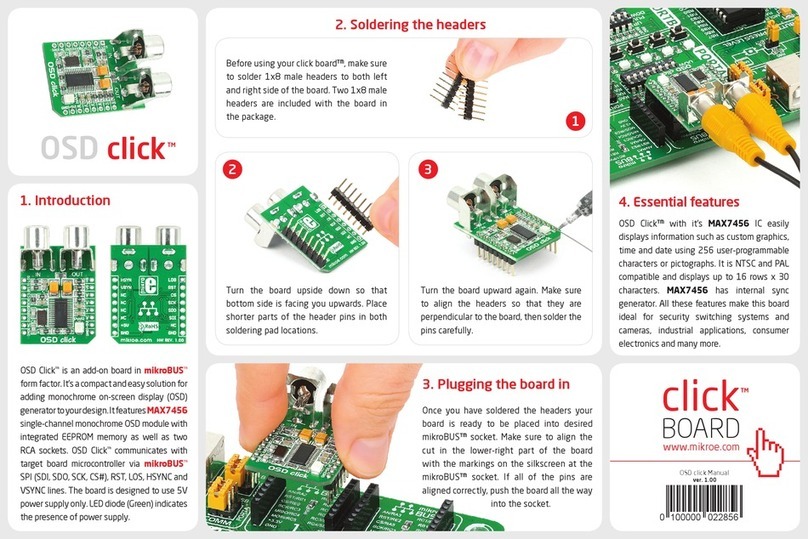
MicroElektronika mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin User manual

mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin™User manual
All MikroElektronika´s development systems represent irreplaceable
tools for programming and developing microcontroller-based devices.
Carefully chosen components and the use of machines of the last
generation for mounting and testing thereof are the best guarantee of
high reliability of our devices. Due to simple design, a large number of
add-on modules and ready to use examples, all our users, regardless
of their experience, have the possibility to develop their project in a fast
and efcient way.
Development system
If you want to learn more about our products, please visit our website at www.mikroe.com
If you are experiencing some problems with any of our products or just need additional information, please place your ticket at
www.mikroe.com/en/support
If you have any questions, comments or business proposals, do not hesitate to contact us at of[email protected]

TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS
I want to express my thanks to you for being interested in our products and for having condence in
Mikroelektronika.
The primary aim of our company is to design and produce high quality electronic products and to constantly
improve the performance thereof in order to better suit your needs.
The NXP name, logo and products names are trademarks of NXP Inc. in the U.S.A and other countries.
DISCLAIMER
All the products owned by MikroElektronika are protected by copyright law and international copyright treaty.
Therefore, this manual is to be treated as any other copyright material. No part of this manual, including
product and software described herein, may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, translated or
transmitted in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of MikroElektronika. The
manual PDF edition can be printed for private or local use, but not for distribution. Any modication of this
manual is prohibited.
MikroElektronika provides this manual ‘as is’ without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied,
including, but not limited to, the implied warranties or conditions of merchantability or tness for a particular
purpose.
MikroElektronika shall assume no responsibility or liability for any errors, omissions and inaccuracies that may
appear in this manual. In no event shall MikroElektronika, its directors, ofcers, employees or distributors be
liable for any indirect, specic, incidental or consequential damages (including damages for loss of business
prots and business information, business interruption or any other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use
of this manual or product, even if MikroElektronika has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
MikroElektronika reserves the right to change information contained in this manual at any time without prior
notice, if necessary.
HIGH RISK ACTIVITIES
The products of MikroElektronika are not fault – tolerant nor designed, manufactured or intended for use or
resale as on – line control equipment in hazardous environments requiring fail – safe performance, such as
in the operation of nuclear facilities, aircraft navigation or communication systems, air trafc control, direct
life support machines or weapons systems in which the failure of Software could lead directly to death,
personal injury or severe physical or environmental damage (‘High Risk Activities’). MikroElektronika and its
suppliers specically disclaim any expressed or implied warranty of tness for High Risk Activities.
TRADEMARKS
The Mikroelektronika name and logo, the Mikroelektronika logo, mikroC, mikroC PRO, mikroBasic, mikro-
Basic PRO, mikroPascal, mikroPascal PRO, AVRash, PICash, dsPICprog, 18FJprog, PSOCprog, AVR-
prog, 8051prog, ARMash, EasyPIC5, EasyPIC6, BigPIC5, BigPIC6, dsPIC PRO4, Easy8051B, EasyARM,
EasyAVR5, EasyAVR6, BigAVR2, EasydsPIC4A, EasyPSoC4, EasyVR Stamp LV18FJ, LV24-33A, LV32MX,
PIC32MX4 MultiMedia Board, PICPLC16, PICPLC8 PICPLC4, SmartGSM/GPRS, UNI-DS are trademarks
of Mikroelektronika. All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies.
All other product and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks
or copyrights of their respective companies, and are only used for identication or explanation and to the
owners’ benet, with no intent to infringe.
©MikroelektronikaTM, 2011 All Rights Reserved.
Nebojsa Matic
General Manager

