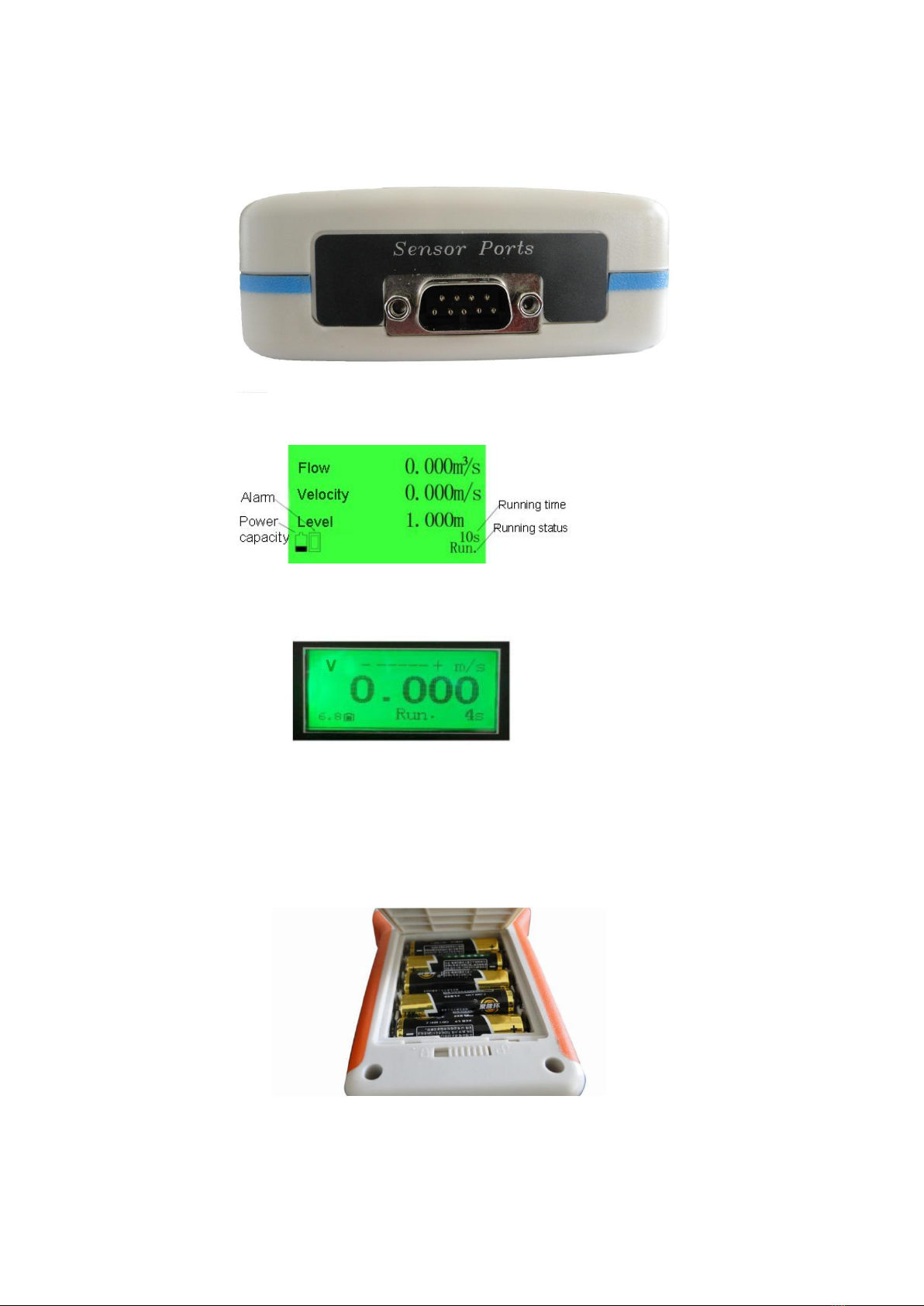
Display: LCD big screen back light display, flow(Ⅱ-model), accumulative
total(Ⅱ-model), level(Ⅱ-model), flow direction, electric quantity, alarm information,
running time, running status;
Physical interface: RS485(optional);
Conductivity: >20µs/cm;
Medium temperature: 0℃~60℃;
Ambient temperature: -10℃~50℃;
Display digits: 3 digits(X.XXX);
Size:204*100*35mm(Display);
Size:Φ32×460(mm)(Sensor);
Measuring rod:Normal 500mm×Sections (500mm×optional sections) or lifting
accessories.
IV. Working principle
The MGG/KL-DCB portable electromagnetic velocity/flow meter depends on the
Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. The conductive liquid cut the magnetic line
and cause induced electromotive force when do the direction perpendicular to the
magnetic field lines in the alternating magnetic field along the measuring pipe. So we
install a pair of electrodes on the pipe wall which orthogonal with sounding pipe axis and
magnetic line. The electrodes can detect the induced electromotive force. It should be
directly proportional with the flow. Then the liquid’s flow will be exported by the detection.
