The number of starts should be spread over the hour.
8 - STARTING THE PUMP UNIT
An electro-pump must never be run dry. This is very
important to ensure the mechanical seal remains
watertight.
–For three-phase units, make sure that the direction of
rotation is that indicated by the arrow on the fan cover,
by running the motor for a couple of turns.
–If the direction of rotation is reversed, modify the
connection to the motor terminal block by reversing 2 power
supply wires.
–After starting, once the motor has reached its operating
speed, make sure that the back pressure is normal and
not subject to significant fluctuations. If this is not the
case, stop the electro-pump and check that the level of
liquid in the pan is more than 100 mm above the suction
inlet filter as indicated in section 6.2.
–If the motor is not running fast enough, check the
connection.
–Take care not to leave the pressure valve closed for
more than 5 minutes.
–With the electro-pump operating normally, measure the
maximum current drawn on each phase. Set the circuit-
breaker definitively, for a slightly higher current than the
maximum measured. This must never exceed the current
indicated on the motor identification plate.
–Check that the voltage between phases at the motor
terminals is correct.
–Any disruption to operation indicates abnormal electro-
pump operation (voltage drop, loss of phase, incorrect
setting, foreign body in the pump, sludge, etc.).
–The electro-pump should turn smoothly without
vibrating.
–Never run the electro-pump with the pressure valve
closed.
–If difficulties are experienced with priming when the
electro-pump is started, either there is insufficient liquid
in the pan or the pump has been drained and an air
pocket is blocking the top of the pump. In this case,
drain the pump by unscrewing the plug shown in the
diagram at the end of this document.
–Motor. Drain holes: To drain condensates formed
during cooling of the machines, there are holes in the
lowest points in the motor housing or shields depending
on the operating position. From time to time, the plastic
plugs covering these holes should be removed and then
replaced.
9 - STOPPING THE PUMP UNIT
–Switch off the electrical supply to the motor.
–In the event of a prolonged stop and/or where there is
a risk of freezing, drain the pan and the delivery pipe or
take appropriate precautions against freezing.
10 - SERVICING
PV4 and PIV6 series electro-pumps require very little
servicing.
•The bearings are permanently greased.
•Only the mechanical seal may need to be changed if
noticeably worn or leaking.
•Electro-pumps installed as backup equipment should be
run for a short time once a week to ensure that they are
working properly.
It is recommended that the current consumption should
be checked occasionally. If this should rise without
the flow increasing, this indicates an operating fault
or particularly harsh operating conditions, which should be
rectified. In any event, it is recommended that the electro-
pump should be dismantled after 2 years or 10,000 hours
of operation in order to examine parts subject to wear
(mechanical seal, turbine, etc.)
11 - DISMANTLING - REASSEMBLY
An electro-pump must be dismantled and reassembled
by personnel qualified to carry out this type of work.
Where one or more components of the electro-pump are
being replaced (spare parts) it is essential that only parts
supplied by LEROY-SOMER are used. Failure to comply
with this instruction invalidates the guarantee and relieves
the manufacturer of responsibility for any malfunction.
Any person working on an electro-pump is responsible
for the consequences.
Before commencing work on the electro-pump:
–Disconnect the electricity supply to the motor.
–Close the pressure valve.
–Check that the pump body is not under pressure.
11.1 - Removing the motor
The motor can be easily disconnected without removing
the pump.