3
mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. General information
......................................................................................................................
4
2. LPC2214 microcontroller
..............................................................................................................
5
3. Programming the microcontroller
.................................................................................................
8
4. Voltage regulator
..........................................................................................................................
13
5. MicroSD connector
.......................................................................................................................
14
6. Flash module
................................................................................................................................
15

4mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
1. General information
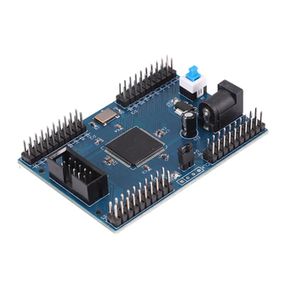
MikroBoard for ARM 144-pin is primarily intended to be connected to the EasyARM v6 development system but can
also be used as a stand-alone device. The board features the LPC2214 microcontroller, ash module, USB connector,
microSD connector, JTAG connector, USB UART, voltage regulator and connectors that enable connection with the
development system.
Figure 1-1: mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin

5
mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
LPC2214 is connected to on board modules via pins which are also connected to CN1 and CN2 connectors. These two
connectors enable the board to be connected to the EasyARM v6 development system or some other device.
2. LPC2214 microcontroller
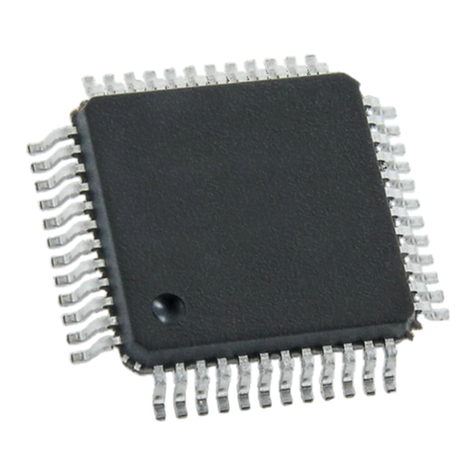
The LPC2214 microcontroller in 144-pin LQFP package is soldered on the mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin. Some of its
key features are:
- 16/32-bit ARM7TDMI-S microcontroller in a LQFP144 package
- 16 kB on-chip static RAM and 256 kB on-chip ash program memory. 128-bit wide interface/
accelerator enables high speed 60 MHz operation.
- In-System Programming (ISP) and In-Application Programming (IAP) via on-chip bootloader software.
Figure 2-1: LPC2214 microcontroller

6mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
R7
10K
R8
10K
X1
14.74568MHz
C1
22pF
C2
22pF
R13
1K
D1
N41481
R14
001
RESET
VCC-3.3
22C
100nF
T1
MCU-RST#
VCC-3.3
C3
100nF
VCC-3.3
C4
100nF
VCC-3.3
C5
100nF
VCC-3.3
C6
100nF
VCC-3.3
C7
100nF
VCC-3.3
C8
100nF
VCC-3.3
C9
100nF
VCC-3.3
C10
100nF
VCC-3.3
C11
100nF
VCC-3.3
C12
100nF
VCC-3.3
C13
100nF
VCC-1.8
C14
100nF
VCC-1.8
C15
100nF
VCC-1.8
C16
100nF
VCC-3.3
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
LPC2214
P1.27
V18
GND
V3
P3.23
P3.22
P0.0
P1.31
P3.21
P3.20
P3.19
P3.18
P3.17
P0.1
P0.2
V3
P1.26
P3.16
GND
P3.15
P3.14
V3
P3.13
GND
P0.3
P3.12
P0.6
P0.4
P3.11
P0.7
P1.25
P3.10
P1.24
P0.5
P3.9
P3.8
P3.7
V18A
XTAL1
XTAL2
P1.28
GND
GNDA-PPL
P2.21
P2.20
RESET
P2.19
P2.18
P2.17
P2.16
P2.15
P2.14
GND
P2.13
P1.29
P2.12
P2.11
V3
P2.5
P0.20
P2.9
P1.30
P0.19
P2.8
V3
P0.18
P2.7
GND
P2.10
P2.6
V18
P2.4
P2.22
P2.3
GND
P2.2
P2.1
V3
GND
P1.20
P0.17
P0.16
P0.15
P2.0
P3.30
P3.31
P1.21
V3
GND
P0.14
P1.0
P1.1
P3.0
P3.1
P0.11
P0.10
P3.2
P1.23
V3
P1.22
P3.3
P0.9
P0.13
P3.4
P0.8
P0.12
GND
P3.5
P3.6
V3
GND
P0.21
P0.22
P0.23
P1.19
P0.24
GND
P2.23
P2.24
P2.25
P2.26
V3A
P1.18
P2.27
P2.28
P2.29
P2.30
P2.31
P0.25
GND
V3
NC
P3.29
P0.29
P0.27
P3.28
P0.30
P1.17
P3.27
P1.16
P0.28
P3.26
P3.25
P3.24
Figure 2-2: LPC2214 microcontroller with oscillators connection schematic
The LPC2214 microcontroller is connected to the X1 oscillator. The X1 oscillator generates a clock used for the operation
of the microcontroller. The microcontroller can be cleared by feeding the reset pin with a logic 0, i.e. by pressing the
RESET button.

