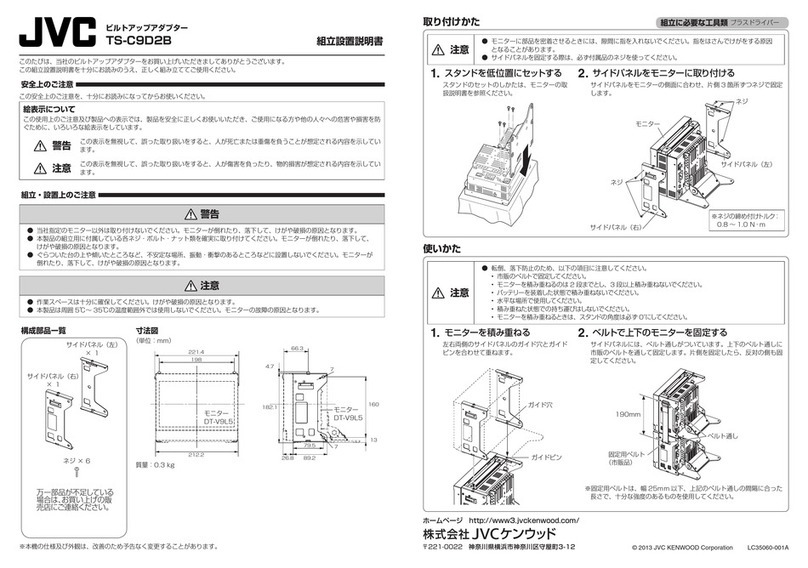
3
1Introduction
Thank you for purchasing Micronet SP907G 54M Wireless LAN USBAdapter.
This quick installation guide is aimed at easy installation procedures of this
device. Before installation, please read the following procedures carefully.
Micronet SP907G Wireless LAN USB Adapter is a next generation wireless
LAN solution. It is compliant with IEEE 802.11g standard operating in the same
2.4GHz radio band, so SP907G can also work smoothly with existing IEEE
802.11b WLAN equipments and provide higher speed connectivity between
mobile stations in a Wireless LocalArea Network.
1.1 Package Content
SP907G 54M Wireless USB Adapter
Driver and Manual CD
Quick Installation Guide
1.2 Features
Compliant with IEEE802.11g and IEEE802.11b wireless standards
Support modulation with Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
technology and Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
technology for IEEE802.11b/g
USB 2.0 interface
Operate in 2.4GHz frequency band
Support auto-data rate selection at 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9 and 6M for
IEEE 802.11g
Interoperate with IEEE802.11b wireless networks at 11M
Support 64(40)/128 bit WEP for network security
Provide Window-based configuration utility
Support Windows 98SE/ME/2000/XP