8
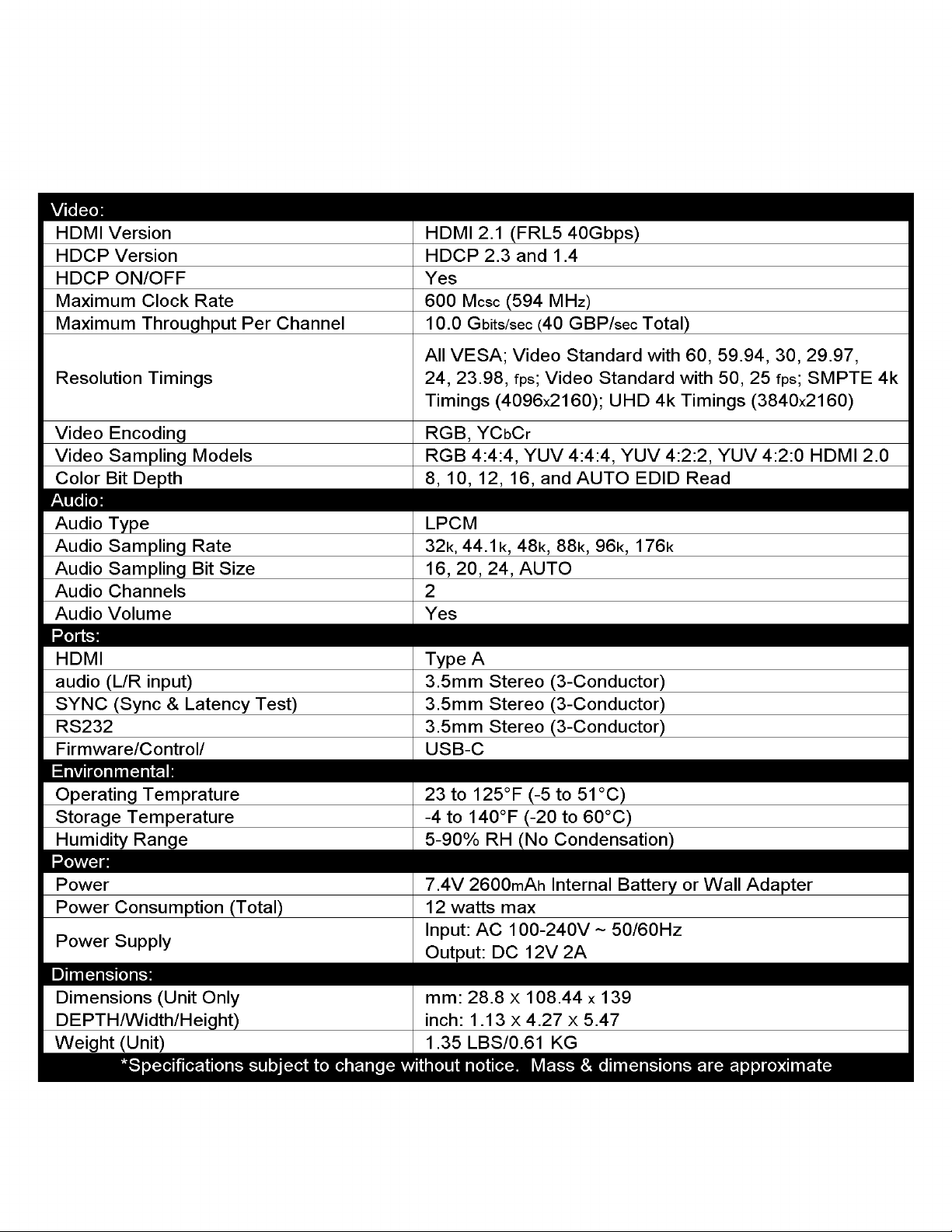
Signal Info:
This menu provides the following information on the source/system under test.
·Timing – Horizontal & Vertical Pixel Count, Progressive or Interlaced Video info, and Refresh Rate
Example - 3840x2160P@60Hz
·Color Space – Provides Color Space and Chroma Subsampling information.
Example - YUV422 means that the color-space is YUV. 422 means that the chroma subsampling is 4:2:2.
·HDCP – Displays HDCP type.
Example - 1.x, or 2.x, or No HDCP.
·Color Depth – The SIX-A-8K will display the bit depth of the signal from 8 to 16 bits. Bit Depth, aka Color Depth, de-
scribes the amount of information stored in each pixel. As you increase bit depth, you also increase the number of colors
that can be represented. In the case of an 8-bit RGB image, each pixel has 8-bits of data per color (RGB). 8 bits of data
x3 channels (RGB) gives us a total of 24 bits. This means each pixel has a total of 256 possibilities. In the case of a 10-
bit RGB image, each pixel has 10 bits of data per color (RGB). 10 bits of data x3 channels (RGB) gives us a total of 30
bits. This means each pixel has a total of 1024 possibilities. Sometimes manufacturer documentation refers to 8-bit as
24 bit and 10-bit as 30 bit, etc. – they are both correct and mean the same thing.
·TMDS Bandwidth – Displays the total bandwidth of the source/system under test.
Example - A 720P signal requires about 2.2 GBPS of bandwidth, 1080P about 4.5 GBPS, and a 4K signal would require
between about 9 to 18 GBPS depending on refresh rate, chroma subsampling, and color depth/bit depth.