7
mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
RX232B SS2#
TX232B SCK2
CS1# MISO2
CS2# MOSI2
RX232A SS1#
TX232A SCK1
SCL MISO1
SDA MOSI1
P0.4
P0.12
P0.20 P1.20
P0.28 P1.28
P2.4 P3.4
P2.12 P3.12
P2.20 P3.20
P2.28 P3.28
P0.5
P0.7
P0.6
P0.14
P0.22 P1.22
P0.30 P1.30
P2.6 P3.6
P2.14 P3.14
P2.22 P3.22
P2.30
P0.1
P0.0
P0.2
P0.3
P3.30
P0.6
P0.4
P0.0 P1.0
P0.8
P0.16 P1.16
P0.24 P1.24
P2.0 P3.0
P2.8 P3.8
P2.16 P3.16
P2.24 P3.24
MCU-RST#
MCU-RST#
P0.2
P0.10
P0.18 P1.18
P1.26
P2.2 P3.2
P2.10 P3.10
P2.18 P3.18
P2.26 P3.26
P0.5
P0.13
P0.21 P1.21
P0.29 P1.29
P2.5 P3.5
P2.13 P3.13
P2.21 P3.21
P2.29 P3.29
P0.7
P0.15
P0.23 P1.23
P0.31 P1.31
P2.7 P3.7
P2.15 P3.15
P2.23 P3.23
P2.31
P0.9
P0.8
P0.25
P1.25
P3.31
P0.19
P0.18
P0.17
P0.20
P0.1 P1.1
P0.9
P0.17 P1.17
P0.25 P1.25
P2.1 P3.1
P2.9 P3.9
P2.17 P3.17
P2.25 P3.25
TD1
P0.3
P0.11
P0.19 P1.19
P0.27 P1.27
P2.3 P3.3
P2.11 P3.11
P2.19 P3.19
P2.27 P3.27
VCC-3.3 VCC-EXT
VCC-1.8 VCC-1.8
VCC-3.3 VCC
CN1 CN2
VCC-3.3
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
LPC2214
P1.27
V18
GND
V3
P3.23
P3.22
P0.0
P1.31
P3.21
P3.20
P3.19
P3.18
P3.17
P0.1
P0.2
V3
P1.26
P3.16
GND
P3.15
P3.14
V3
P3.13
GND
P0.3
P3.12
P0.6
P0.4
P3.11
P0.7
P1.25
P3.10
P1.24
P0.5
P3.9
P3.8
P3.7
V18A
XTAL1
XTAL2
P1.28
GND
GNDA-PPL
P2.21
P2.20
RESET
P2.19
P2.18
P2.17
P2.16
P2.15
P2.14
GND
P2.13
P1.29
P2.12
P2.11
V3
P2.5
P0.20
P2.9
P1.30
P0.19
P2.8
V3
P0.18
P2.7
GND
P2.10
P2.6
V18
P2.4
P2.22
P2.3
GND
P2.2
P2.1
V3
GND
P1.20
P0.17
P0.16
P0.15
P2.0
P3.30
P3.31
P1.21
V3
GND
P0.14
P1.0
P1.1
P3.0
P3.1
P0.11
P0.10
P3.2
P1.23
V3
P1.22
P3.3
P0.9
P0.13
P3.4
P0.8
P0.12
GND
P3.5
P3.6
V3
GND
P0.21
P0.22
P0.23
P1.19
P0.24
GND
P2.23
P2.24
P2.25
P2.26
V3A
P1.18
P2.27
P2.28
P2.29
P2.30
P2.31
P0.25
GND
V3
NC
P3.29
P0.29
P0.27
P3.28
P0.30
P1.17
P3.27
P1.16
P0.28
P3.26
P3.25
P3.24
Figure 2-3: LPC2214 microcontroller with connectors connection schematic

8mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
3. Programming the microcontroller
The microcontroller can be programmed with a bootloader or the JTAG programmer. The use of bootloader is enabled due
to the bootloader code that is loaded into the microcontroller. In order to program the microcontroller with the bootloader,
it is necessary to connect the board to a PC via the CN3 connector and USB cable, Figure 3-1. A .hex code is transferred
from the PC to the microcontroller by using some of the bootloader programs, such as Flash Magic.
The CN3 USB connector is connected to the UART module built into the microcontroller via FTDI module (FT232RL).
When the mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin operates as a stand-alone device, it is necessary to place jumper J2 on the
board. If the board is connected to the EasyARM v6 development system, jumper J2 should be removed.
Figure 3-1: USB connector for programming
A
B
FP1
FERRITE
VCC-3.3
VCC-EXT
OSCI
DTR#
OSCO
TXD
TEST
VCC
RTS#
DSR#
AGND
RESET#
VCCIO
DCD#
NC
GND
RXD
CTS#
CBUS1
USBDM
GND
CBUS2
GND
USBDP
NC
CBUS3
CBUS1
3V3OUT
RI#
CBUS4
FT232RL
U2
VCC-FTDI
C19
100nF
VCC-3.3
C21
100nF
C20
C18
100nF
100nF
VCC-FTDI
E2
10uF
D2
P0.1
RESET
P0.14
P0.0
R17 100
100
100
100
R20
R19
R18
MBRS340T3
CN3
USB-ID ID 4
GND 5
USBDP D+ 3
USBDM D- 2
VCC-USB VBUS 1
USB MINI-B
J2 STANDALONE
VCC
VCC-FTDI
VCC-3.3
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
LPC2214
P1.27
V18
GND
V3
P3.23
P3.22
P0.0
P1.31
P3.21
P3.20
P3.19
P3.18
P3.17
P0.1
P0.2
V3
P1.26
P3.16
GND
P3.15
P3.14
V3
P3.13
GND
P0.3
P3.12
P0.6
P0.4
P3.11
P0.7
P1.25
P3.10
P1.24
P0.5
P3.9
P3.8
P3.7
V18A
XTAL1
XTAL2
P1.28
GND
GNDA-PPL
P2.21
P2.20
RESET
P2.19
P2.18
P2.17
P2.16
P2.15
P2.14
GND
P2.13
P1.29
P2.12
P2.11
V3
P2.5
P0.20
P2.9
P1.30
P0.19
P2.8
V3
P0.18
P2.7
GND
P2.10
P2.6
V18
P2.4
P2.22
P2.3
GND
P2.2
P2.1
V3
GND
P1.20
P0.17
P0.16
P0.15
P2.0
P3.30
P3.31
P1.21
V3
GND
P0.14
P1.0
P1.1
P3.0
P3.1
P0.11
P0.10
P3.2
P1.23
V3
P1.22
P3.3
P0.9
P0.13
P3.4
P0.8
P0.12
GND
P3.5
P3.6
V3
GND
P0.21
P0.22
P0.23
P1.19
P0.24
GND
P2.23
P2.24
P2.25
P2.26
V3A
P1.18
P2.27
P2.28
P2.29
P2.30
P2.31
P0.25
GND
V3
NC
P3.29
P0.29
P0.27
P3.28
P0.30
P1.17
P3.27
P1.16
P0.28
P3.26
P3.25
P3.24
Figure 3-2: USB UART module connection schematic

9
mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
Connect the mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin to available
USB port on your PC.
Download the Flash Magic application from http://www.ashmagictool.com/download.html&d=FlashMagic.exe and
install it on your PC
When the installation is nished double click on the Flash Magic icon
In next few steps is explained how to program microcontroller with bootloader via Flash Magic application.
STEP 1: Connect the system to a PC
STEP 2: Start Flash Magic
STEP 3: Select MCU
Click on the Select Device button
Select MCU from the list
Click OK

10 mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
STEP 4: Settings
From drop-down menu select
the COM port on your PC
Device Manager on your PC contains information on which COM port is used for USB communication with the mikroBoard for ARM
144-pin development system. In this case the COM5 port is used.
Set Baud Rate to 230400
Enter 14.74568 (if you use different
oscillator set the appropriate value in MHz)
Right click on USB port, then on Properties
From pop-up window se-
lect the Port Settings tab
In pop-up window uncheck the Serial
Enumeration option and click OK
Click on the Advanced... button

11
mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
STEP 6: Upload .hex le
STEP 5: Browse for .hex le
Click Start to begin .hex le upload
Click on the Browse button
After progress bar becomes green
the programing is nished
In pop-up window select
the appropriate .hex le
Click on the Open button

