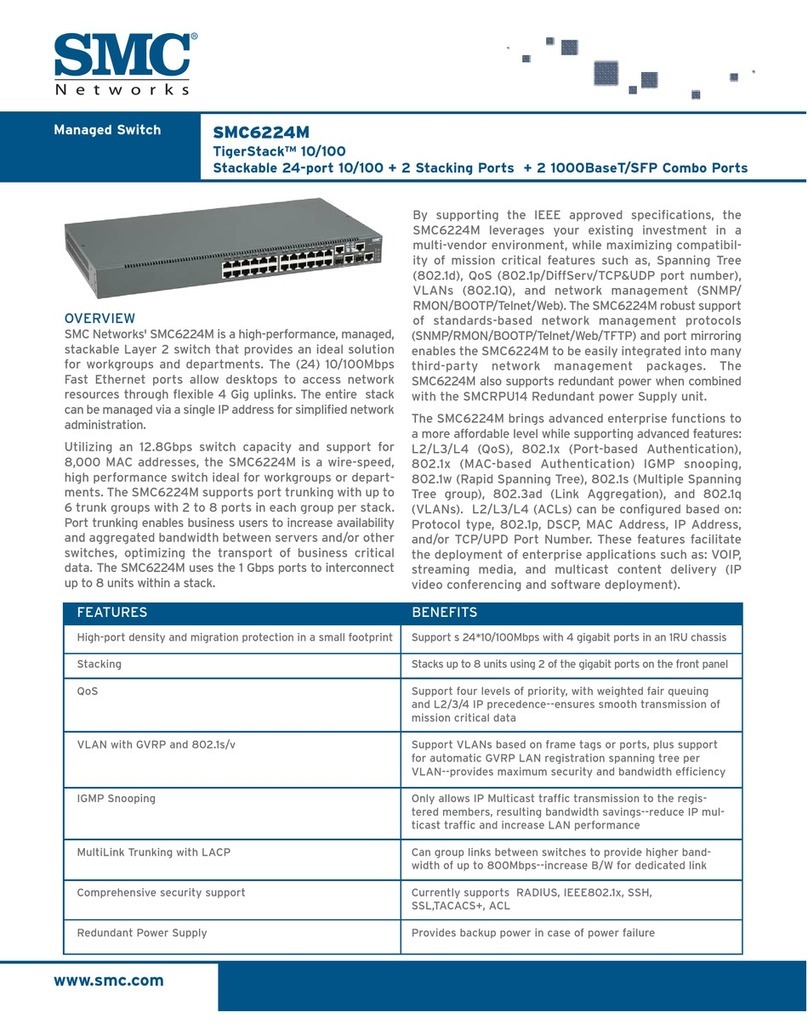
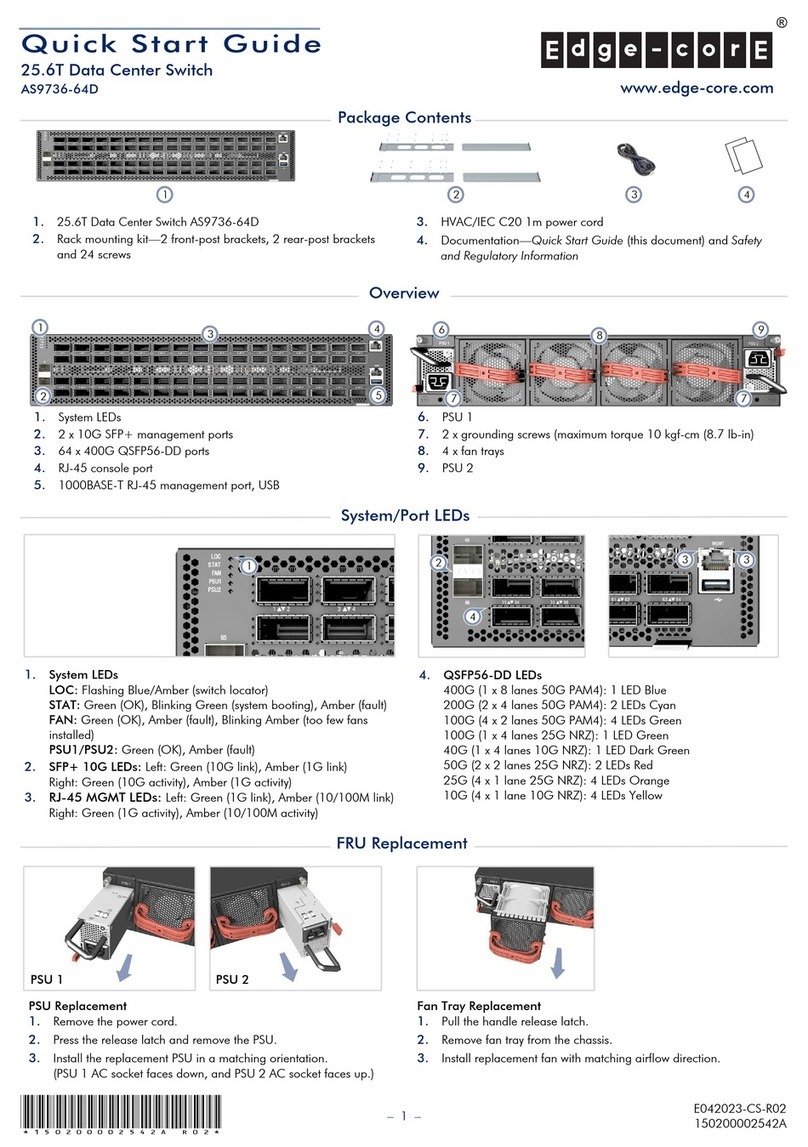
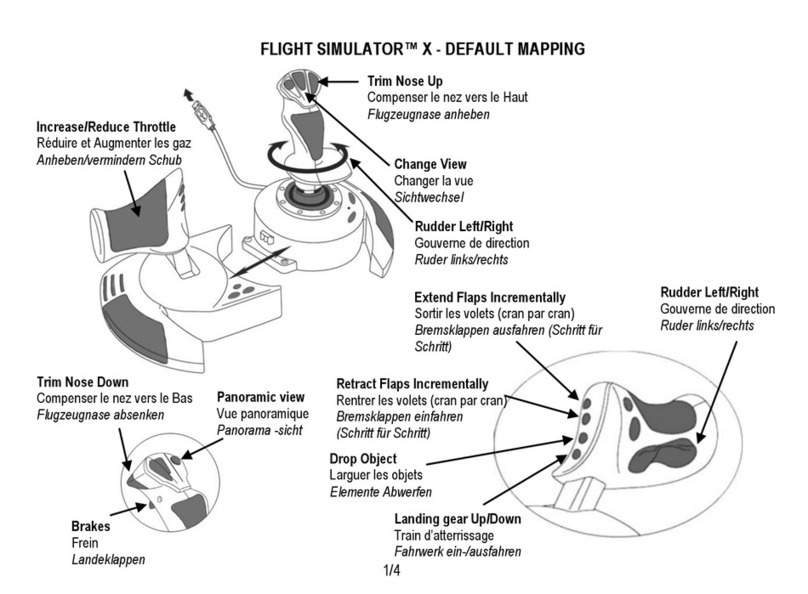
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
ii
Record of Revisions and Updates
Copyright © 2005 McDATA Corporation. All rights reserved.
Printed January 2005
Ninth Edition
McDATA, the McDATA logo, McDATA Eclipse, Fabricenter, HotCAT, Intrepid, Multi-Capable Storage Net-
work Solutions, Networking the World's Business Data, nScale, nView, OPENready, SANavigator, SANpilot,
SANtegrity, SANvergence, SecureConnect and Sphereon are trademarks or registered trademarks of McDA-
TA Corporation. OEM and Reseller logos are the property of such parties and are reprinted with limited use
permission. All other trademarks are the property of their respective companies. All specifications subject to
change.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in a
database or retrieval system, without the prior written consent of McDATA Corporation.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. McDATA Corporation
assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear.
All computer software programs, including but not limited to microcode, described in this document are
furnished under a license, and may be used or copied only in accordance with the terms of such license.
McDATA either owns or has the right to license the computer software programs described in this document.
McDATA Corporation retains all rights, title and interest in the computer software programs.
McDATA Corporation makes no warranties, expressed or implied, by operation of law or otherwise, relating
to this document, the products or the computer software programs described herein. McDATA
CORPORATION DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. In no event shall McDATA Corporation be liable for (a) incidental, indirect,
special, or consequential damages or (b) any damages whatsoever resulting from the loss of use, data or
profits, arising out of this document, even if advised of the possibility of such damages.
Revision Date Description
620-000131-000 6/2001 Initial release of Manual
620-000131-100 11/2001 Update to manual
620-000131-200 5/2002 Update to manual
620-000131-300 9/2002 Update to support EFCM 6.1and 6.2
620-000131-400 10/2002 Update to support EFCM 6.1, 6.2, & 6.3
620-000131-500 2/2003 Update to support E/OS 5.1 and EFCM 7.0
620-000131-600 8/2003 Update to support E/OS 5.2 and EFCM 7.2
620-000131-610 11/2003 Update to support E/OS 6.0
620-000131-620 1/2005 Update to support E/OS 7.0