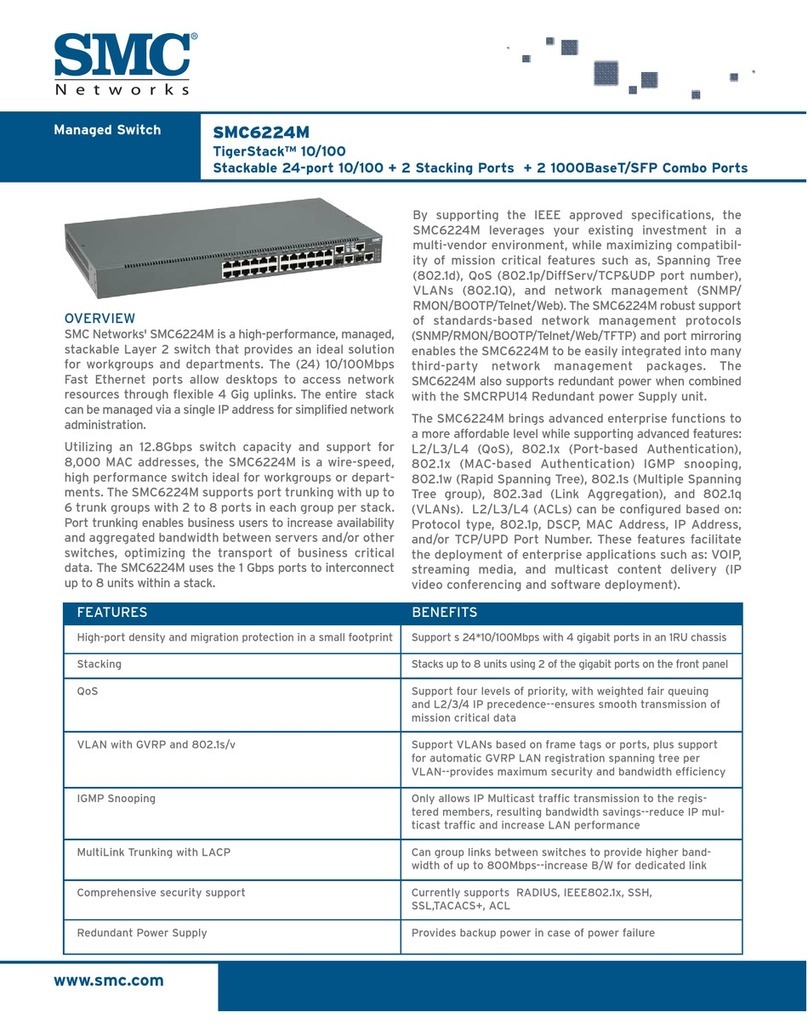
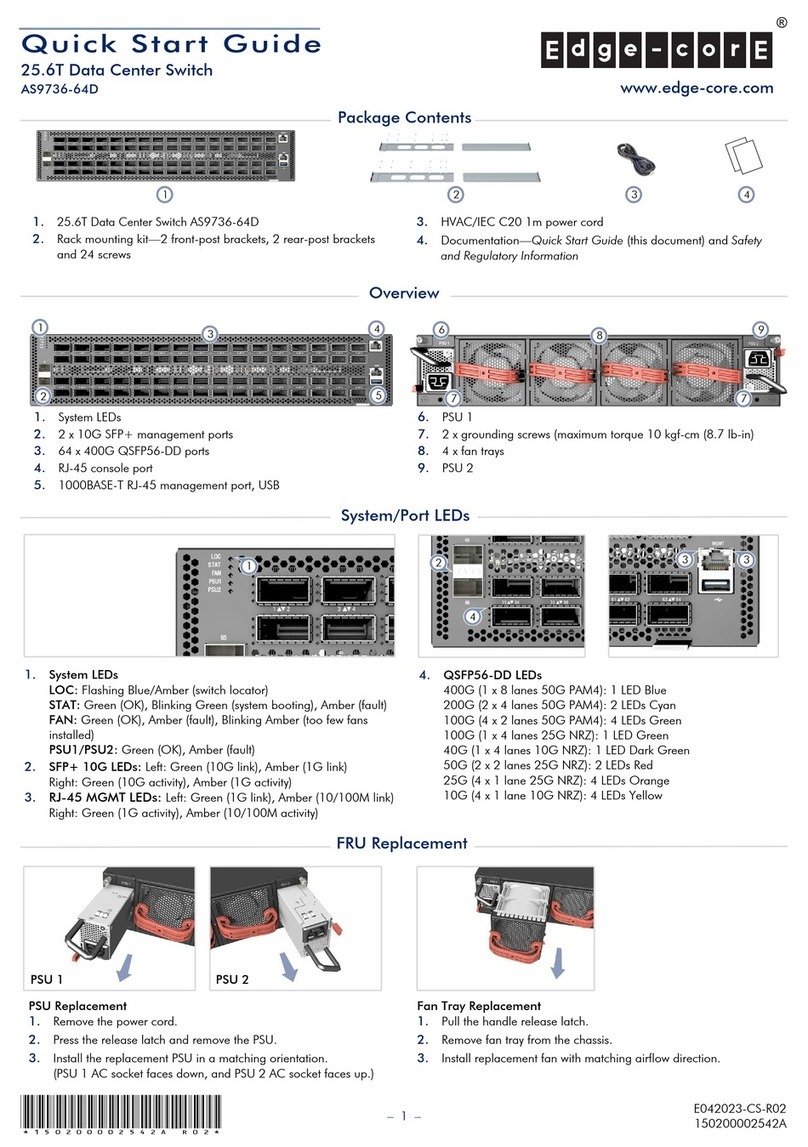
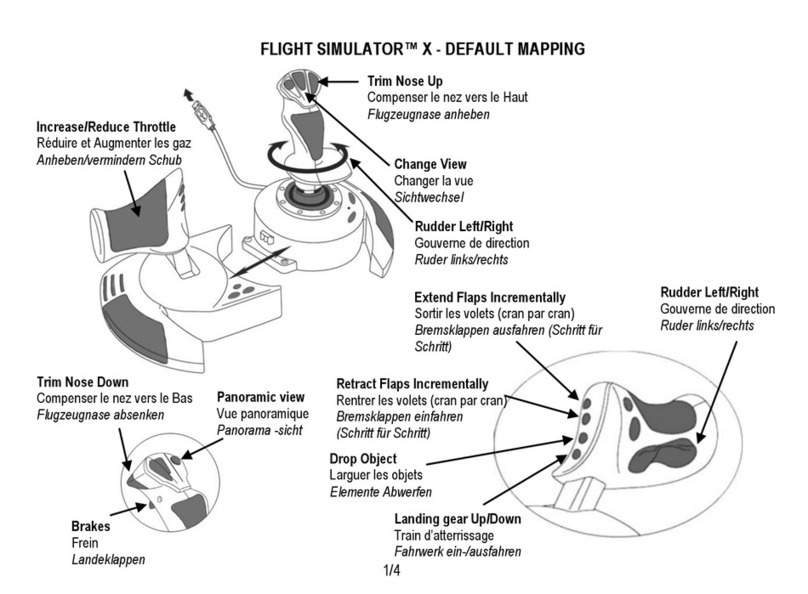
05
AMS
1 Technical Description
1. General
The “ AMS” series of switchgear is an air insulated, factory -assembled and type tested medium voltage
switchgear for indoor installations.The switchgear is an air insulated metal enclosed fully withdrawable
switchgear design, fittedwith Vacuum Circuit Breakers.
The AMS switchgear is fitted with VEP Embedded Pole Vacuum withdrawable circuit breakers. The
switchgear is of a front access design that allows efficient space utilisation within the switchroom. The
switchgear is designed for maximum safety, with all operations performed behind closed doors for
optimum safety, this includes isolationwithdrawal and application of earths via integral fault making
earthing switches to power circuits. The door to the circuit breaker compartment is interlocked such that
the door cannot be opened unless the circuit breaker is withdrawn to the isolated position, behind the
closed door. The circuit breaker status of open/closed/ racked in /racked out can be inspected through
the viewing window on the circuit compartment door.
In addition to VEP Embedded Pole Vacuum withdrawable circuit breakers, the switchgear can also be
equipped with vacuum contactor, and a voltage transformer truck. The switchgear is designed to meet
various system configurations as per individual project requirement.
The switchgear features partitioningbetween the busbars, the circuit breaker, the low voltage compartment
and the cable compartment. The generously dimensioned low voltage compartment is designed to both
