Nedap uPASS TARGET User manual

uPASS TARGET
installation guide
2016-03-16 | v1.05 | 5481163

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Content
2/36
CONTENT
1INTRODUCTION _______________________________________________________ 3
1.1 SUPPORTED TAGS _______________________________________________ 3
1.2 TAG SECURITY __________________________________________________ 4
2INSTALLATION ________________________________________________________ 5
2.1 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ___________________________________________ 5
2.2 MOUNTING INSTRUCTIONS _______________________________________ 5
2.2.1 READER DIMENSIONS______________________________________ 5
2.2.2 WALL MOUNTING BRACKET_________________________________ 6
2.2.3 POLE MOUNTING SET ______________________________________ 7
2.2.4 WEATHER PROTECTION HOOD MOUNTING____________________ 8
3CONNECTIONS ________________________________________________________ 9
3.1 POWER SUPPLY ________________________________________________ 11
3.2 COMMUNICATION ______________________________________________ 12
3.2.1 RS-422 / RS-485_________________________________________ 12
3.2.2 WIEGAND / MAGSTRIPE ___________________________________ 13
3.2.3 ETHERNET_______________________________________________ 14
3.2.4 USB ____________________________________________________ 15
3.2.5 NEDAP ANTENNA INTERFACE ______________________________ 16
3.3 DIGITAL I/O____________________________________________________ 17
3.3.1 GENERAL PURPOSE INPUTS / LED AND RELAY CONTROL _______ 17
3.3.2 READER DISABLE_________________________________________ 18
3.3.3 EXTERNAL ANTENNA______________________________________ 18
4TRANSIT COMPATIBLE MODE ___________________________________________ 19
4.1 TOOLING______________________________________________________ 19
4.2 SWITCH SETTINGS ______________________________________________ 19
5UHF FREQUENCIES____________________________________________________ 20
6READER CONFIGURATION______________________________________________ 21
6.1 UHFTOOL SOFTWARE ___________________________________________ 21
6.2 CONNECTING __________________________________________________ 21
6.3 SETTINGS _____________________________________________________ 22
6.3.1 CHANGE BAUD RATE______________________________________ 22
6.3.2 READ DATA______________________________________________ 23
6.3.3 DECODE NEDAP XS_______________________________________ 24
6.3.4 RELAY / TIMING __________________________________________ 25
6.3.5 LED CONTROL ___________________________________________ 26
6.4 EXPERT SETTINGS ______________________________________________ 27
6.4.1 OUTPUT ________________________________________________ 27
6.4.2 OUTPUT MESSAGE FORMAT________________________________ 28
6.4.3 EXTRA OUTPUT __________________________________________ 28
6.4.4 FREQUENCY_____________________________________________ 28
6.4.5 READ RANGE ____________________________________________ 29
6.4.6 ANTENNA _______________________________________________ 29
7FIRMWARE UPDATE ___________________________________________________ 30
ATECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS ___________________________________________ 31
BPART NUMBERS ______________________________________________________ 33
CFCC / IC STATEMENT __________________________________________________ 34
DDISCLAIMER _________________________________________________________ 35
EDOCUMENT REVISION_________________________________________________ 36

