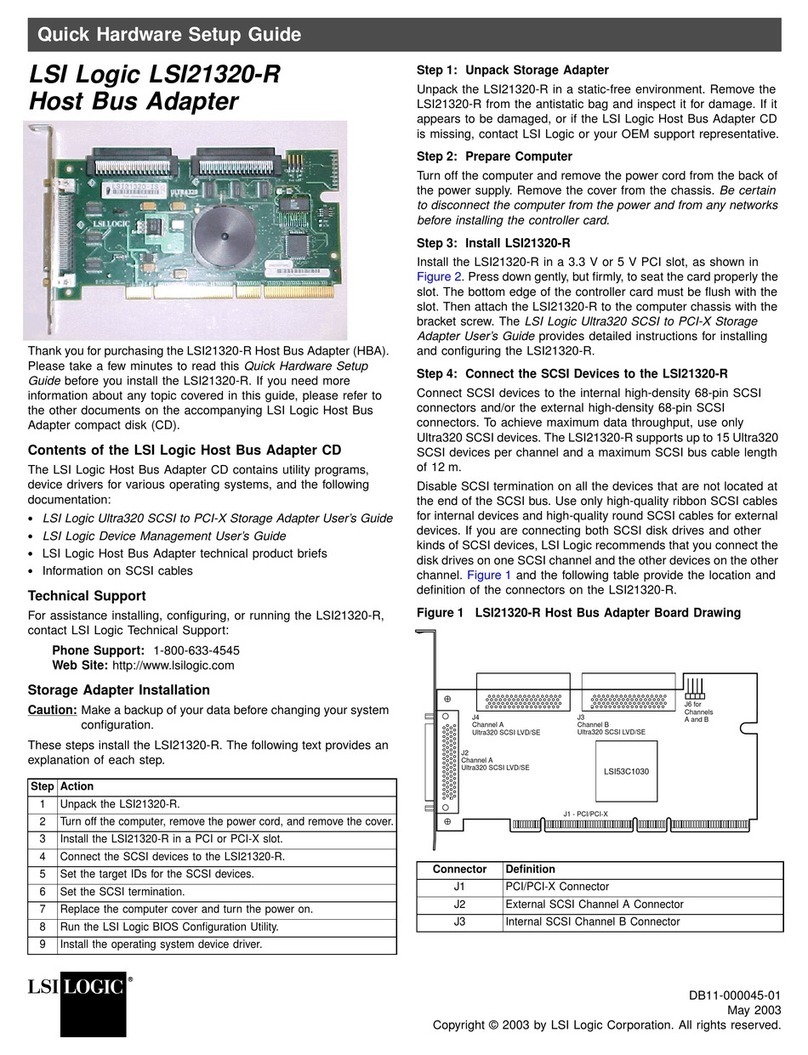
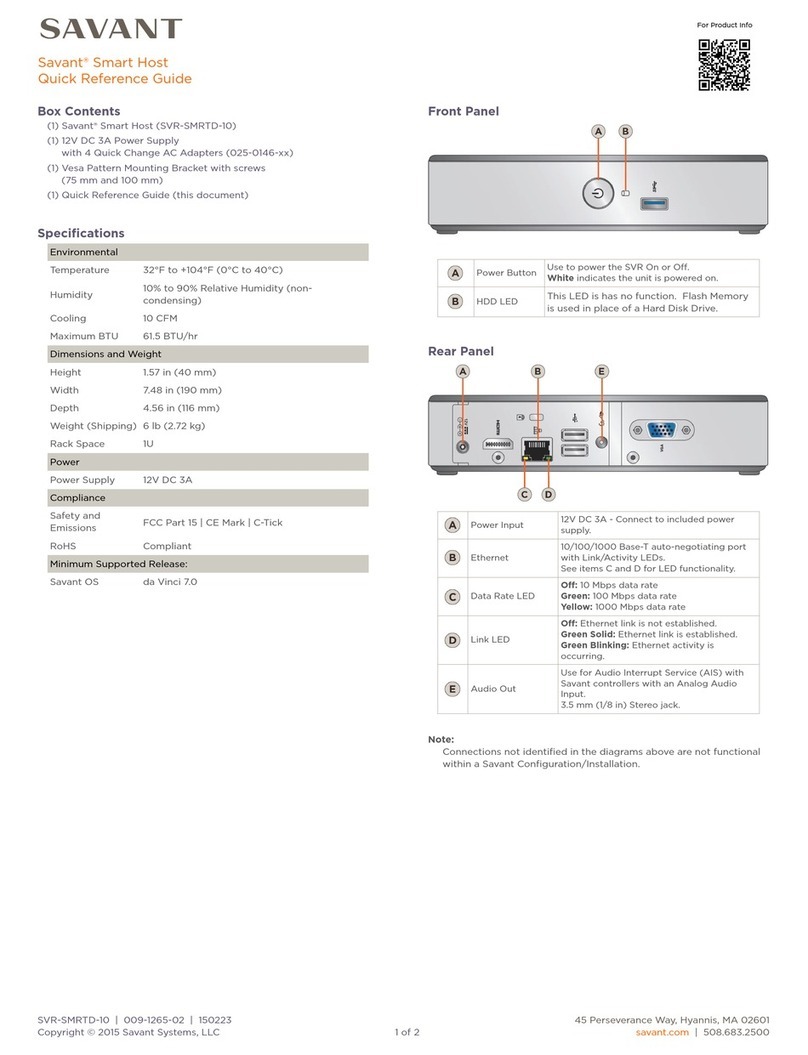
MasterOperations ................................................. 26
ToMasterTransmitData ....................................... 26
To Master Receive Data ........................................ 27
SlaveOperations .................................................. 28
ToSlaveTransmitamessage.................................... 28
To Slave Receive a message .................................... 28
Uninstalling iPort Utility Pack ........................................... 28
Part 3
Programmer’s Reference ASCII Command Interface Definitions
Quick Start ........................................................... 30
ASCII Command Interface Definitions .................................... 31
Synchronous Interface Events ........................................ 32
iPort/AFMReset ............................................. 32
StatusDisplay ............................................... 33
RS-232 Baud Rate ............................................ 33
Close I2CConnection ......................................... 34
Set Destination I2CSlaveAddress................................ 34
Echo/PromptControl ......................................... 34
FlowControl ................................................ 34
I2CGeneralCallControl ....................................... 35
HexOnlyDisplayControl ...................................... 35
Set iPort/AFM’s Own I2CSlaveAddress .......................... 36
I2CBusClockRateControl..................................... 36
CommandMenuDisplay ....................................... 36
iNterruptSignalControl/Status .................................. 37
Open I2CConnection .......................................... 37
MasterReadMessage.......................................... 38
SlaveTransmitMessage........................................ 39
MasterTransmitMessage ...................................... 40
Set I2CBustimeoUtinmsec ................................... 41
DisplayFirmwareVersion...................................... 41
eXtendedCommands .......................................... 41
Display Tx bYte Count ........................................ 44
Asynchronous Interface Events ....................................... 45
SlaveTransmitRequest ........................................ 45
Slave Receive Complete ........................................ 45
General Call Receive Complete .................................. 45
I2CBusTime-outDetected ..................................... 46