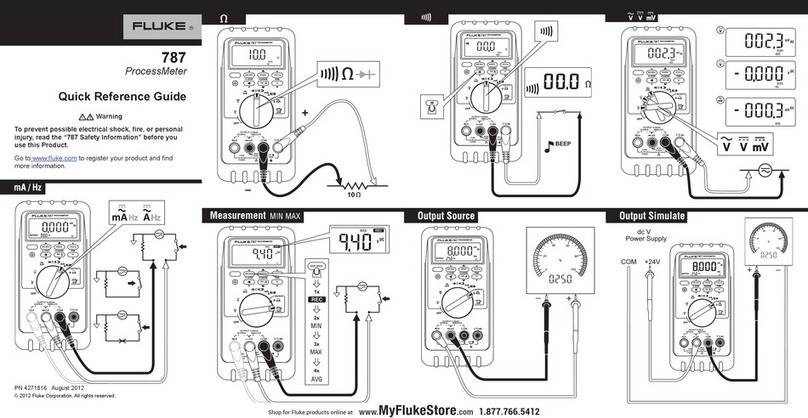
NIREOS GEMINI 2D User manual

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
1 | Page
Subject tochange without notice
Document Version: 2.2-A
13/12/2019

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
2 | Page
Contents
1. Introduction ....................................................................................................................................3
1.1 Brief Description...................................................................................................................... 3
1.2 Information, Warnings and Safety Instructions....................................................................... 3
1.2.1 Hazardous Voltage...........................................................................................................3
1.2.2 Unpacking........................................................................................................................4
1.2.3 Laser safety......................................................................................................................4
1.2.4 Installation Instructions...................................................................................................4
1.2.5 Connection Instructions ..................................................................................................4
2. Setup and Adjustments ................................................................................................................... 5
2.1 Hardware................................................................................................................................. 5
2.1.1 Connections.....................................................................................................................5
2.1.2 Mechanical Mounting...................................................................................................... 5
2.1.3 Optical Alignment............................................................................................................6
2.1.4 Optical Features .............................................................................................................. 7
2.1.5 External Controls ............................................................................................................. 7
2.2 Software ................................................................................................................................11
2.2.1 Software Installation Guide ........................................................................................... 11
2.2.2 Software Examples ........................................................................................................ 12
3. Appendix .......................................................................................................................................13
3.1 Technical Data .......................................................................................................................13
3.2 Available Versions and Descriptions*....................................................................................14
3.3 Mechanical Drawings ............................................................................................................15

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
3 | Page
1. Introduction
1.1 Brief Description
The GEMINI 2D is an ultra-stable interferometer, capable of generating two delayed and phase-locked
replicas of the input light. The relative delay T1between these two replicas can be controlled by the
user via software with extremely high reproducibility and phase stability (<1 attosecond, corresponding
to <λ/1000 in the visible spectral region). This delay is introduced by mechanically moving an optic with
a motorized positioner, whose position can be controlled via software. Its exceptional stability is made
possible thanks to the employed common-path geometry, that makes the device completely insensitive
to external noise and vibrations. During the scan of the delay T1, the absolute arrival time of one of the
two replicas is kept fixed. The GEMINI 2D Interferometer is thus the ideal device for generating a pair
of replicas (i.e. controlling the state of polarization) of the incoming light with interferometric stability.
The device works over a broad spectral range (from the Ultraviolet to the Mid-Infrared) and it is also
compatible with ultrashort few-optical-cycle pulses, making it perfectly suitable e.g. for generating a
pair of pump pulses in two-dimensional spectroscopy measurements.
1.2 Information, Warnings and Safety Instructions
1.2.1 Hazardous Voltage
The Controller Module can generate high output currents at high voltages. They may cause serious or
even lethal injury if used improperly. Therefore, the equipment should only be operated by personnel,
which is adequately trained and educated to prevent any improper use. Please follow general accident
prevention rules:
•Never touch any part that might be connected to an output with a high voltage.
•Do not connect products from other manufacturers to the output connectors.
•Never use equipment that is damaged in any way.
•The Controller Module contains no user serviceable parts. Never open the case. Procedures
which require opening the case must only be carried out by authorized, qualified and trained
personnel.
Output connectors with dangerous signals are labelled with the following symbol:
Figure 1
: "Caution, risk of electric shock" symbol.