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Introduction
3/36
1INTRODUCTION
The uPASS Target reader offers long range (up to 10 meters / 33 feet) identification
using the latest UHF technology. Based on passive (battery free) UHF tags the uPASS
Target offers a cost effective and enduring solution for long range identification.
The uPASS Target reader can be placed near the entrance, door or gate on poles or
on the wall with help of the mounting brackets.
The uPASS Target includes a RS-485/RS-422, Wiegand/Magstripe, Nedap antenna,
TCP/IP and a relay interface. With these interfaces the uPASS Target can be
connected to an Access Control System for authorization. The relay interface can be
used for operating external device (for example doors and gates) based on UHF tag
recognition or external control.
The uPASS Target has 3 digital inputs. With these inputs color of the LED, activation
of the relay and the activation of the UHF reader can be controlled.
The uPASS Target reader features a TRANSIT compatible mode. In this mode the
reader is fully compatible with the Nedap TRANSIT, supporting any firmware version
developed for the TRANSIT reader, for example P61, P81 and Q70. See chapter 4 for
details how to enable the TRANSIT compatible mode.
1.1 SUPPORTED TAGS
Any EPC Class 1 Gen 2 tag is supported by the uPASS Target and will output on the
RS-422, RS-485 or Ethernet interfaces. Also special formatted Nedap UHF tags are
supported for output on special interfaces. The following formats are supported:
Nedap UHF Wiegand tags
These tags will contain all Wiegand information including facility code and parity
bits. All Wiegand formats can be supported. The reader transparently sends this
information via the Wiegand outputs. There is no need to change any DIP-switches
or configuration settings. See chapter 3.2.2 for wiring details.
Nedap UHF Magstripe tags
These tags will contain all Magstripe information. The reader transparently sends this
information onto the Magstripe interface. There is no need to change any DIP-
switches or configuration settings. See chapter 3.2.2 for wiring details.
Nedap UHF XS tags
These tags are especially programmed in the same format as our 2.45GHz TRANSIT
tags (Compact-Tag, Window-Button and Heavy-Duty-Tag). The tags will also have a
customer-code and id-number. The reader will modulate the tag-info onto the
Nedap antenna interface output, which can be connected to Nedap AEOS access
control hardware such as the AP1001. These UHF tags will also work in TRANSIT
compatible mode.
Note
The Wiegand output format
is determined by the tag
and not by the reader.
Note
The Magstripe output
format is determined by the
tag and not by the reader.
Note
See also the 'decode Nedap
XS' feature as described in
chapter 6.3.3.

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Introduction
4/36
1.2 TAG SECURITY
EPC (Electronic Product Code) tags were introduced as a possible successor to the
barcode with added functionalities. The tag emits its EPC in plain text. This makes
the tags vulnerable to cloning and counterfeiting attacks. Unlike many 13MHz
smartcards, EPC tags do not support any DES, 3DES or AES encryption.
EPC tags contain a data field known as the Tag Identifier (TID). At the discretion of
the EPC manufacturer, the value may be factory programmed and locked, ensuring
that tags have a unique identity and (theoretically) cannot be cross-copied. This TID
based anti-cloning mechanism is not considered to be a strong protection.
Nedap UHF tags support a locked serialized TID and the uPASS Target reader can be
configured to read the TID data field and send its data to the Access Control System
for verification.
By default the uPASS Target reader is configured to read any EPC tag.
We encourage customers to enable the TID-check. But also advise not to completely
rely on this methods in high-security applications.
Tag security is not evaluated by UL.

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Installation
5/36
2INSTALLATION
2.1 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
The following safety precautions shall be observed during normal use, service and
repair.
The uPASS Target shall only be installed and serviced by qualified service
personnel.
Disconnect the power supply before (dis)connecting any wires, uPASS
Target is NOT hot-swappable, so when making or changing connections,
power must be switched OFF.
To be sure of safety, do not modify or add anything to the uPASS Target
other than mentioned in this installation guide or indicated by Nedap N.V.
2.2 MOUNTING INSTRUCTIONS
The uPASS Target can be mounted to any surface with the wall mounting bracket and
Pole Mounting Set (see appendix B for part numbers). The uPASS Target can be
“aimed” at the desired detection area with the mounting brackets.
2.2.1 READER DIMENSIONS
The dimensions of the uPASS Target reader can be seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1: uPASS Target dimensions

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Installation
6/36
2.2.2 WALL MOUNTING BRACKET
The Wall Mounting Bracket is supplied with the uPASS Target reader. When the Wall
Mounting Bracket is assembled mount it to the wall (or the Pole Mounting Set) based
on the dimension in Figure 2. The uPASS Target can be “aimed” with the Wall
Mounting Bracket and when the bolts are tightened it will stay in place.
Figure 2: Wall Mounting Bracket

