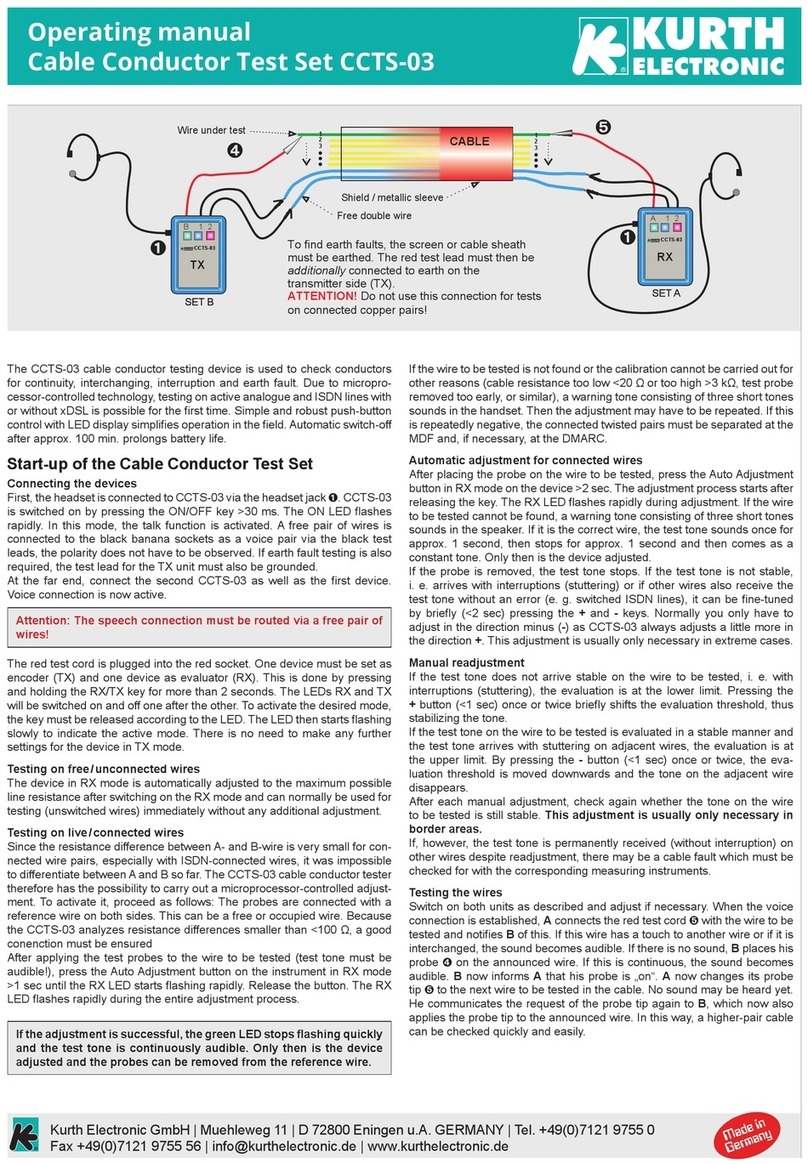
3.
Touch
the
test
pmbe
tips
to
the
circuit 'Jnder test;
be
sure
to
observe correct polaritv.
4.
Rcad
the
voltage
on
the
black DC scales.
S. For voltages between
300
and
600.
set
the
range switch
ta
300&UP and plug the ted test lead into
the
DC600V
jack. For voltages between
600
and
1200.
leave
the
range
at
300&UP and
plug
the red
test
lead
into
the
DC1200V jatk.
USE
EXTREMECAREWHENUSING THESE RANGES.
AC
VOLTAGE
MEASUREMENTS
WARNING ) USE EXTREME CARE WHEN
MAK-
ING MEASUREMENTS FOR HIGH
VOLTAGE;
DO NOT TOUCH TERMINALS
OR
PROBE
ENDS.
1. Plug
the
test
leads
into
the
cor'rect jacks.
2.
Set
the range switch
to
one
of
the
ACV positions.
(lt
is best
to
start
at
the
top
and
work
dawn.)
If you're uncertain
about
voltage leve!, start with 1200V
range as noted in
step
5.
3. T
ouch
the
test probe tips
to
the
circuit
under
test.
4.
Read
the
voltage
on
the
red AC scales.
5.
For
voltages between
600
and
1200, set
the
rangeswitch
to
600&UP and plug
th
e red test lead ln
to
the
AC1200V
jack.
-6-
, RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS
Before taking
any
resistance measurements, disconnect
the
power
to
the
unit
under
test
and discharge
the
capacitors.
1t
is best
to
remove batteries and unplug lîne cards.
WARNING t DO NOT APPLY VOLTAGE
TO
MEASURING TERMI
NAL
WH
ILE
RANGE SWITCH
IS
IN
OHM POSITION.
1. Plug the test
leads
into
the 8 COMand
(!)V.fl-Ajatks.
2.
Set
the
range switch
to
onè
·
of
the OHMS positions;
touch
the
test
probe
tips
to
.g
ether
and adjust
the
OHM
ADJ
UST
control
to
brîng
the
pointer
to
the
"0"
on
the
top
(green) OHMS scale.
3.
Now,
touch
the
probe tips across
the
circuit
or
part
under
test.
4.
Read
the
resistance
on
the green OHMS scale;
use
the
proper multiplier
to
obtain
the
co~rect
value (R times
1.
1
O.
100
,
or
1000, depending
on
the
position
of
the
range switch).
Notes: When you
are
unable
to
·adîust
the
pointer
to
"0"
on
the
OHMS scale, the
battery
must
be
replaced, When
measuring resistance,
it
is best
to
disconnect
one
side
of
the
part
und
er test.
(The-
remainder
of
the
circuit will
not
interferewith
the
r'eadings.)
Note
for Testing Semiconductor
Junc
tions: When
attempt-
ing
to
ident
ify cathode and anode ends
or
the
type
of
tran-
sistor (PNP
or
NPN),
the
actual
po
l
arity
of
the tester's
voltage is opposite
of
the
lead colors.
The
red
lead is
the
negative source.
The
black lead
Js
positive.
- 7-