The induced electromotive force signal will be converted to standard DC current
signal(0~10)mA, (4~20)mA or (0~5)kHz frequency output which was directly proportional
with flow signal by amplification of converter. So the measurement comes out.
The velocity equation
(K is induced electric potential magnification);
E--- Induced potential (V);
--- Mean velocity when the fluid cross the electrode surface in range;
B--- Magnetic induction intensity;
D--- Induction electric potential spacing.
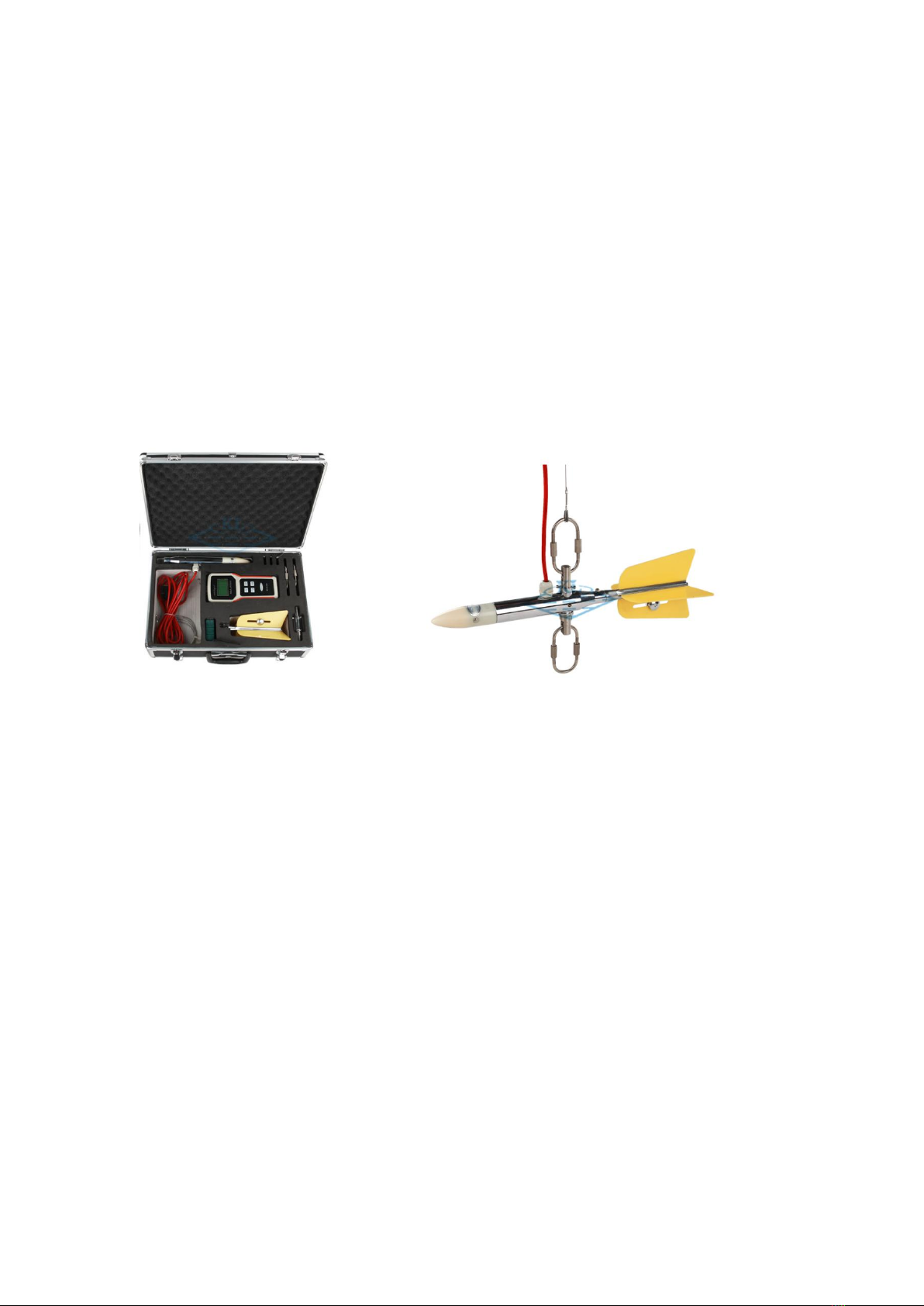
V. Structure
The instrument structure divides into three parts: electromagnetic velocity sensor
(III-model includes level sensor), flow display and wading rod(or suspension wire).
VI. Assemble and introduction
6.1 Flow display terminals