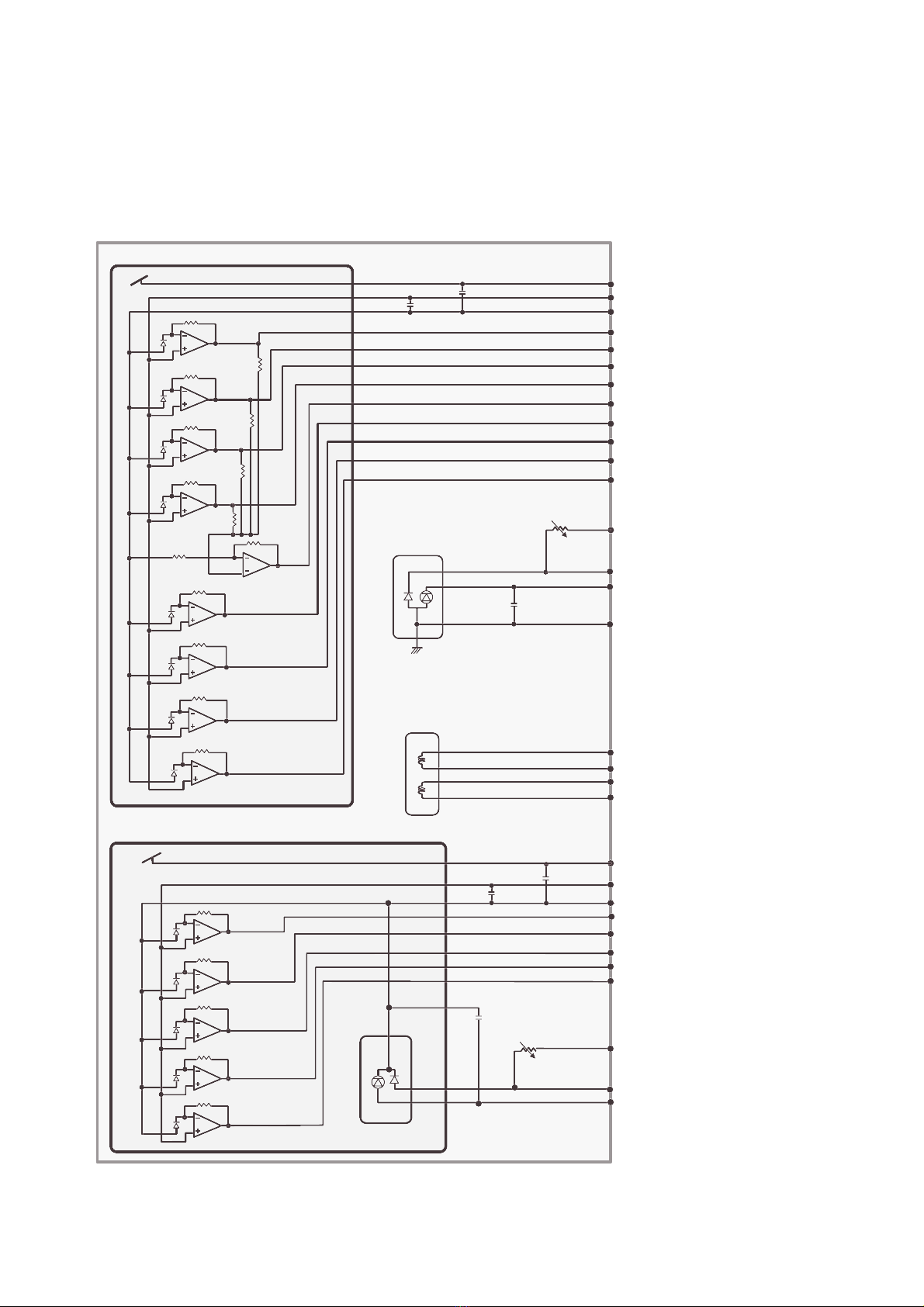
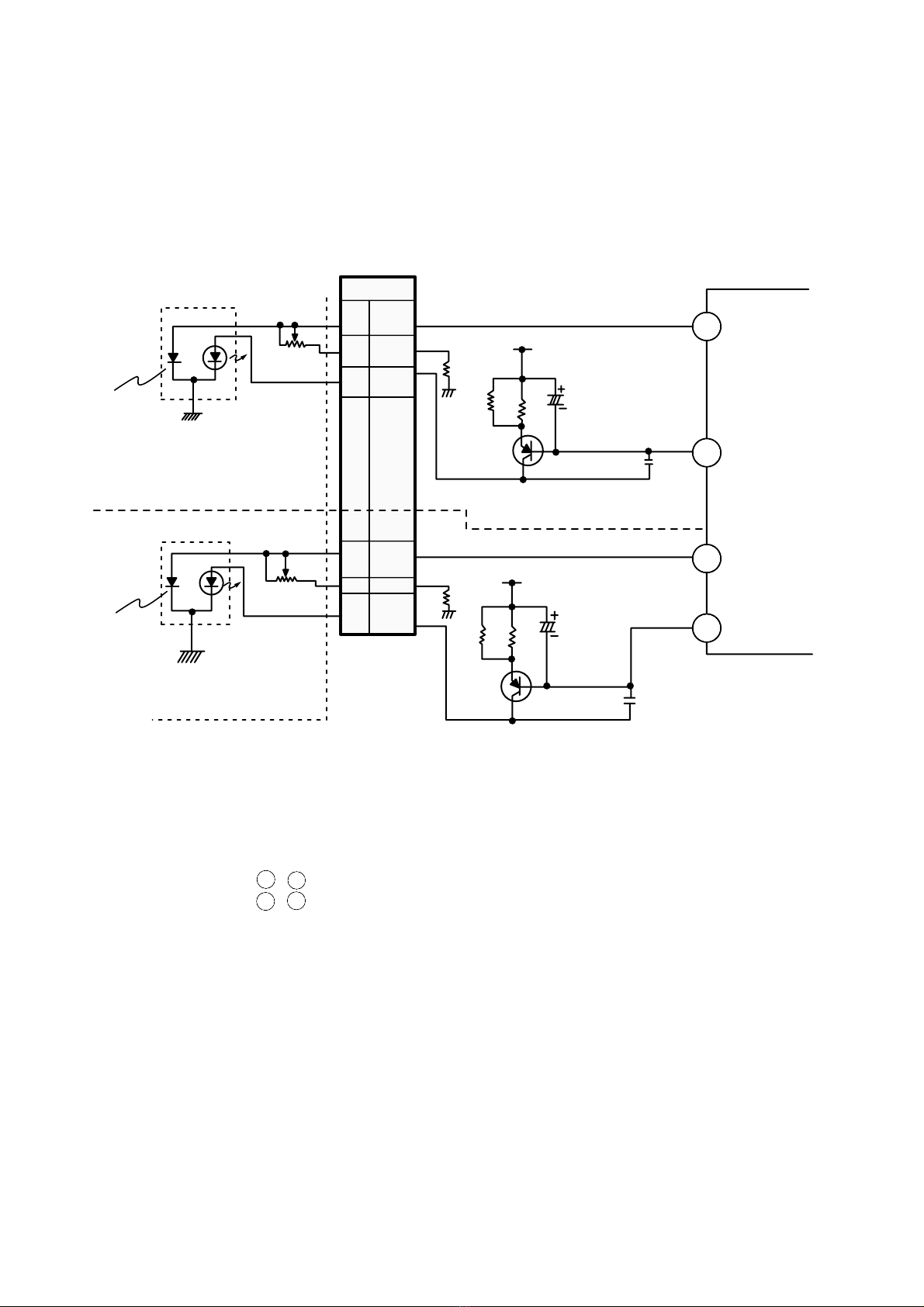
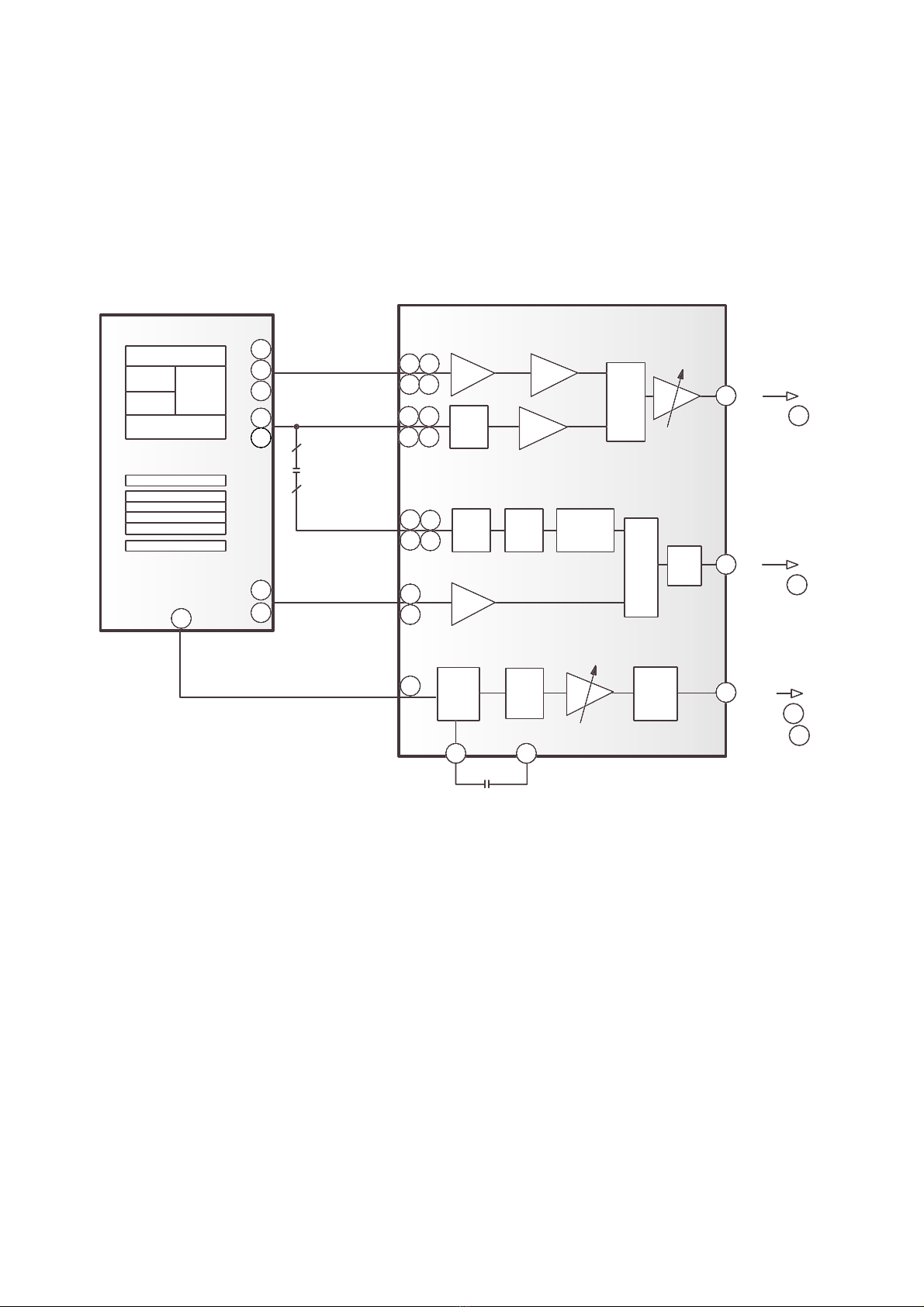
3
INTRODUCTION
GENERAL FEATURE
SPECIFICATIONS
1. SUPPORTED SYSTEM
• IBM Compatible Pentium 133MHz or Above (with PIO mode 4, TX chip set recommended)
2. SUPPORTED OS
3. GENERAL PERFORMANCE
• Data Transfer Rate ...........................................................................................Sustained Data Transfer Rate
DVD (Outer side) : Approx. 10,800 kbytes/sec
DVD (Inner side) : Approx. 4,725 kbytes/sec
CD (Outer side) : Approx. 6,000 kbytes/sec
CD (Inner side) : Approx. 2,625 kbytes/sec
• Data Buffer Capacity.......................................................................................................................512 kbytes
• Access Time...................................................................Random Access DVD : 120ms Typical (8X)
CD : 100ms Typical (40X)
4. POWER REQUIREMENTS