modern and conventional control and protection systems. The AMS control panels can be combined
The functionalunits of the switchgear are guaranteed arc proof in accordance with the AS and IEC
Standards. All the start -up, maintenance and service operations can be carried out from the front.
The switchgear is designed in accordance with the Australian and IEC Switchgear Standards. The
switchgear is fully type tested and compliant with AS 62271.200:2005 and IEC 62271-200, Ed1.0
(2003). And the vacuum circuit breaker is fully type tested and compliant with AS 62271.100:2005
and IEC
62271-100, Ed 1.2 (2006). In addition to AS and IEC standards the switchgear also meets the
requirements of DIN and VDE (German) Standards.
•The main characteristicsof the switchgear are as follows:
•Metal-clad, air-insulated switchgear.
•Suitable for medium voltage distribution.
•Guaranteed arc-proof units.
•Factory-tested for indoor installations.
•Tested in accordance with AS and IEC Standards.
•Wide range of functional units available for all installation solutions.
•Compartments segregated by metallic partitions.
•Modular structure, easily built -up.
•
•Highly effective use of space.
•Start-up, maintenance and service operations can be carried out from the front.
•Apparatus handling with the door closed.
•Units can be installed against the wall.
•Limited and simple maintenance activities.
•Complete with mechanical safety interlocks.
•Earthing switchwith full making capacity.
•Designed to guarantee maximum service continuity.
•Conventional or integrated protection and measurement systems.