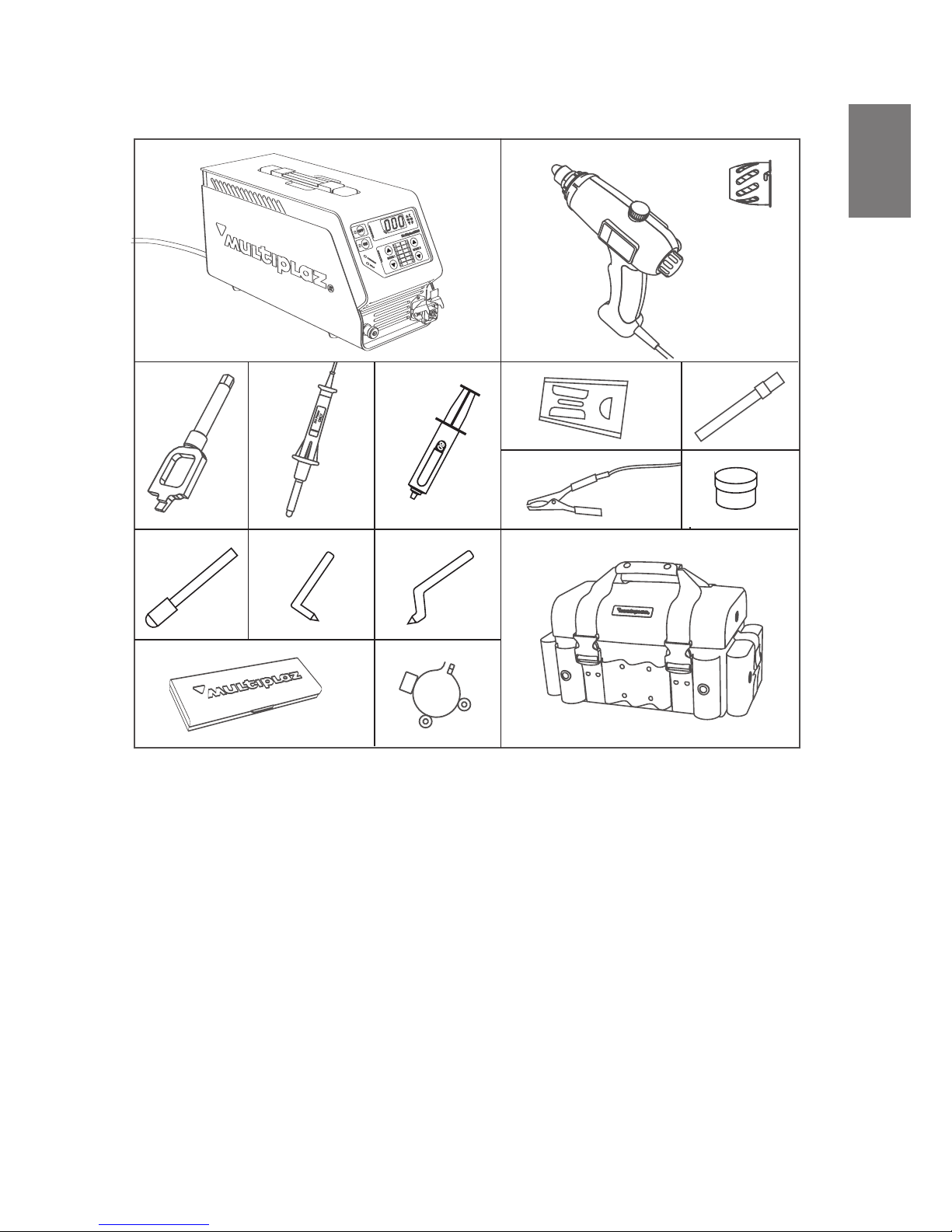
1. ystem Application
The Multiplaz-3500 portable system is designed for manual plasma cutting, welding,
soldering, braze welding, and brazing (joining of dissimilar metals) of ferrous and non-
ferrous metals including alloyed and unalloyed steels, cast iron, copper and copper-
base metals, stainless steel, aluminum and aluminum alloys The system can be used
to perform separation plasma cutting of various nonconductive nonflammable materials
including cement, concrete, brick, haydite aggregate, quartz glass, etc.