·HDR Metadata – This indicates whether HDR is present in the signal or not. If HDR metadata is present in the signal
HDR METADATA will say HDR10/Standard DV/Low-Latency (Dolby Vision Low-Latency). If HDR metadata is not present
in the signal HDR METADATA will say None.
·Audio Sampling Frequency – Displays the audio sampling frequency of the incoming signal(ex. 48K, 88K, 176K, etc.).
Sample rate is the number of samples of audio carried per second, measured in Hz or kHz (one kHz being 1000 Hz). For
example, 44,100 samples per second can be expressed as either 44,100 Hz, or 44.1 kHz.
·Audio Sampling Size – Displays the audio sample size (ex 16-bit, 24-bit, etc.). Higher bit depth means higher-resolu-
tion audio and a better representation of the original analog sound wave.
·Audio Channel Allocations – Displays which audio channels that are active in the HDMI stream.
Example - C, FR, FL (Center, Front Right, Front Left).
·Audio Coding Type – Displays the type of the incoming audio stream.
Example - LPCM (Linear Pulse Code Modulation).
Example - If the audio sampling size says “Refer to Stream Header” you must refer back to the source and conrm ex-
actly which type of audio signal is being output.
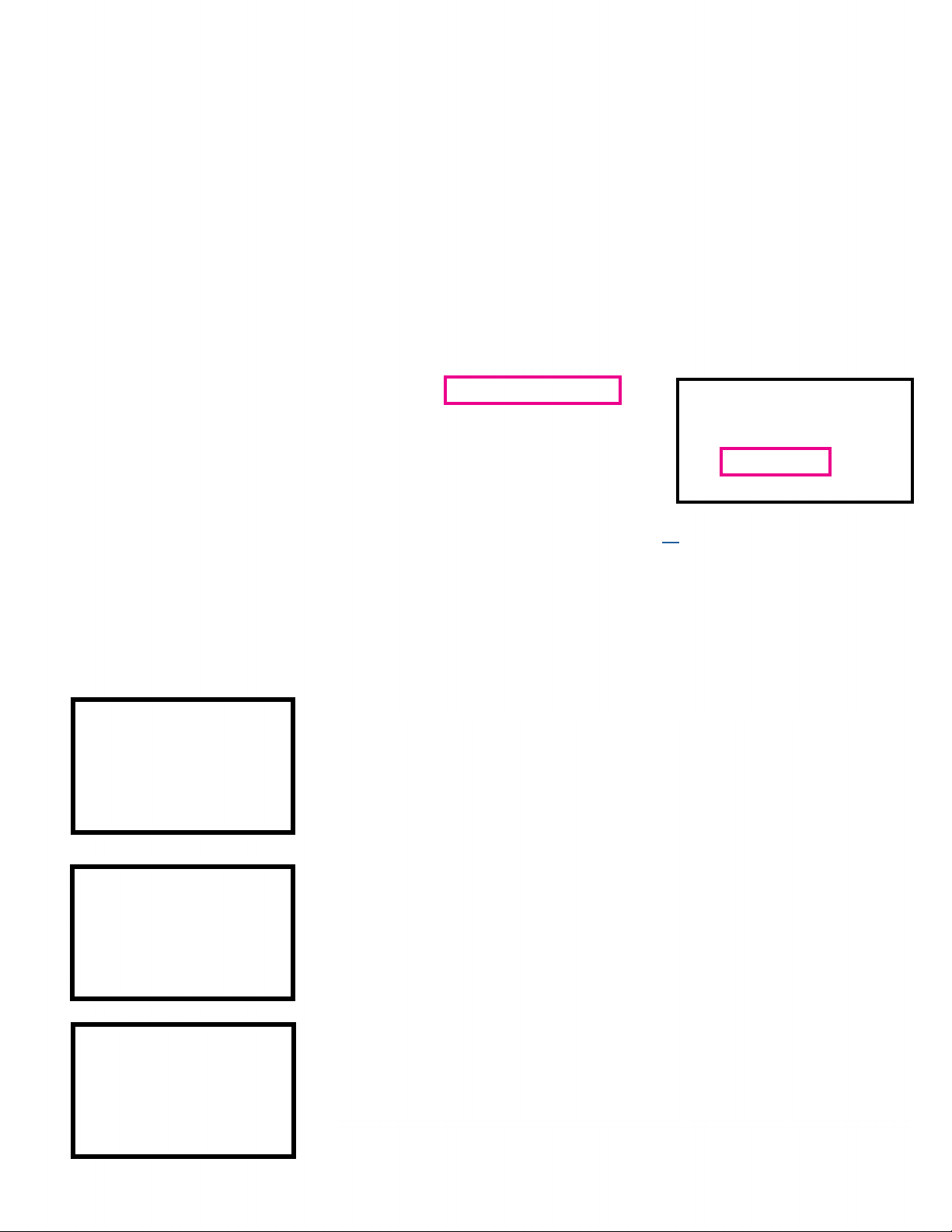
·ACR N/CTS - (Audio Clock Regeneration) The source
device sends N (Dividing ratio of video clock to TMDS
clock) and CTS (Cycle Time Stamp) values to the sink
device for regenerating the audio clock. See expected
values to the right for a 48K, 96K and 192K sampling
frequencies. Credit AES.