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Installation
7/36
2.2.3 POLE MOUNTING SET
The Pole Mounting Set has to be ordered separately (see appendix B).
The uPASS Target can be mounted to round poles with maximum diameter of 190
mm / 7.48 inches and square poles with maximum diameter of 150 mm / 5.90
inches using the Pole Mounting Set. The Wall Mounting Bracket is mounted on the
Pole Mounting Set.
Figure 3: Pole Mounting Set

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Installation
8/36
2.2.4 WEATHER PROTECTION HOOD MOUNTING
After the mounting of the uPASS Target an optional weather protection hood can be
placed. The weather protection hood protects the uPASS Target from excess heat
caused by sun irradiation. It is advised to install the weather protection hood if the
ambient temperatures are 40°C (104°F) or higher and more than 2 hours of direct
sunlight on the uPASS Target housing.
The weather hood can be placed over an already mounted uPASS Target (some bolts
need to be loosened). It is recommended that the connections to uPASS Target are
made before mounting the weather protection hood. If the weather protection hood
is mounted the connectors are hard to reach.
The weather protection hood has to be ordered separately (see appendix B).
Figure 4: Weather Protection Hood

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
9/36
3CONNECTIONS
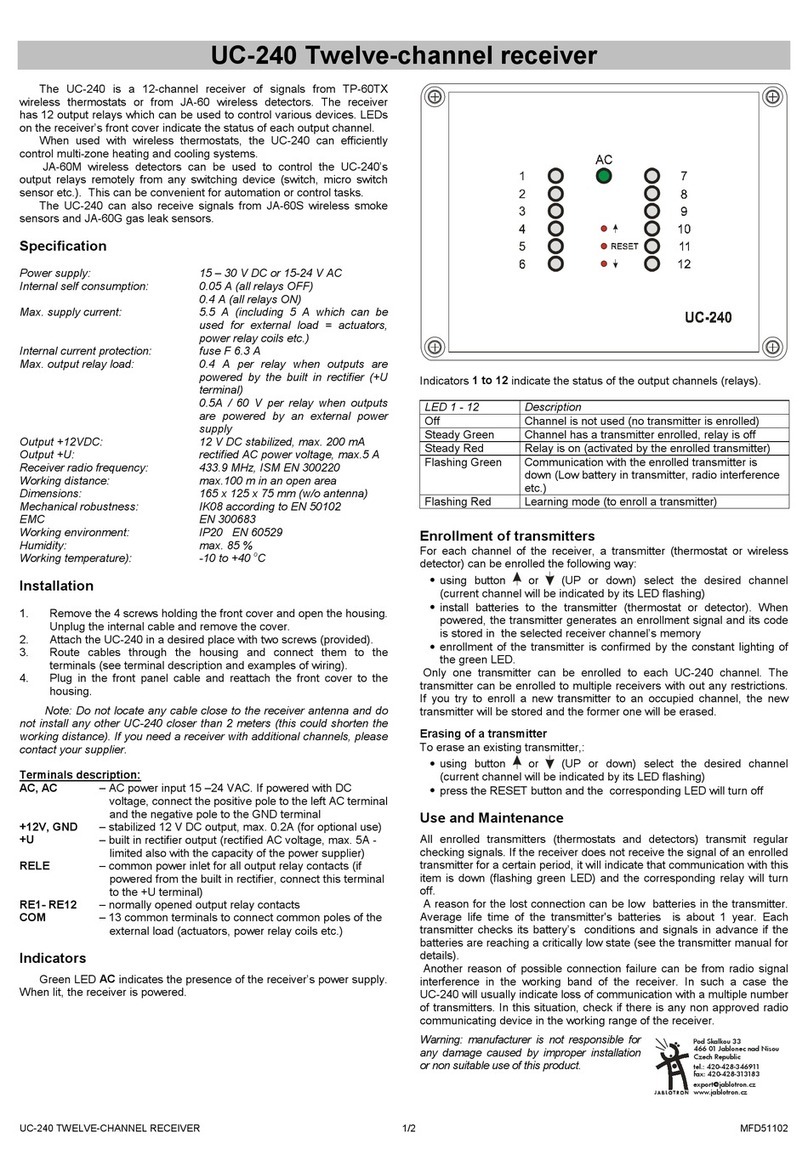
The uPASS Target has 7 connectors at the bottom of the device (see Figure 5). CONN.
2, CONN. 3 and CONN. 5 are shielded connectors. All connectors shown in this
chapter are seen from the outside. All connectors for the cables are supplied (except
mini USB and TNC (Ext. Ant.)).
The connection aren’t secured and the communication isn’t encrypted. If safety is
paramount it is recommended to place the connectors and cables so they cannot be
accessed outside the security zone.
Figure 5: uPASS Target connectors
Figure 6 shows a simplified schematic overview for most of the uPASS Target
connections. This figure shows the overview when the reader is in normal UHF (not
TRANSIT compatible) mode determined by SW1-1 (see chapter 4).
3 Points (A, B and C) control the direction of the serial interface to USB, RS-422, RS-
485 or one Ethernet channel (the other is fixed to the UHF processor):
A. When the USB cable is connected, the USB interface is used
B. The “main comm. interface” setting (see chapter 6.4.1) determines the use
of Ethernet or RS-422/RS-485
C. Determined by SW1-2 (located near the USB port) RS-422 or RS-485 is
used
Figure 6: Schematic overview UHF mode