(ethanol)
es
of
er
Caution
The circuit breaker in the wall receptacle circuit should be rated for at least 25 for
110V and at least 16A for 220V
1. pecifications
4 S
.
,
The device works from the household electric system, using for welding and brazing a
water solution of ethyl alcohol , and for cutting just water. The device can work
on any water, and quality of welding and cutting do not depend on quality of water.
However, to increase service life and simplification of maintenance service, it is better
to use water with small amount of minerals, the best is distilled water.
!
А
.
5 S
Electrical Supply V (single phase ............ ...........
Supply Frequency Hz .............
Maximum Power Requirement, KWt .... for network voltage 220V
Power Supply Weight kg
Torch Weight dry kg .................... ...
Liquid Consumption, liters hour......... ....... .
Idle Voltage, V (not to exceed)....................
Torch Steam Pressure, bar...... ..
Duty Cycle
Power Supply Dimensions (l x h x w) mm................
Torch Dimensions (l x h x w) mm.............. .
Power Cable Length m.....
Torch Cable Length m... ..
, ) ............................... ........
, . ...................................................................
...... .......
, ..........................................................................
( ), . .............................................. ............
/ .................... ...................... ........
...............................................
........................................................... ....
, .................................
, ..................................... .........
, ........................................................................
, ................................................................. .........
for network voltage 110V
, %............................. ..
(l x h x w) inch................
(l x h x w) inch................ .............
.......
........................................................... ....
, ................................
, ................................
............1 -2
... ............50-60
............3
........................8
.................. .. 9
.................. ,25
...................... 8
..... ......... ,4-1,2
.380 х190 х140
х
........................2
........ ...........
00 53
..
......... .5
......... 2.0
. 0,
0
6
. 0
....................100
.15,0 x 7,5 x 5,5
..205 194 60
....8,1 x 7,4 2,4
..... 2
............
.х х
8
1
418
6.
.
Copper and Copper-Base Metal Welding and Braze welding Technology
Copper fillers, copper-zinc fillers, copper-phosphorous fillers, and specialized fluxes are used in the course of welding and braze
welding
It is best to use simple water rather than a water/alcohol mixture and preliminary heating of workpiece for braze welding of copper.
( , , .)
.
Copper Brass Bronze, etc
Welding and braze welding modes are shown in Table 5
Table 5 Copper and Copper-Base Metal Welding and Braze Welding.
*.Ethanol concentration in water/alcohol mixture is shown in parentheses
** .This process uses simple water
Material Workpiece
Geometry
Primary
Dimension mm, Type of
Process
Filler Diameter
mm
,
Flux MODE I /
MODE II
Control Setting
V
,
None 2 / 4
3 / 4
160 - 180
150 - 170
2
d
d
= 5
= 5
Copper Wire
+
Copper
Copper
Busbar
+
Busbar
None 1 /
2 /
off
off
160 - 190
150 - 170
2 5.
d
d
= 1 2
= 1 2
.
.
Welding
(50%)*
+
Brass
Brass
Plate
Plate
+
1 /
2 /
off
off
160 - 190
150 - 170
2 5.
d
d
= 1 2
= 1 2
.
.
Welding
(50%)
+
Brass
Brass
Plate
Plate
+
None 1 /
2 /
off
off
160 - 190
150 - 170
3
d
d
= 2 5
= 2 5
.
.
Braze welding
(50%)
Copper
Copper
+
Plate
Plate
+
None 2 / 4
3 / 4
160 - 180
150 - 170
2
d
d
= 6
= 6
Butt Welding**
+
Copper
Copper
Plate
Plate
+
Butt Welding**
None 2 / 4
3 / 4
160 - 180
150 - 170
2
d
d
= 4 5
= 4 5
.
.
Butt Welding**
Copper
+
Copper
Plate
Plate
+
Filler or Braze
Brass Wire
Copper Wire
Brass Wire
Copper Wire