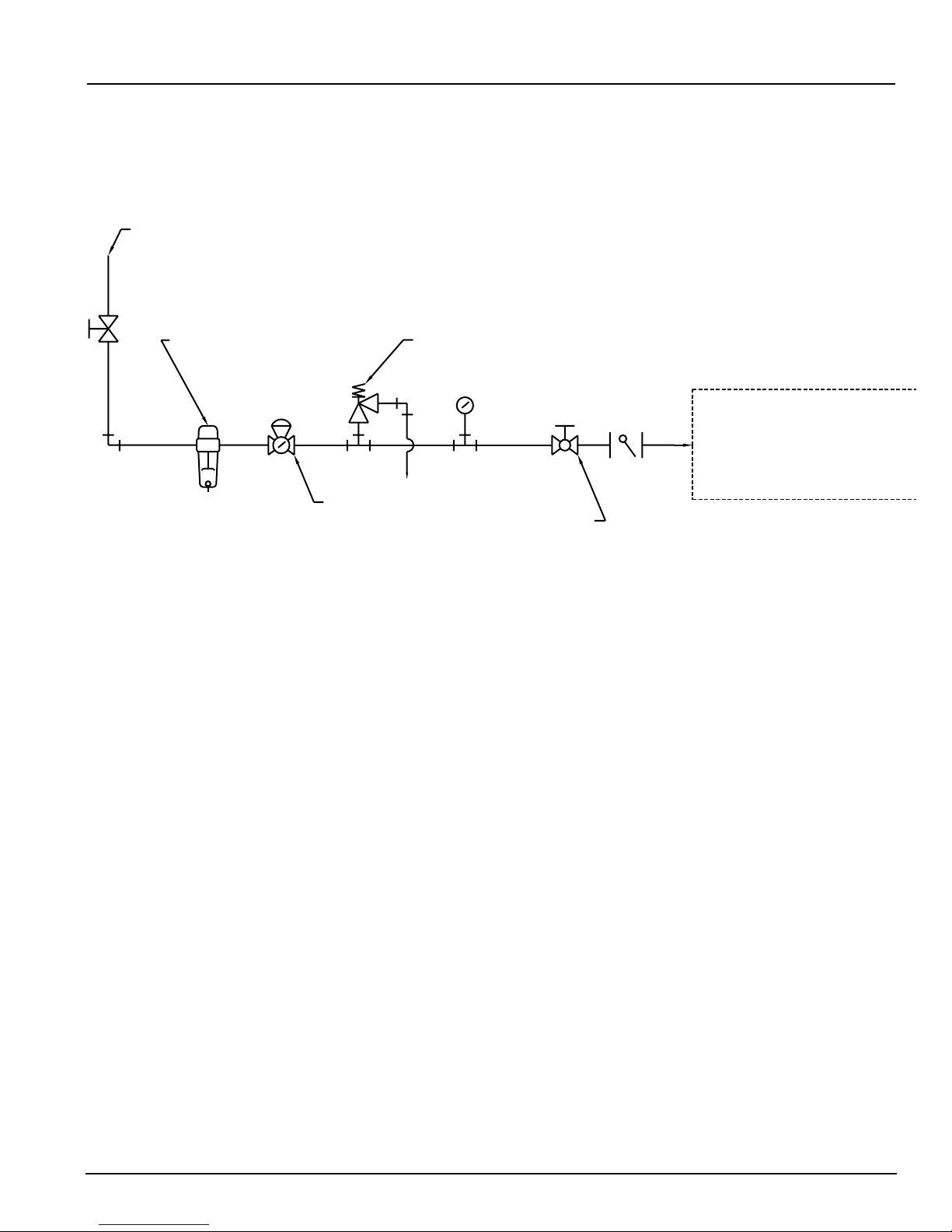
The motive gas (normally steam or compressed air) is piped to the float assembly (1/2˝ npt connection)
through a strainer and a pressure reducing valve.
The equalization (vent) connection on top of the pump tank should be connected to the receiver. The equal-
ization line should not be reduced in size and be installed with minimal restrictions. If the equalization line
is more than 36” in length, the pipe size should be increased at least three pipe sizes. In cases where a
combustible liquid is being handled or the motive used is combustible, the vent must go to a flare or flame.
For LROO and LOOO models, friction loss through the piping should be kept to a minimum. Therefore, pipe
reducers should not be used and pipe runs kept to a minimum. All hand valves should be full port if at all
possible. It is recommended that isolation hand valves be installed to aid in the maintenance of the units.
Some suggested locations are: upstream of the inlet check valve, downstream of the outlet check valve, in
the motive line ahead of the strainer, in the equalization line between the float assembly and the receiver,
and ahead of the pressure reducing valve.