12 mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
The microcontroller can also be programmed with the JTAG programmer, Figure 3-3. In addition, this programmer can
also be used to test the operation of the microcontroller.
In order to enable the JTAG programmer to be used, it is necessary to place jumper J1 in the ENABLE position, Figure
3-5. If the JTAG programmer is not used for programming, jumper J1 should be removed from the board, Figure 3-6.
Figure 3-3: JTAG connector
R1
10K
10K
10K
10K
10K
10K
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
P1.26
P1.26
P1.31
P1.31
VTref
nTRST
TDI
TMS
TCK
RTCK
TDO
nSRST
DBGRQ
DBGACQ
P1.27
P1.27
P1.28
P1.28
MCU-RST#
P1.30
P1.30
P1.29
P1.29
CN4
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
J4
VCC-3.3
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
LPC2214
P1.27
V18
GND
V3
P3.23
P3.22
P0.0
P1.31
P3.21
P3.20
P3.19
P3.18
P3.17
P0.1
P0.2
V3
P1.26
P3.16
GND
P3.15
P3.14
V3
P3.13
GND
P0.3
P3.12
P0.6
P0.4
P3.11
P0.7
P1.25
P3.10
P1.24
P0.5
P3.9
P3.8
P3.7
V18A
XTAL1
XTAL2
P1.28
GND
GNDA-PPL
P2.21
P2.20
RESET
P2.19
P2.18
P2.17
P2.16
P2.15
P2.14
GND
P2.13
P1.29
P2.12
P2.11
V3
P2.5
P0.20
P2.9
P1.30
P0.19
P2.8
V3
P0.18
P2.7
GND
P2.10
P2.6
V18
P2.4
P2.22
P2.3
GND
P2.2
P2.1
V3
GND
P1.20
P0.17
P0.16
P0.15
P2.0
P3.30
P3.31
P1.21
V3
GND
P0.14
P1.0
P1.1
P3.0
P3.1
P0.11
P0.10
P3.2
P1.23
V3
P1.22
P3.3
P0.9
P0.13
P3.4
P0.8
P0.12
GND
P3.5
P3.6
V3
GND
P0.21
P0.22
P0.23
P1.19
P0.24
GND
P2.23
P2.24
P2.25
P2.26
V3A
P1.18
P2.27
P2.28
P2.29
P2.30
P2.31
P0.25
GND
V3
NC
P3.29
P0.29
P0.27
P3.28
P0.30
P1.17
P3.27
P1.16
P0.28
P3.26
P3.25
P3.24
Figure 3-4: JTAG module connection schematic
Figure 3-5: JTAG is enabled
Figure 3-6: JTAG is disabled

13
mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
4. Voltage regulator
The microcontroller require dual power supply: 1.8V for CPU and 3.3V for I/O. The board is powered with the 5V power
supply voltage via the CN3 USB connector supplied on the board.
If the board is powered by the development system (EasyARM v6), the function of the voltage regulator remains the
same. In this case, it is necessary to remove jumper J2 (STANDALONE), Figure 4-3.
VCC
VCC
VCC-3.3
VCC-1.8
VIN
VIN
Adjust
REG1
REG2
VOUT
VOUT
MC33269DT-3.3
LM317
1
1
3
3
2
2
E1
E5
E4
E3
10uF
10uF
10uF
10uF
VCC
R16
2K2
R9
220
R10
100
LD1
POWER
C17
100nF
Figure 4-2: Voltage regulator connection schematic
Figure 4-1: Voltage regulator
Figure 4-3: Standalone mode disabled Figure 4-4: Standalone mode enabled