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
10/36
Figure 7 shows a simplified schematic overview for most of the uPASS Target
connections. This figure shows the overview of the reader in TRANSIT compatible
mode determined by SW1-1 (see chapter 4).
Also in TRANSIT compatible mode there are three points (A, B and C) that control the
direction of the serial interface to USB, RS-422, RS-485 or one Ethernet channel (the
other is fixed to the UHF processor):
A. When the USB cable is connected, the USB interface is used
B. The “main comm. interface” setting (see chapter 6.4.1) determines the use
of Ethernet or RS-422/RS-485
C. Determined by SW1-2 (located near the USB port) RS-422 or RS-485 is
used
Figure 7: Schematic overview TRANSIT mode

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
11/36
3.1 POWER SUPPLY
The uPASS Target requires an external power supply. It is possible to power the
uPASS Target by connecting a DC power supply. Another possibility is to power the
uPASS Target by Power over Ethernet (PoE).
If both are connected, the power source depends on the DC power supply voltage.
The DC power supply is used if its voltage is higher than 13.6V. Otherwise the Power
of Ethernet is used
DC power supply
A DC power supply can be connected to the uPASS Target via CONN. 5. This DC
power supply must be able to deliver 12Vdc/1.5A or 24Vdc/0.75A.
Figure 8: CONN. 5
Pin
Function
1
-
2
Ground
3
DC+
4
-
Table 1: Power supply connection
Power over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet operates over Ethernet cables. CONN. 4 is a RJ45 Ethernet
connection and can be used for Power over Ethernet. The uPASS Target requires
IEEE802.3at (Power over Ethernet Plus).