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
4 | Page
1.2.2 Unpacking
Please be careful when unpacking the GEMINI-2D Interferometer and the Controller Module. Inspect
the products for signs of damage and only use equipment that shows no signs of damage. In case of
any damage, contact NIREOS for replacement. Please save all packing materials in case you would like
to transport or ship the product again.
1.2.3 Laser safety
Please be always careful and wear laser safety glasses when using the GEMINI-2D Interferometer with
laser radiation, as there could be some back reflected or scattered light exiting from the input or output
apertures.
1.2.4 Installation Instructions
The Controller Module must be installed horizontally with 3 cm air circulation area behind the
ventilator. Insufficient air flow can cause overheating, which can result in a limited functionality of the
controller.
1.2.5 Connection Instructions
Never use any other connecting cables than the connecting gear that you obtained from NIREOS. Never
use any third-party adapters or cables. This can cause failure or malfunction.
The system is NOT hot-pluggable. Always make sure to power down the device before connecting or
disconnecting any plugs. The only exception to this is the USB or Ethernet cables which may be removed
or attached during operation.
NOTE: Please be careful in handling the GEMINI-2D Interferometer. Do not try to pull the white cable
exiting the device. Always check the cable for possible signs of wear or damage. In case of any damage,
contact NIREOS for replacement.

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
5 | Page
2. Setup and Adjustments
2.1 Hardware
2.1.1 Connections
•Connect the Controller Module to the AC adapter;
•Connect the Controller Module to the computer with the USB cable;
•Connect the Controller Module to the GEMINI 2D Interferometer with the DSUB-15 cable.
Figure 2
: Picture of the Controller Module showing the connections.
NOTE: Remember to install horizontally the Controller Module, with 3 cm air circulation area behind
the ventilator.
2.1.2 Mechanical Mounting
If needed, there are 4 threaded holes (M6 threads) to screw 4 posts to the GEMINI 2D Interferometer,
that can be thus clamped and locked on an optical table. For more details regarding the position of the
threaded holes, please go to Section 3.3 “Mechanical Drawings”.
NOTE: Please always handle with care the GEMINI 2D Interferometer. Sudden movements or shocks
can cause a misalignment or break of the optics inside the device.

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
6 | Page
2.1.3 Optical Alignment
•POLARIZATION
The first optical element of the GEMINI 2D Interferometer is a polarizer (P1) mounted on a
rotation mount that can be rotated by the user. It is recommended to make sure that the first
polarizer is oriented at ±45° and to enter the device with a beam linearly polarized at ±45°, to
maximize the light throughput.
Inside the GEMINI 2D, the ±45° polarized light is divided into two replicas, one with vertical
polarization and one horizontal polarization, that are delayed by T1. At the output of the GEMINI
2D, another polarizer (P2, mounted on a rotation mount) shall be oriented at ±45° to project
the two replicas onto the same state of polarization.
NOTE: Please note that the direction of polarization is indicated by the 0° angle on the graduate scale.
NOTE: The polarizer P2 must be oriented at 0° (along the vertical direction) only when the precise
optical alignment procedure is necessary (for more information, please check the document “Report:
Calibration and Characterization”, paragraph 2).
NOTE: Never enter with a beam having perpendicular polarization with respect to the orientation of
the first polarizer. In that case, the throughput of the device would be close to 0%.
•BEAM ALIGNMENT
For a proper alignment of the beam, you can use the two apertures on the front and back faces
of the GEMINI 2D Interferometer. You can finely adjust the diameter size of the two apertures
depending on your beam size.

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
7 | Page
2.1.4 Optical Features
•RELATIVE DELAY T1
Depending on your version of the GEMINI 2D Interferometer, the relative delay T1can be:
Symmetric (“SYM”). The moving replica is scanned in time in a symmetric way around
the “TIME ZERO” with respect to the fixed replica. The delay T1can be varied from –T
to T.
Asymmetric (“ASY”). The moving replica is scanned in time in an asymmetric way
around the “time zero” with respect to the fixed replica. The delay T1can be varied
from –δT to 2T (approximately).
Figure 3
: Possible delay T1configurations. Top: “SYM” configuration; bottom: “ASY”
configuration.
NOTE: Please check the table in Section 3.1 “Technical Data” for more quantitative details.
2.1.5 External Controls
•TIME ZERO Control
The GEMINI 2D isalready set with T1=0. However, shipment and handling can cause small
misalignments of the optics that can cause a shift in T1. In this case, the relative delay T1can be
finely tuned by the user by rotating the manual control “TIME ZERO” with a screwdriver (see
Figure 4).
NB. A change in the "TIME ZERO" by rotating the manual control could lead to the need to
perform a recalibration procedure of the delay axis. For more details, please contact NIREOS
customer service at [email protected]

