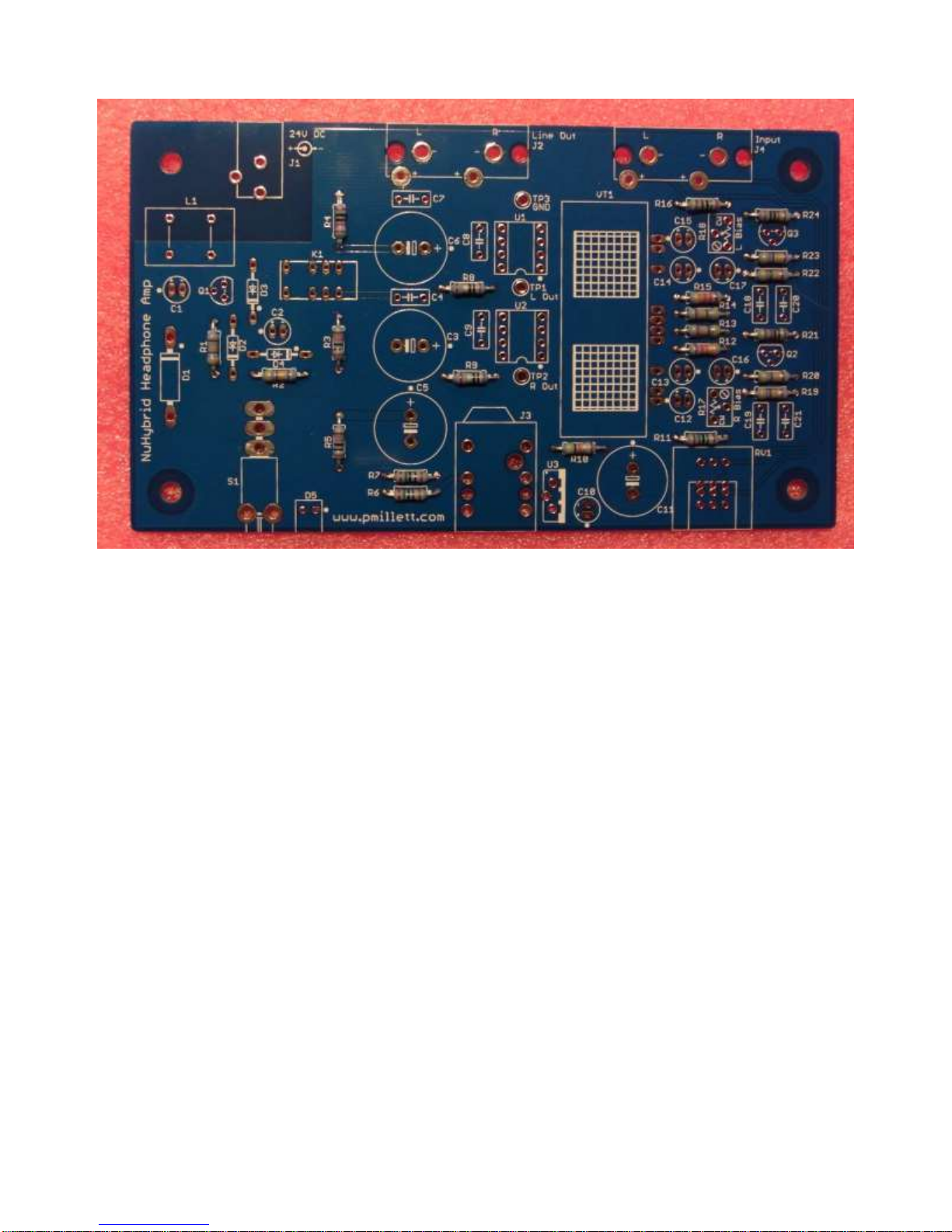
"NuHybrid" Solid-State Headphone Amplifier
Assembly instructions
What you need:
The bare PCB plus Korg Nutube 6P1 (from pmillett.com via eBay)
The parts (from Mouser)
A soldering iron and solder (Tin/Lead 63/37 is the easiest to work with - lead-free
solder is more difficult)
Wire cutters ("diagonal cutters")
DMM (Digital Multimeter)
The following are optional, but recommended:
Needle-nose pliers
To order the parts from Mouser, go to
http://www.mouser.com/ProjectManager/ProjectDetail.aspx?AccessID=b68a30231c, or go to the
"Tools" page at http://www.mouser.com/Tools/Tools.aspx and enter this access code in "Cart
Sharing" towards the bottom of the page: b68a30231c
The Mouser BOM includes all of the parts needed to build the NuHybrid except for the PCB
and the Korg Nutube, which are available from http://stores.ebay.com/pmillett. You can also
refer to the bill of materials at the end of this document for additional info.
Occasionally one of the parts on the BOM may be out of stock. The BOM has some
suggestions for alternate parts that can be used instead, as well as alternate parts that are
available from Digi-Key. Note that the Mouser BOM may be updated from time to time as
parts become difficult to source.
When assembling, keep the BOM and schematic handy, in case you have any questions
about what parts go where.
It is assumed that the builder has some basic electronics knowledge, like knowing which end
of the soldering iron to hold in the hand, and hopefully some experience building electronics.
However, this is a very easy project and is suitable for a first-time builder.
If you are new to soldering, it's highly recommended that you review one or more of the
excellent on-line soldering tutorials. Just search "soldering tutorial" on the web and/or
YouTube.
There is nothing sacred about the order that is listed for assembly. It can be convenient to
build starting with low-profile components, and work your way up to taller parts, so it's easier
to solder on the board backside. That is the way the instructions read. But you can install
parts in any order you want.