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
12/36
3.2 COMMUNICATION
3.2.1 RS-422 / RS-485
The RS-422 and RS-485 interfaces are located in the unshielded CONN. 1. The RS-
422 or RS-485 communication can be used for communication with the Access
Control System, configuration settings and firmware update.
Only the RS-422 or the RS-485 interface can be active (not both), this is determined
by SW1-2 (located near the USB port). If SW1-2 is switched OFF, the RS-485
interface is used. Otherwise the RS-422 interface is used. For the RS-422 / RS-485 to
work, no USB should be connected and the “main comm. interface” must be set
correctly (see chapter 6.4.1).
The maximum cable length for both interfaces is 65 meters / 213 feet. This distance
can be increased
1
by adding termination resistors, using twisted cables and/or
configuring a lower baud rate (see chapter 6.3.1).
The communication protocol used for the RS-422 and RS-485 can be found in the
uPASS firmware guide. It isn’t possible to use the communication protocol in a bus,
only point-to-point communication is possible. The default communication settings
are 115200 Baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit and no parity.
By default the serial interface is connected to the UHF processor but can be
connected to the TRANSIT compatible processor, see chapter 4.
Figure 9: CONN. 1
Pin
Function RS-4222
Function RS-485
1
TX-
-
2
TX+
-
3
RX-
B
4
RX+
A
5
Ground
Ground
Table 2: RS-422 and RS-485 connection
1
RS-422 can reach 1500 meters / 4900 feet at 90000 Baud
RS-485 can reach 1200 meters / 4000 feet at 8333 Baud
2
TX (transmit) is the uPASS Target transmit line.
RX (receive) is the uPASS Target receive line.

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
13/36
3.2.2 WIEGAND / MAGSTRIPE
The Wiegand and Magstripe interfaces are located in shielded CONN. 2. The
Wiegand and Magstripe communication can be used for communication with to
Access Control System only.
The Wiegand and Magstripe can operate with a cable length of 150 meters / 490
feet.
By default the interface is connected to the UHF processor but can be connected to
the TRANSIT compatible processor, see chapter 4.
If connected to the UHF processor, Nedap UHF Wiegand tags generate a Wiegand
message on the interface and Nedap UHF Magstripe tags generate a Magstripe
message on the interface.
Other UHF tags do not generate a message on this interface, unless the 'Extra output'
settings are used. (See chapter 6.4.3)
The Wiegand/Magstripe output format is determined by the programmed format of
the tag. Make sure to order the correct tag programming format if you want to use
the Wiegand or Magstripe interface. See UHF How To Order Guide for more
information about ordering the UHF tags. Refer to the uPASS firmware guide for
details over the Wiegand/Magstripe timing.
In case the TRANSIT compatible processor is selected, the same connections are
used. Remember that in this case the tags must be programmed in the Nedap UHF
XS format. Refer to the corresponding TRANSIT firmware guide for protocol details.
Figure 10: CONN. 2
Pin
Function Wiegand
Function Magstripe
1
-
-
2
Data 0
Clock
3
-
Card loaded
4
Data 1
Data
5
-
-
6
Ground
Ground
7
Ground
Ground
8
-
-
Table 3: Wiegand and Magstripe connection

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
14/36
3.2.3 ETHERNET
An Ethernet connection is located in CONN. 4. The Ethernet interface can be used for
communication with the Access Control System, configuration and firmware update
up to a distance of 100 meters / 328 feet.
The uPASS Target is equipped with two TCP/IP Channels. Channel 1 (default 10001)
is connected to UHF processor or TRANSIT compatible processor. Channel 2 (default
10002) is always connected to the UHF processor with a baud rate of 115200.
The reader automatically gets an IP address from a DHCP server. The IP address
assigned can be found based on the MAC address of the uPASS Target (located on
the sticker). An example if the tool Lantronics Device Installer
The Ethernet module can be configured to have a static IP address. This can be done
by the web interface:
Open the browser and go to the IP address of the reader
Fill in the username and password (by default both blank)
Open “Network” and select “Use the following IP configuration:”
Fill in the required fields
Click OK and Apply Settings
The communication protocol used for the Ethernet is the same as for RS-422 and can
be found in the firmware guide. If the baud rate of the reader is changed the
Ethernet setting for Channel 1 must change. This can be done by the web interface:
Open the browser and go to the readers IP address
Fill in the username and password (by default both blank)
Open “Channel 1” - “Serial Settings”
Check if the “Port Settings” match the reader serials settings (as for USB or RS-
422/RS-485)
Click OK and Apply Settings
By default channel 1 is not connected. To connect channel 1, the “main comm.
interface” (chapter 6.4.1) needs to be set to TCP/IP. It is also possible to connect to
the TRANSIT compatible processor, see chapter 4. Make sure the serial settings of
the Ethernet configuration match the setting of the TRANSIT compatible processor.
Figure 11: CONN. 4

