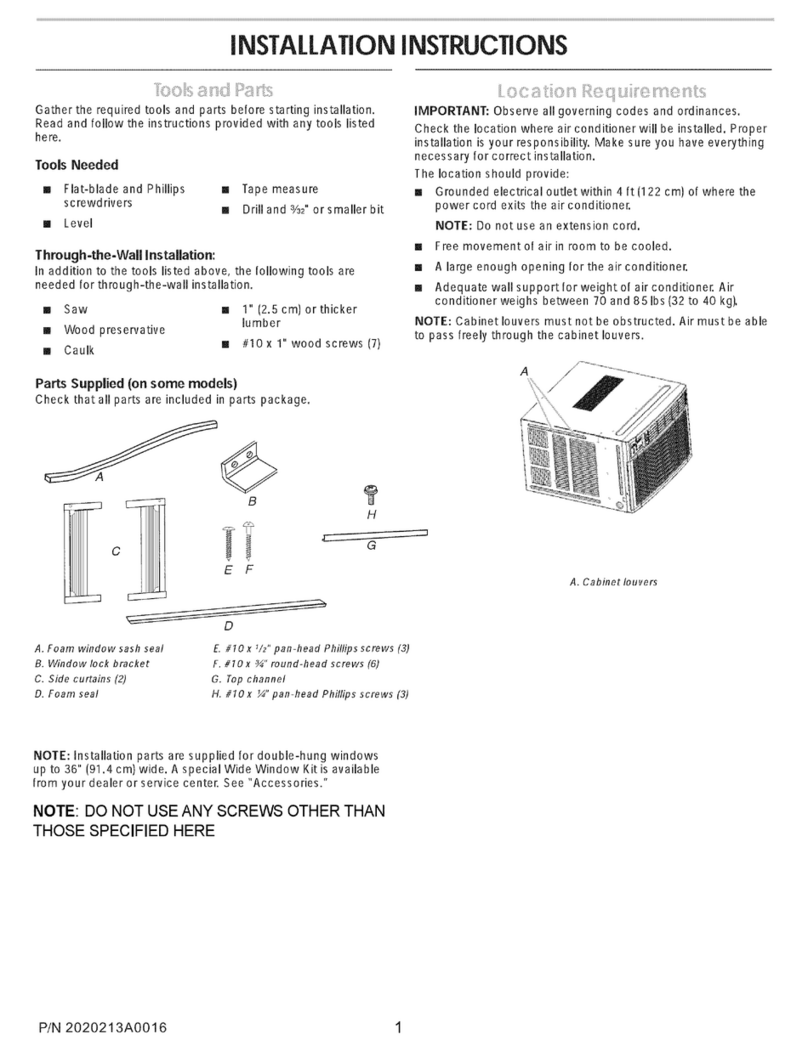
Products, INC.
TR-134 System Service Manual
Sep 15/95
Page 2
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM - SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
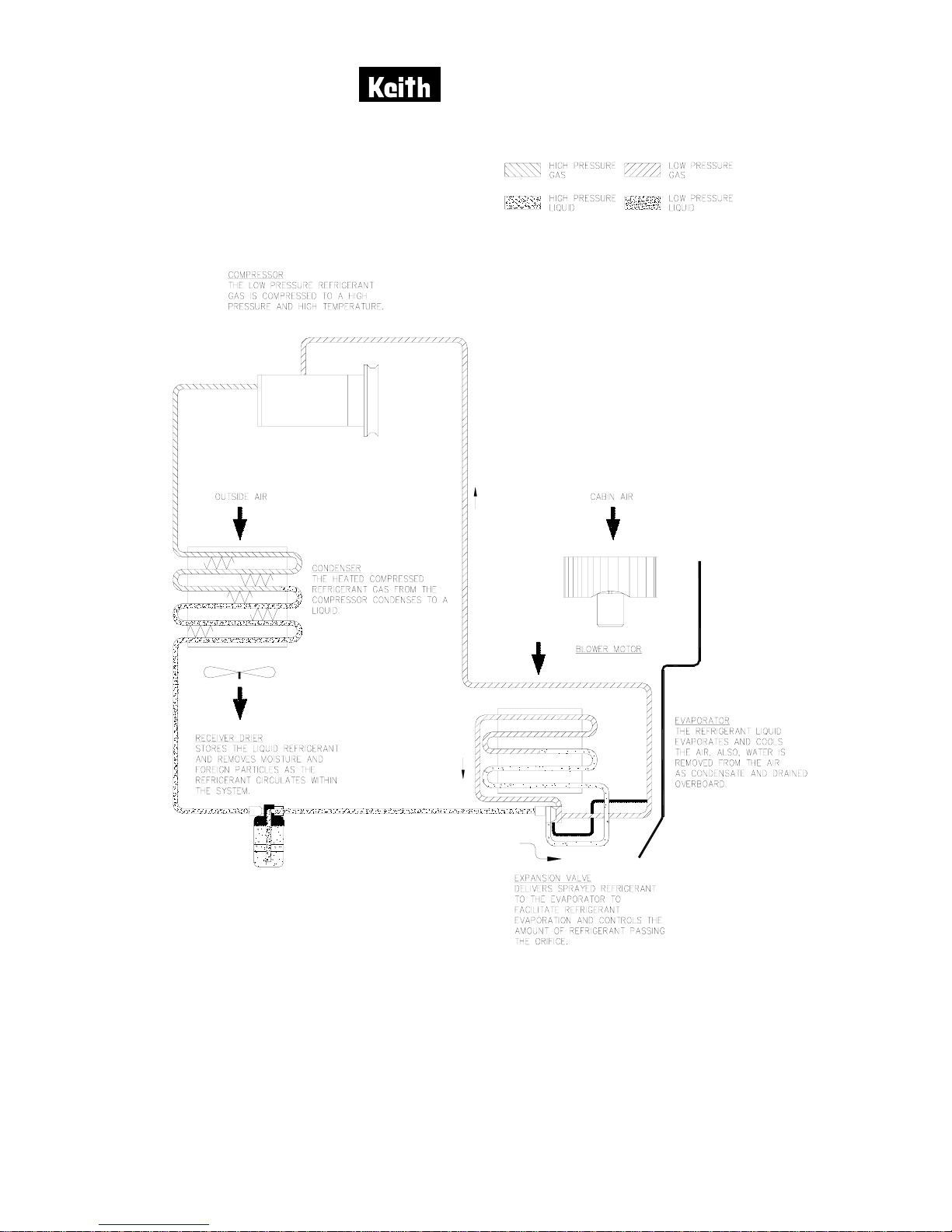
1. VAPOR CYCLE SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The Keith Products vapor cycle air conditioning system uses liquid refrigerant
R134a to cool the aircraft cabin. The major components for the R134a air
conditioning system consists of a receiver/dryer, expansion valve, evaporator,
compressor and condenser to cool the aircraft cabin. Figure 1 shows an
operational schematic of the air conditioning system.
The receiver/drier stores liquid R134a refrigerant under pressure. The drier portion
of the assembly removes any traces of moisture that may have accumulated in the
system. Liquid refrigerant flows from the receiver drier through the expansion valve
where the refrigerant pressure is reduced, allowing it to spray into the evaporator.
At the same time, a blower driven by an electric motor passes air over the
evaporator. This air is cooled since heat is removed from the air by the evaporation
of the refrigerant in the evaporator. The evaporator produces water due to
condensation. This water drains overboard through a line attached to the
evaporator cover.
The refrigerant leaves the evaporator as a gas. This gas is pumped by the
compressor, raising its pressure and temperature. This high temperature gas then
flows to the condenser. Cooling air, driven by another electric blower motor,
passes over the condenser, cooling and therefore condensing the refrigerant to a
liquid. The liquid refrigerant then enters the receiver/drier, repeating the process.
The plumbing which connects the compressor, condenser and the evaporators,
consists of rubber based hoses with a nylon barrier. The fittings are permanently
swaged onto the hoses. Some systems that have been converted from R12 to
R134a refrigerant use Barb Lok hose fittings. Fittings are either "o-ring" type or
use flared connections. Sealant is used on the fitting mating surfaces to prevent
refrigerant leaks. Two R134a service valves are sized differently to avoid incorrect
cross-connecting when gaining access to the plumbing for system recharging.
The compressor on Keith Products air conditioning systems is driven either by an
electrical motor, or by the engine. Listed below is a more detailed description of
electric and engine driven compressor systems.