Maxim Integrated Page 6 of 15
Hardware Implementation and Interface Power
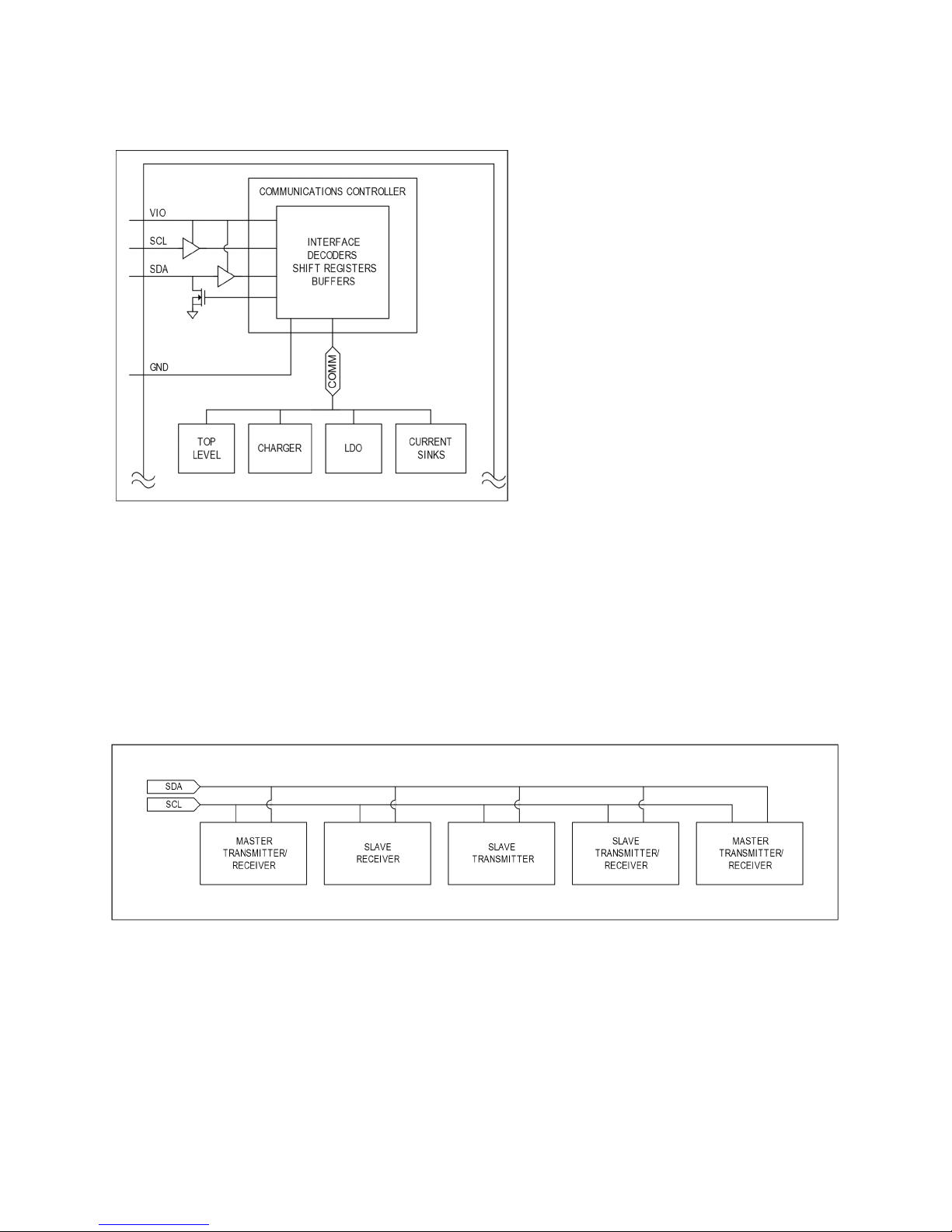
The MAX77734 I
2
C interface derives its power from V
IO
. Typically, a power input such as V
IO
would
require a local 0.1μF ceramic bypass capacitor to ground. However, in highly integrated power
distribution systems, a dedicated capacitor might not be necessary. If the impedance between V
IO
and
the next closest capacitor (≥0.1μF) is less than 100mΩin series with 10nH, then a local capacitor is not
needed. Otherwise, bypass V
IO
to GND with a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor.
V
IO
accepts voltages from 1.7V to 3.6V. Cycling V
IO
does not reset the I
2
C registers. V
SYS
must drop below
SYSPOR for the registers to reset. When V
IO
is less than V
IOUVLO
and V
SYS
is less than V
SYSUVLO
, SDA and
SCL are high impedance. Note that I
2
C is an open-drain bus and requires pullup resistors. Typical
applications place these pullups near the host controller.