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
8 | Page
Figure 4
: Picture of the GEMINI 2D, showing the “TIME ZERO” manual control.
How to properly find TIME ZERO?
There are 3 different ways to properly find the correct T1.
To do that, always enter the GEMINI 2D Interferometer with a broadband light (coherent or
incoherent) and be sure that the two output replicas have parallel polarization at ±45°.
•Using a spectrometer
Measure the light exiting the GEMINI 2D with a spectrometer. In this configuration, the
spectrometer measures the spectral interference between the two replicas delayed by
T1. If T1≠0, then the measured spectrum is characterized by spectral fringes, which gets
larger as the delay T1 goes to zero. When T1=0, the measured spectrum corresponds to
the spectrum of the input light, without spectral fringes. This effect is shown in Figure
5 for 3 different values of T1(0, 15 and 150 fs).
Figure 5
: Spectra of the light exiting the GEMINI 2D measured at different values of T1.

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
9 | Page
•Using a photodiode
Measure the light exiting the GEMINI 2D with a single-pixel photodiode while scanning
the delay T1 via software (the delay can be controlled by moving the motorized
positioner by a few millimetres). Associate to each position of the motor (in mm) the
corresponding signal acquired from the photodiode. The result is the so-called
interferogram (shown in Figure 6) as a function of the position of the motor (which is
proportional to T1). If the light has a sufficiently broad spectrum, the peak of the
interferogram clearly indicates the exact TIME ZERO position.
Figure 6
: Interferogram of a broadband light exiting the GEMINI 2D measured with a
single-pixel detector.
•By eye
If the input light has a broad spectrum, the TIME ZERO can be found simply by looking
at the light spot transmitted by the GEMINI 2D. When T1≠0 the spot has the same
colour of the incoming light (Figure 7(a)). When T1approaches 0, spatial fringes start
to appear (see Figure 7(b)). TIME ZERO corresponds approximately to the central point
of the spatial fringe pattern (see Figure 7(c)).
Figure 7
: Pictures of the light spot transmitted by the GEMINI-2D at different values
of T1.

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
10 | Page
•DISPERSION Control
The dispersion introduced by the GEMINI 2D Interferometer can be finely and continuously
adjusted by rotating the control “DISPERSION” with a screwdriver (see the Figure 8). By rotating
in the direction of the + (-), you increase (decrease) the positive dispersion.
Figure 8
: Picture of the GEMINI 2D, showing the “DISPERSION” manual control.
NOTE: As these two controls (TIME ZERO and DISPERSION) modify the total thickness of material
travelled by light, please note that they affect also the arrival time of the fixed replica, which can be
slightly anticipated or delayed, depending on the direction of rotation of the control screws (a clockwise
rotation leads to an increase of the thickness of the material, so that the replica is delayed; an anti-
clockwise rotation leads to a decrease of the thickness of the material, so that the replica is anticipated).

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
11 | Page
2.2 Software
2.2.1 Software Installation Guide
Please note that the positioner inside the interferometer that acts on the delay τis from Smaract GmbH.
INSTALLING MCS SOFTWARE
In the NIREOS pen drive you will find a link with all the software needed to use the Controller Module
and to develop your own software. Run the installer MCS_Installer in the MCS folder. In the installation
you must first select the software folder where most of the files will be installed (default: C:\SmarAct).
The installer allows to select different software components for installation:
•Select MCS Tools and Programs to install utilities like the firmware updater and the
configuration tool.
•The installation of USB support drivers, needed for communicating with MCS devices
over USB, can be disabled by deselecting the Support for MCS with USB Interface
option. USB support is not needed if only MCS with RS232 interface will be used.
However, if the USB support is not installed, the software will not be able to connect
to MCS with a USB interface and will show errors. If the option is selected, the installer