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
15/36
3.2.4 USB
The uPASS Target reader features a mini USB interface for service, installation and
firmware upgrade purposes. The USB interface creates a virtual COM port that can be
used the same way as a normal (serial) COM port.
The communication protocol for the USB can be found in the firmware guide. The
default communication settings are 115200 Baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit and no
parity.
By default the interface is connected to the UHF processor, but can be connected to
the TRANSIT compatible processor, see chapter 4.
Figure 12: Mini USB interface (with SW1)
USB Driver installation
Make sure your computer is connected to the internet. The driver should install
automatically via Windows update when the uPASS Target reader is connected to
your PC via the USB cable. Follow the driver installation wizard. If you do not see the
Windows update pop-up, you can manually install the driver. To manually install,
you need to go to FTDI’s website at www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm and
download the VCP (Virtual Com Port) drivers for your operating system. Drivers for
OS X and Linux are available as well.

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
16/36
3.2.5 NEDAP ANTENNA INTERFACE
The Nedap antenna interface is used to connect the uPASS Target to Nedap AEOS
access control hardware such as the AP1001. The uPASS reader simulates a 120 kHz
Nedap proximity card to the AP1001. This only works with Nedap-XS and EM4102
formatted UHF tags.
The uPASS Target can replace the 120 kHz antenna. The “HF Data” must be
connected to the “ANT” connection and the “Ground” to “GND” (see Figure 13).
Figure 13: Replacement of 120 kHz antenna
Another possibility is to leave the 120 kHz in place and connect the uPASS Target.
That way 120 kHz and uPASS Target both can be used (see Figure 14).
Figure 14: Addition to 120 kHz antenna
The Nedap antenna interface is located at CONN. 3.
Figure 15: CONN. 3
Pin
Function
1
-
2
HF Data
3
-
4
-
5
Ground
Table 4: Nedap antenna connection

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
17/36
3.3 DIGITAL I/O
3.3.1 GENERAL PURPOSE INPUTS / LED AND RELAY CONTROL
Two general purpose inputs are located in CONN. 2
By default the input and relay interfaces are connected to the UHF processor, but
can be connected to the TRANSIT compatible processor, see chapter 4.
If connected to the UHF processor, the inputs can control the LED at the front of the
reader to provide feedback and a relay for switching devices (for example doors or
gates).
The front LED need to be configured as Remote (see chapter 6.3.5) to control them
by the input pins. Input1 controls the “UnLock” (UL) color of the LED and input 2
controls the Not Authorized (NA) color of the LED.
The relay is by default set to automatic mode. The relay is activated for every tag
read and stays activated for the tag hold time (see chapter 6.3.4). If the automatic
mode is switched off, the relay is operated by input 1.
By default the inputs are at 5V level and are controlled by pulling them to ground.
The input pins are short-circuit protected.
If connected to the TRANSIT compatible processor, the function of the inputs can be
used for other purposes. See corresponding TRANSIT firmware guide.
Figure 16: CONN. 2
Pin
Function
1
Input 1 / UL
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
Ground
7
Ground
8
Input 2 / NA
Table 5: General input connection
Figure 17: CONN. 3
Pin
Function
1
Relay NO
2
-
3
Relay NC
4
Relay COM
5
-
Table 6: Relay connection