• Voltage ........................................................................................................................................+5V DC +5%
+12V DC +5%
• Ripple .....................................................................................................................................+5V : 100mVp-p
+12V : 100mVp-p
• Current .........................................................................................+12V : 400mA (Average), 0.9A (Maximum)
+5V : 500mA (Average), 1.2A (Maximum)
5. AUDIO PERFORMANCE
• Frequency Response......................................................................................................20Hz~20KHz(+ 3dB)
• S/N Ratio (IHF-A+20kHZ LPF) ..........................................................................88 dB (Typical at 1 KHz 0dB)
80 dB (Limit at 1 KHz 0dB)
• T.H.D. (IHF-A+20kHZ LPF)...............................................................................0.05% (Typical at 1 KHz 0dB)
0.15% (Limit at 1 KHz 0dB)
• Channel Separation (IHF-A+20kHZ LPF) .................................................................................75 dB(Typical)
70 dB(Limit)
• Output Voltage (1kHz 0dB) 47KΩLoad ..................................................................................0.8Vrms +20%
• Headphone Level (1kHz 0dB) 33ΩLoad.................................................................................0.8Vrms +20%
•Enhanced IDE interface
•Internal 5.25 inch, halfheight DVD-ROM Drive
•120ms (Typical) Random Access Time (DVD)
•100ms (Typical) Random Access Time (CD)
•Supports 8X (max) Rotational Modes in DVD Mode
•Supports 40X (max) Rotational Modes in CD Mode
•Max 10,800 kB/sec Sustained Transfer rate in DVD mode
•Max 6,000 kB/sec Sustained Transfer rate in CD mode
•Photo-CD Multisession Disc Spec compliant
•Multimedia MPC-3 Spec compliant
•Power Tray Loading/Ejection Mechanism
•3-Way Eject Support (Software, Open/Close Button,
Emergency Eject)
•Closed Enclosure
•Built-in ATAPI Interface Controller
•Software Volume Control
•Easy CD-Audio Play front panel Controls
•Front panel Volume Control for Headphone Output
•Built-in MODE-1 ECC/EDC
•MTBF (125,000H) POH (at 10% Utilization)
•PIO Mode 4 & Multiword DMA Mode 2 Support
•ULTRA DMA 33 support
•Horizontal/Vertical Mounting
•Digital audio output connector
•Digital audio through ATAPI Interface
•Spin-down Mode for energy saving
•MS-DOS (Ver 3.1 or Higher)
• Windows 3.1/95/98/2000
• Windows NT (Ver 4.0)
• OS/2 Warp (Ver 3.0)
• Solaris (Ver 2.4 or Higher)
• Linux ’96 Slacware (Ver 3.1.0)
This service manual provides a variety of service
information. It contains the mechanical structure of
the DVD-ROM Drive together with mechanical
adjustments and the electronic circuits in schematic
form. This DVD-ROM Drive was manufactured and
assembled under our strict quality control standards
and meets or exceeds industry specifications and
standards.