To do this, remove:
–the protective grille
–the 4 coupling sleeve locking screws
–the 4 screws and their washers
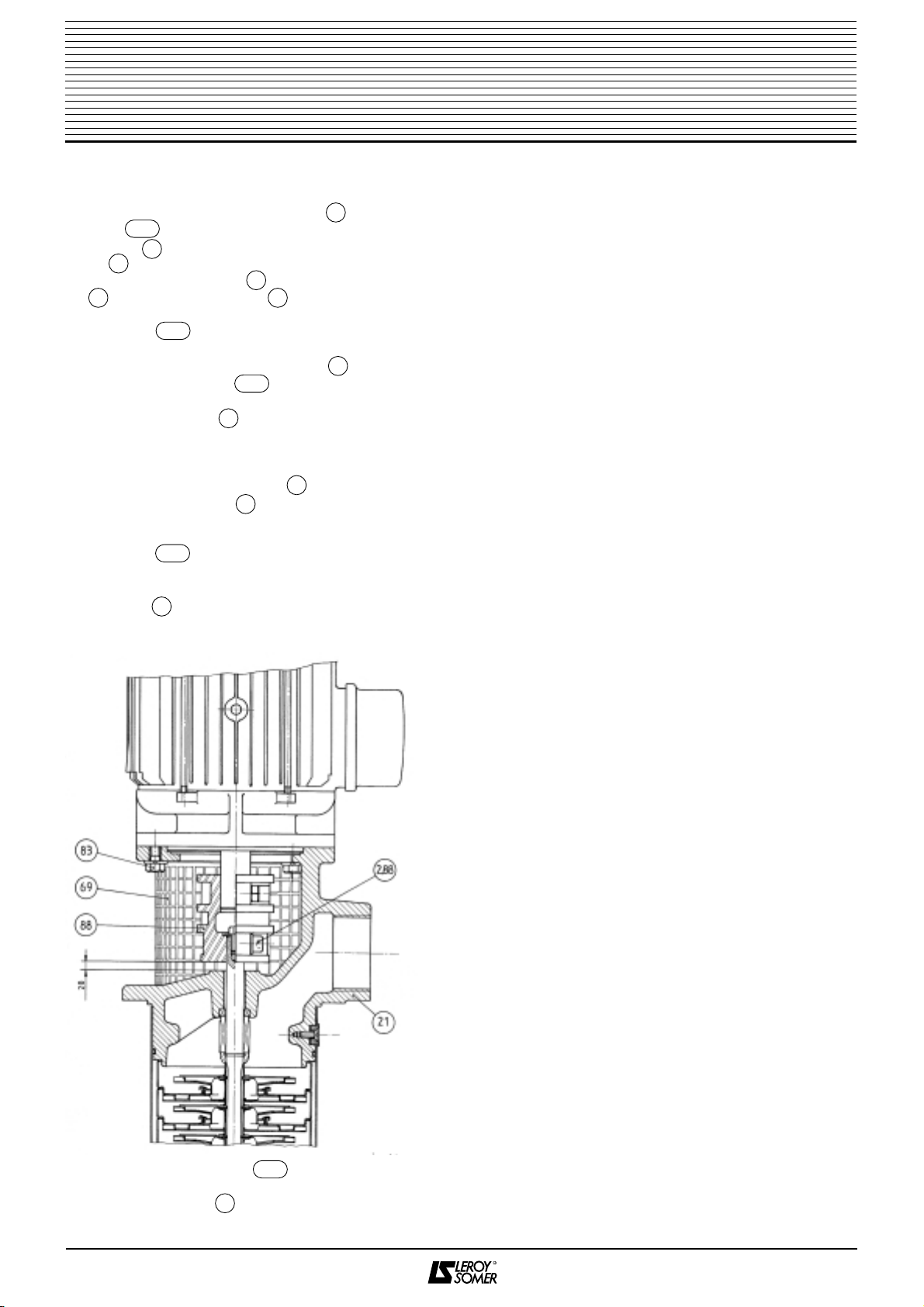
11.2 - Removing the hydraulic unit
After removing the delivery pipe and the fixing for
mounting the pump on the pan, remove the pump from
the pan, drain it and position it vertically with the delivery
head at the bottom.
4
PV4 - PIV6
electro-pumps
Running the electro-pump on empty is
absolutely prohibited.
Motor
power Max. number of starts
per hour
≤0.55 kW 40
0.75 to 1.1 kW 35
1.5 to 3 kW 30
4 to 7.5 kW 20