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
Connections
18/36
3.3.2 READER DISABLE
The reader disable input is located in CONN. 2. The reading of the uPASS Target can
be disabled with the RDIS input. This input is commonly used in combination with a
sensor (e.g. inductive loop) that detects the presence of a person or vehicle. The
RDIS is by default 5V can be controlled by pulling it to ground (pin is short-circuit
protected). When the RDIS input is 0V the reader is disabled.
This function works in both Normal mode and TRANSIT compatible mode.
Figure 18: CONN. 2
Pin
Function
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
RDIS
6
Ground
7
Ground
8
-
Table 7: Reader disable connection
3.3.3 EXTERNAL ANTENNA
It is possible to connect an external Nedap UHF antenna to the uPASS Target reader.
The external UHF antenna can be used in 3 possible configurations (see chapter
6.4.6):
1. Internal only. This mode is used if no external antenna is connected.
2. External only. This mode is used if the uPASS reader cannot be mounted at
the location but an antenna can, the reader can be place at another location
and connect to the antenna.
3. Internal and external. The antennas can be installed in two separate
locations (for in/out lane separation).
The external antenna is located at Ext. Ant. connection. The connection is a reverse
polarized TNC connector.
Only Nedap antennas shall be connected.

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
TRANSIT compatible mode
19/36
4TRANSIT COMPATIBLE MODE
The uPASS Target has a TRANSIT compatible processor. This processor is capable of
running the TRANSIT software (e.g. P61, P81 and Q70). To select this mode the
dipswitch SW1-1 (located near the USB port see chapter 3.2.4) must be switched ON.
If the TRANSIT compatible mode is selected, most inputs and outputs are switched to
the TRANSIT processor. This means that configuration of the UHF processor (e.g. LED
operation, frequency setting and TRANSIT switch settings) is not possible anymore
via RS-485, RS-422, USB or TCP/IP Channel 1. Configuration via TCP/IP Channel 2 is
still possible.
Make sure the serial setting of the Ethernet are correctly configured to work in the
TRANSIT compatible mode. This can differ based on firmware version and DIP-switch
settings (see the TRANSIT firmware documentation). The serial settings of the
Ethernet can be changed with the web interface:
Open the browser and go to the readers IP address
Fill in the username and password (by default both blank)
Open “Channel 1”- “Serial Settings”
Check if the “Port Settings”match the reader serials settings (as for USB or RS-
422/RS-485)
Click OK and Apply Settings
The only UHF tags that are read in TRANSIT compatible mode are Nedap UHF XS and
Nedap UHF EM4102 tags.
4.1 TOOLING
The TRANSIT compatible mode requires the tooling used for the TRANSIT readers.
To update the TRANSIT compatible processor, the “PICload”tool can be used.
To test if a P81 firmware is working correctly “P81Test” can be used.
These tools can be downloaded from https://portal.nedapidentification.com.
4.2 SWITCH SETTINGS
The TRANSIT software is configured by hardware DIP switches (see corresponding
firmware documentation of the TRANSIT). These DIP switches are not available on
the uPASS Target and are therefore emulated. The uPASS reader has to be
configured to the right settings. This can be done with the UHFTOOL, see chapter
6.3.3 (make sure the SW1-1 is OFF while configuring).

UPASS TARGET | INSTALLATION GUIDE
UHF Frequencies
20/36
5UHF FREQUENCIES
Radio Regulations
The uPASS Target reader is available in two regions.
The uPASS Target Region 1 operates in the 865 –868 MHz (ISM) band.
The uPASS Target Region 2 operates in the 902 –928 MHz (ISM) band.
Regulations in this band are not standardized world-wide. Generally the regulations
can be divided into several regions. When ordering an uPASS Target reader this
region must be specified (see UHF How To Order Guide).
Per region a specific frequency band is available. This frequency band is divided into
frequency channels. If local radio regulations require frequency hopping (FHSS),
then the uPASS Target automatically selects and uses the available channels.
Frequency channel selection
If no frequency hopping is required, it is still advised to use frequency hopping.
Frequency hopping is less sensitive for interferences.
Selecting a fixed frequency can be realized with the UHFTOOL (see chapter 6.4.4).
This is only possible if frequency hopping is not required. Select a free frequency
channel to achieve the best performance and to avoid interference from other
readers or equipment.
Other manuals for uPASS TARGET
1
Table of contents