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
12 | Page
will ask for permission to run the Usb-To-Serial driver installer at the end of the
installation process. The driver can also be installed manually by running the program
CDMxxxx_Setup.exe in the Drivers folder in the NIREOS pen drive.
•For developing applications with LabVIEW select LabVIEW Integration. If more than
one LabVIEW version is installed, you can choose the version to install the LabVIEW
commands in one of the next steps. To install additional LabVIEW versions just run the
installer again and select another LabVIEW version (the other software doesn't have
to be installed again). Note that the LabVIEW commands are only available for MCS
devices with USB interface.
•Select C Programming Libraries to install libraries and header files for writing your own
programs in C or C++ (or other languages that are compatible with the programming
libraries).
WHERE FILES ARE INSTALLED
The MCS folder is inside the Smaract folder which you have selected during installation.
The Programs folder contains tools and applications for the MCS.
Documentation is installed in the Documentation folder in the MCS folder.
If LabVIEW Integration was selected in the installer, the MCS LabVIEW commands are installed in the
program folder of the selected LabVIEW version and can be dragged directly from a LabVIEW
commands palette into your program. LabVIEW programming examples are installed in the folder
SmarAct\MCS\LabVIEW\Examples.
The software development kit (SDK) for developing programs with the MCS C API is installed under
SmarAct\MCS\SDK if C Programming Libraries is selected. This path is defined in the environment
variable MCS_SDK which can be used in development tools to find the SDK folder.
The installer creates shortcuts to programs and documents in the Start menu.
2.2.2 Software Examples
In the NIREOS pen drive you will find a link to useful software examples written in LabView. For more
details, please read the “COMPLETE OPERATIONAL EXAMPLE (LABVIEW AND NI-DAQ)” manual.

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
13 | Page
3. Appendix
3.1 Technical Data
VERSION
S
M
L
Spectral range [nm]
300 - 3500
Max. Delay T1[fs @ λ=600 nm]
SYM
± 400 ± 700 ± 1050
ASY
-100 → 700 -100 → 1300 -100 → 2000
Delay T1Stability
< 1 attosecond
Modes of Operation
Continuous Scan or Step Scan
Dimensions [mm]
147.5 x 175.5 x 98
Weight [kg]
1
NOTE: in Step Scan mode, the user can select the desired Waiting Time for each delay T1via software.
Figure 10
: Maximum delay T1relative to the asymmetric (ASY) configuration achievable with the three
different models (S, M and L) as a function of wavelength.

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
14 | Page
3.2 Available Versions and Descriptions*
The GEMINI 2D Interferometer is available in different versions:
GEMINI-(2D).xxx.y
(2D): A GEMINI 2D Interferometer is designed to:
•Keep the introduced dispersion constant during a scan of the delay T1;
•Keep the absolute arrival time of one of the two replicas fixed during a scan of the delay
T1.
NOTE: NIREOS also produces a simpler version of interferometer (GEMINI Interferometer), which is
suitable for those cases where the control on dispersion and on the absolute arrival time are not an
issue (for example, for time-resolved measurements in which the interferometer is placed after the
sample or for steady-state measurements). For more information and possible applications of the
xxx: Configuration of the relative delay T1(SYM: symmetric, ASY: asymmetric). For more details,
please read the paragraph “RELATIVE DELAY T1” in Section 2.1.4.
y: Maximum achievable relative delay T1(S: small, M: medium, L: long). For more details, please
read the table in Section 3.1.
Example: GEMINI-2D.ASY.L:
Interferometer with dispersion and absolute arrival time controls, asymmetric configuration of the
delay T1, “long” maximum achievable delay T1(T1=2000 fs at λ=600 nm).
*For customized products or more information, please contact NIREOS at info@nireos.com

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
15 | Page
3.3 Mechanical Drawings
Units: mm
GEMINI 2D Interferometer
NIREOS
59.3

NIREOS | GEMINI 2DINTERFEROMETER | USER TECHNICAL MANUAL 2.2-A
16 | Page

Table of contents
Popular Measuring Instrument manuals by other brands

BRUEL & KJAER
BRUEL & KJAER 4448 Field guide

Agilent Technologies
Agilent Technologies 2100 Bioanalyzer System Installation and safety guide

Industrial Scientific
Industrial Scientific AirAware instruction manual

Teledyne
Teledyne T3LCR1002 quick start guide

Bender
Bender ISOMETER IRDH275 manual

CORNING
CORNING Lambda Plus instruction manual