14 mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
5. MicroSD connector
There is a connector CN5 provided on the board that enables the use of microSD card. When inserted, the microSD
card provides additional memory space that the microcontroller can use to store data. Communication between the
microSD card and the microcontroller is performed via the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI).
Figure 5-1: MicroSD connector
FERRITE
FB2
VCC-MMC
VCC-3.3
E6
10uF
R12
100K
VCC-MMC
VCC-MMC
P0.18
P0.17
P0.19
P0.25 CS
Dout
Din
SCK
CN5
VCC-3.3
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
LPC2214
P1.27
V18
GND
V3
P3.23
P3.22
P0.0
P1.31
P3.21
P3.20
P3.19
P3.18
P3.17
P0.1
P0.2
V3
P1.26
P3.16
GND
P3.15
P3.14
V3
P3.13
GND
P0.3
P3.12
P0.6
P0.4
P3.11
P0.7
P1.25
P3.10
P1.24
P0.5
P3.9
P3.8
P3.7
V18A
XTAL1
XTAL2
P1.28
GND
GNDA-PPL
P2.21
P2.20
RESET
P2.19
P2.18
P2.17
P2.16
P2.15
P2.14
GND
P2.13
P1.29
P2.12
P2.11
V3
P2.5
P0.20
P2.9
P1.30
P0.19
P2.8
V3
P0.18
P2.7
GND
P2.10
P2.6
V18
P2.4
P2.22
P2.3
GND
P2.2
P2.1
V3
GND
P1.20
P0.17
P0.16
P0.15
P2.0
P3.30
P3.31
P1.21
V3
GND
P0.14
P1.0
P1.1
P3.0
P3.1
P0.11
P0.10
P3.2
P1.23
V3
P1.22
P3.3
P0.9
P0.13
P3.4
P0.8
P0.12
GND
P3.5
P3.6
V3
GND
P0.21
P0.22
P0.23
P1.19
P0.24
GND
P2.23
P2.24
P2.25
P2.26
V3A
P1.18
P2.27
P2.28
P2.29
P2.30
P2.31
P0.25
GND
V3
NC
P3.29
P0.29
P0.27
P3.28
P0.30
P1.17
P3.27
P1.16
P0.28
P3.26
P3.25
P3.24
R11
10K
P0.24
P0.24
CDG
Figure 5-2: microSD connector connection schematic
A
B
The pins’ designations have the
following meaning:
CS - Chip Select
Din - Master Out/Slave In (MOSI)
SCK
- Clock
Dout - Master In/Slave Out (MISO)

15
mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
6. Flash module
Flash module provides additional 8Mbit of ash memory that the microcontroller can use via the Serial Peripheral
Interface (SPI).
U3
M25P80
CS
SDO
WP
GND
VCC
HOLD
SCK
SDI
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
R15
100K
C23
100nF
P0.23
P0.4
P0.6
P0.5
VCC-3.3
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
LPC2214
P1.27
V18
GND
V3
P3.23
P3.22
P0.0
P1.31
P3.21
P3.20
P3.19
P3.18
P3.17
P0.1
P0.2
V3
P1.26
P3.16
GND
P3.15
P3.14
V3
P3.13
GND
P0.3
P3.12
P0.6
P0.4
P3.11
P0.7
P1.25
P3.10
P1.24
P0.5
P3.9
P3.8
P3.7
V18A
XTAL1
XTAL2
P1.28
GND
GNDA-PPL
P2.21
P2.20
RESET
P2.19
P2.18
P2.17
P2.16
P2.15
P2.14
GND
P2.13
P1.29
P2.12
P2.11
V3
P2.5
P0.20
P2.9
P1.30
P0.19
P2.8
V3
P0.18
P2.7
GND
P2.10
P2.6
V18
P2.4
P2.22
P2.3
GND
P2.2
P2.1
V3
GND
P1.20
P0.17
P0.16
P0.15
P2.0
P3.30
P3.31
P1.21
V3
GND
P0.14
P1.0
P1.1
P3.0
P3.1
P0.11
P0.10
P3.2
P1.23
V3
P1.22
P3.3
P0.9
P0.13
P3.4
P0.8
P0.12
GND
P3.5
P3.6
V3
GND
P0.21
P0.22
P0.23
P1.19
P0.24
GND
P2.23
P2.24
P2.25
P2.26
V3A
P1.18
P2.27
P2.28
P2.29
P2.30
P2.31
P0.25
GND
V3
NC
P3.29
P0.29
P0.27
P3.28
P0.30
P1.17
P3.27
P1.16
P0.28
P3.26
P3.25
P3.24
Figure 6-2: Flash module connection schematic
Figure 6-1: Flash memory

16 mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page
2.54mm
55.12mm
104.08mm
Figure 6-3: Dimensions of the mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin

17
mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page

18 mikroBoard for ARM 144-pin
MikroElektronika
page

TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS
I want to express my thanks to you for being interested in our products and for having condence in
Mikroelektronika.
The primary aim of our company is to design and produce high quality electronic products and to constantly
improve the performance thereof in order to better suit your needs.
The NXP name, logo and products names are trademarks of NXP Inc. in the U.S.A and other countries.
DISCLAIMER
All the products owned by MikroElektronika are protected by copyright law and international copyright treaty.
Therefore, this manual is to be treated as any other copyright material. No part of this manual, including
product and software described herein, may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, translated or
transmitted in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of MikroElektronika. The
manual PDF edition can be printed for private or local use, but not for distribution. Any modication of this
manual is prohibited.
MikroElektronika provides this manual ‘as is’ without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied,
including, but not limited to, the implied warranties or conditions of merchantability or tness for a particular
purpose.
MikroElektronika shall assume no responsibility or liability for any errors, omissions and inaccuracies that may
appear in this manual. In no event shall MikroElektronika, its directors, ofcers, employees or distributors be
liable for any indirect, specic, incidental or consequential damages (including damages for loss of business
prots and business information, business interruption or any other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use
of this manual or product, even if MikroElektronika has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
MikroElektronika reserves the right to change information contained in this manual at any time without prior
notice, if necessary.
HIGH RISK ACTIVITIES
The products of MikroElektronika are not fault – tolerant nor designed, manufactured or intended for use or
resale as on – line control equipment in hazardous environments requiring fail – safe performance, such as
in the operation of nuclear facilities, aircraft navigation or communication systems, air trafc control, direct
life support machines or weapons systems in which the failure of Software could lead directly to death,
personal injury or severe physical or environmental damage (‘High Risk Activities’). MikroElektronika and its
suppliers specically disclaim any expressed or implied warranty of tness for High Risk Activities.
TRADEMARKS
The Mikroelektronika name and logo, the Mikroelektronika logo, mikroC, mikroC PRO, mikroBasic, mikro-
Basic PRO, mikroPascal, mikroPascal PRO, AVRash, PICash, dsPICprog, 18FJprog, PSOCprog, AVR-
prog, 8051prog, ARMash, EasyPIC5, EasyPIC6, BigPIC5, BigPIC6, dsPIC PRO4, Easy8051B, EasyARM,
EasyAVR5, EasyAVR6, BigAVR2, EasydsPIC4A, EasyPSoC4, EasyVR Stamp LV18FJ, LV24-33A, LV32MX,
PIC32MX4 MultiMedia Board, PICPLC16, PICPLC8 PICPLC4, SmartGSM/GPRS, UNI-DS are trademarks
of Mikroelektronika. All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies.
All other product and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks
or copyrights of their respective companies, and are only used for identication or explanation and to the
owners’ benet, with no intent to infringe.
©MikroelektronikaTM, 2011 All Rights Reserved.
Nebojsa Matic
General Manager

mikroBoard for ARM 64-pin™User manual
All MikroElektronika´s development systems represent irreplaceable
tools for programming and developing microcontroller-based devices.
Carefully chosen components and the use of machines of the last
generation for mounting and testing thereof are the best guarantee of
high reliability of our devices. Due to simple design, a large number of
add-on modules and ready to use examples, all our users, regardless
of their experience, have the possibility to develop their project in a fast
and efcient way.
Development system
If you want to learn more about our products, please visit our website at www.mikroe.com
If you are experiencing some problems with any of our products or just need additional information, please place your ticket at
www.mikroe.com/en/support
If you have any questions, comments or business proposals, do not hesitate to contact us at of[email protected]
Table of contents
Other MicroElektronika Microcontroller manuals
Popular Microcontroller manuals by other brands
Microchip Technology
Microchip Technology EVB-LAN9254-DIGIO user guide

Velleman
Velleman KA01 manual

Nvidia
Nvidia Tegra Ventana Hardware Setup and Android Gingerbread Install Guide

Nvidia
Nvidia JETSON TX1 user guide
Nordic Semiconductor
Nordic Semiconductor nRF9160 user guide

Microchip Technology
Microchip Technology STK600 user guide