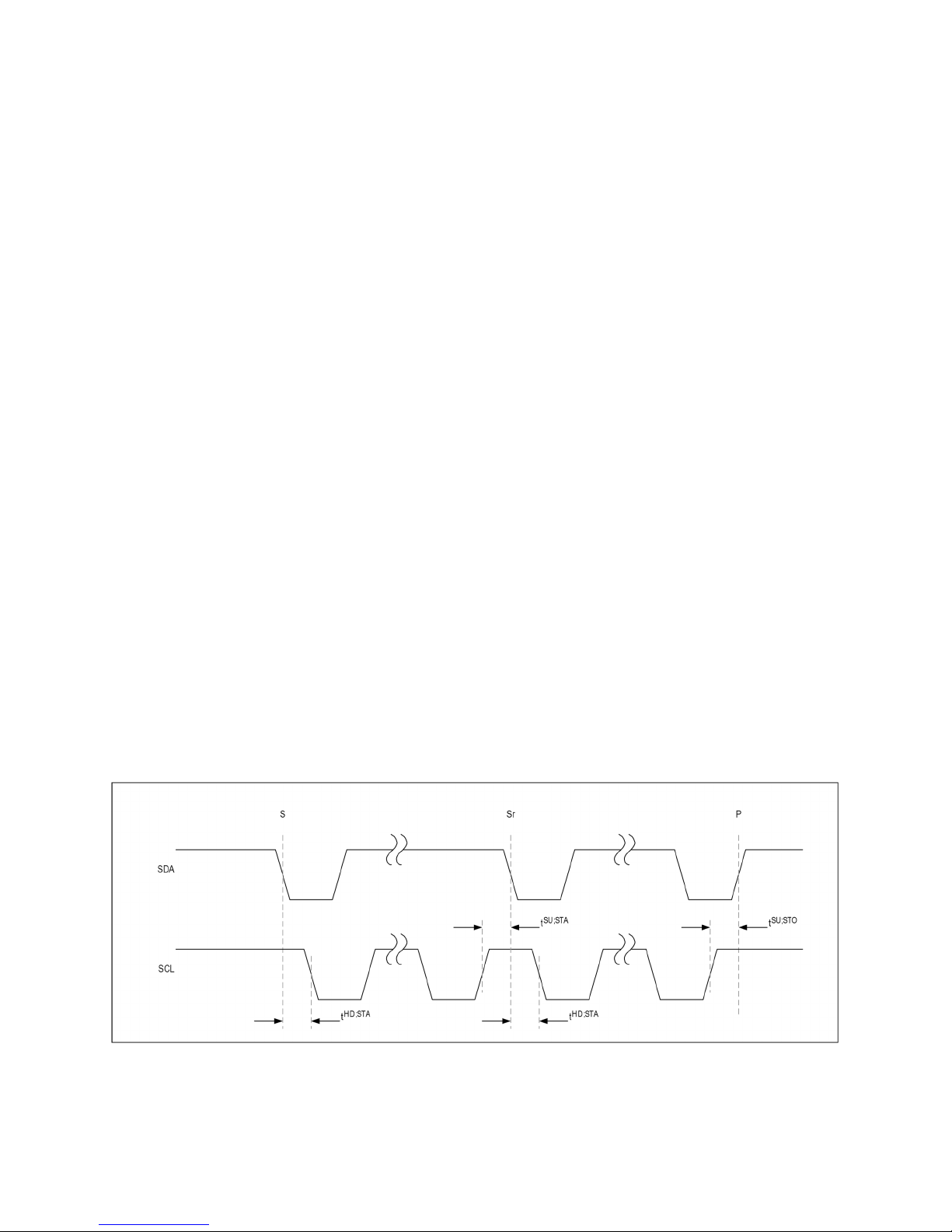
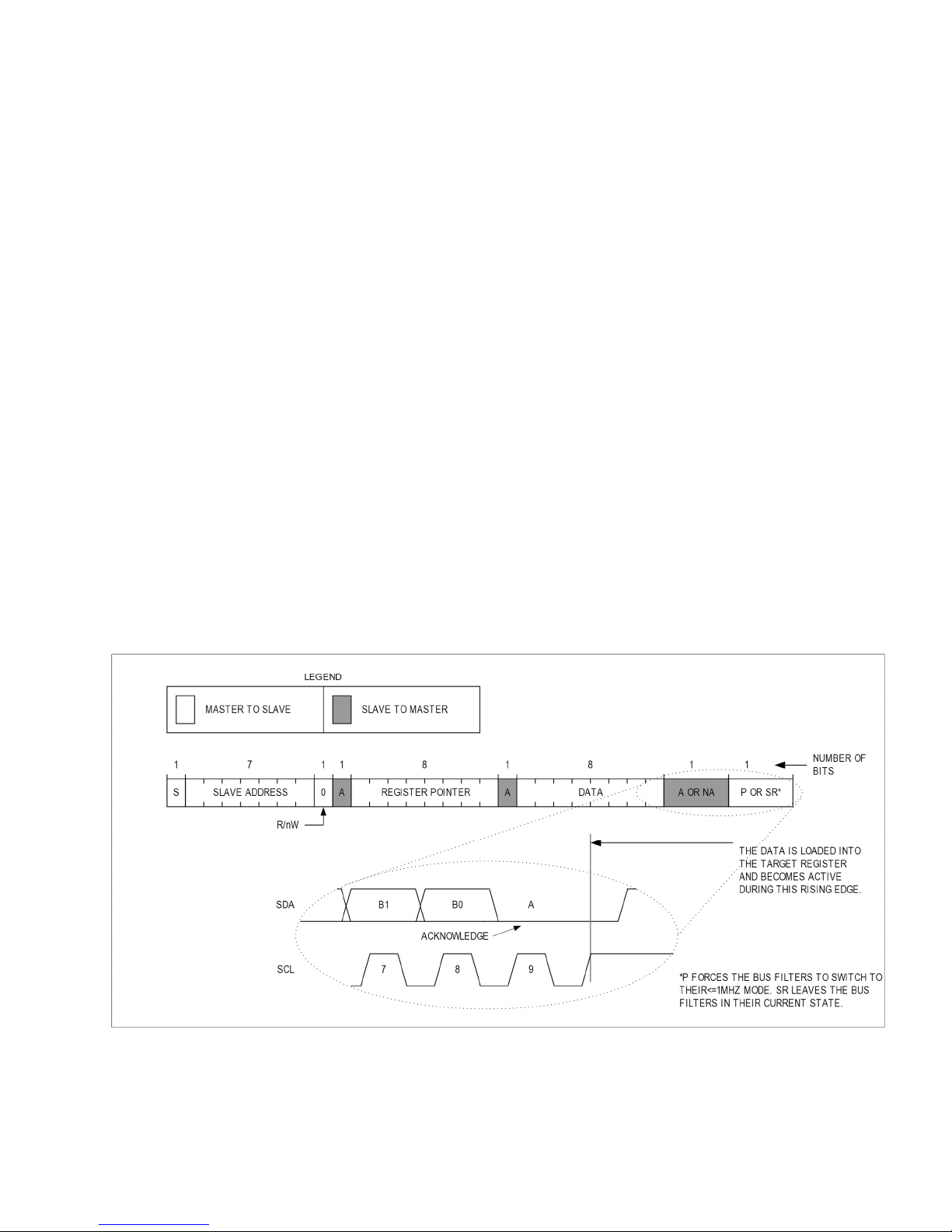
Data Transfer
One data bit is transferred during each SCL clock cycle. The data on SDA must remain stable during the
high period of the SCL clock pulse. Changes in SDA while SCL is high are control signals. See the I
2
C
START and STOP Conditions section. Each transmit sequence is framed by a START (S) condition and a
STOP (P) condition. Each data packet is nine bits long: eight bits of data followed by the acknowledge
bit. Data is transferred with the MSB first.
START and STOP Conditions
When the serial interface is inactive, SDA and SCL idle high. A master device initiates communication
by issuing a START condition. A START condition is a high-to low transition on SDA with SCL high. A
STOP condition is a low-to-high transition on SDA, while SCL is high.
A START condition from the master signals the beginning of a transmission to the MAX77734. The
master terminates transmission by issuing a not-acknowledge followed by a STOP condition (see the
Acknowledge Bit section for information on not-acknowledge). The STOP condition frees the bus. To
issue a series of commands to the slave, the master can issue repeated START (Sr) commands instead
of a STOP command to maintain control of the bus. In general, a repeated START command is
functionally equivalent to a regular START command.
When a STOP condition or incorrect address is detected, the MAX77734 internally disconnects SCL
from the serial interface until the next START condition, minimizing digital noise and feedthrough.
Figure 3. I
2
C START and STOP conditions.