NOXAS Connection Kit User manual

Connection Kit Manual 04/18/2008 Page 1 of 4
NØXAS Connection Kit
Multi-Purpose Audio/Interface Board
The Connection Kit board is designed to meet a wide range of needs. The on-board
LM386 audio amplifier can be used to drive a speaker from your PicoKeyer for code
practice. An additional input channel lets you mix receiver audio with filtered, smoothed
Morse ID tones for repeater or EchoLink/IRLP nodes. A PTT circuit can be used with
many brands of handheld transceivers (Yaesu, Alinco, Icom, etc) for over-the-air code
practice, node ID, fox hunt transmitters, etc. Input conditioning circuits can be used to
convert inverted logic signals or signals up to 24V for use as ID-O-Matic inputs.
Features
•Sidetone filter and level control to smooth out sidetone from square-wave sources
•Audio amplifier/mixer for repeater or node ID, code practice, etc.
•PTT pull-up circuit for handheld transceivers
•Two input conditioning circuits with voltage limiting and selectable polarity
convert signals up to 24V to TTL levels
•Can plug directly onto ID-O-Matic PCB piggy-back style

Connection Kit Manual 04/18/2008 Page 2 of 4
Kit Construction:
Keep semiconductor parts in the anti-static packaging until you are ready to use them.
Always use good static control practices when working with static sensitive parts. This
means you should wear a grounding strap or work on a static-dissipative work surface.
Use a grounded tip soldering iron. When soldering small parts it is a good idea to use a
small, pencil-type soldering iron of no more than 25 Watts or so, or a temperature
controlled soldering station. Use pliers, clamps or alligator clips as heat sinks to prevent
heat damage to parts while soldering. If you are not fairly experienced with soldering
small parts, you may want to practice on some scrap parts first or get some help.
Work in an area with good lighting. You may want to use a magnifying lens to do some
of the small soldering required. Insert each component from the top of the board (the
side with the white silkscreen lettering), in the order shown in the instructions below. As
each component is installed, solder the leads and trim off excess leads with a small pair
of side cutters.
Before beginning assembly it is a good idea to unpack components, identify each part
and check for any missing parts.
Locate the printed circuit board (PCB). Orient the PCB with the white silk-
screened printing facing up. Use the component markings and outlines to aid in
placing components.
Locate the four .1 µF capacitors. These will be marked “104”. Install in the
locations marked C3, C4, C5 and C8. They are not polarity sensitive, so you do not
have to worry about installing them backwards.
Locate the two .01 µF capacitors. These will be marked “103”. Install these
capacitors in the locations marked C1 and C7.
Locate six 2.2K Ohm resistors (Red-Red-Red). Install these in locations R1, R3,
R4, R5, R6 and R7. (NOTE: You may omit R3 if you do not want PTT coupled to the
audio signal).
Locate the two 100K Ohm resistors (Brown-Black-Yellow). Install these in the
locations marked R2 and R8.
Locate the two 2N7000 MOSFETs. Install these in the locations marked Q1 and Q2.
Make sure to orient the transistors with the flat side facing as indicated by the outline
on the PCB.
Locate the two 1N4732 Zener diodes. Install them in the locations marked D1 and
D2 on the PCB. These parts must be installed with the proper polarity; make sure the
cathode ends (the ends with the black ring) are toward the silk-screened circles on the
PCB.
Install the 8-pin IC socket in location U1. Make sure the notch is oriented toward
the top of the PCB as shown in the component outline.
Locate the 100 µF electrolytic capacitor in location C2. Make sure to observe the
polarity marking on the board. The longer lead should go into the hole marked “+”.
Locate the 10 µF electrolytic capacitor in location C6. Make sure to observe the
polarity marking on the board. The longer lead should go into the hole marked “+”.

Connection Kit Manual 04/18/2008 Page 3 of 4
Install the square trimmer potentiometer in the AUD_LVL position. Be sure to
orient it right side up as indicated. If your potentiometer is a side-adjust style, install
it with the adjustment slot facing the bottom edge of the printed circuit board.
Your kit should contain a 6-pin header strip. Using a small pair of side cutters,
carefully separate it into two 3-pin strips. Install these in locations JP1 and JP2, with
the longer ends facing upward.
If you are building your Connection Kit board to plug onto an ID-O-Matic, locate two
2-position and one 6-position header socket strips. These are the black socket strips
with square holes. Install these on the bottom side of the board in locations J_ID,
TONE and PWR. You can then install header pins on your ID-O-Matic on the power,
audio and JP1 locations.
Apply a source of filtered, regulated DC power between 9 and 16 Volts to your
Connection Kit board via the PWR pads. Ground is on the left, positive is on the
right. Check for DC power not exceeding 16V between pin 4 (-) and pin 6 (+) on
socket U1.
Remove power. Install the LM386 audio amplifier chip in socket U1. Make sure
the notch or Pin 1 indication on the chip is facing up, matching the silk-screened
outline on the PCB.
Your Connection Kit is now ready to use!
Input polarity selection
Your Connection Kit includes two input signal circuits. The inputs are marked INH and
STRT, and the outputs are found in pins J_ID 2 (INHIBIT) and J_ID 3 (START). Input
voltages may be up to 24V DC. The input signals are clipped to 4.7 Volts maximum by
resistors R1 and R7, and Zener diodes D1 and D2. The signals are inverted by
MOSFETs Q1 and Q2.
The logic level of the output signals may be selected using jumpers installed at JP1 and
JP2. Installing the jumper plug from JP1 or JP2 center pin to the “NI” position will use
the non-inverted signal; from the center pin to the “I” position will use the inverted
signal. When used with the ID-O-Matic, this means you would use the “I” position for
active-high COR or squelch input signals, and the “NI” position for active-low inputs.
Audio Inputs & Mixing
Two audio inputs are provided. The TONE input is used for sidetone or Morse ID audio
from an ID-O-Matic, PicoKeyer or other source of square-wave audio Morse ID. The
AUDI input is intended for receiver audio when used in a repeater or node, and can be
left disconnected if no other audio source is used. The volume of the Morse audio from
the TONE input can be adjusted with the trimmer potentiometer.

Connection Kit Manual 04/18/2008 Page 4 of 4
Audio Output
The output audio is supplied to the AUDO pad through a 10 µF capacitor. It is sufficient
to drive a speaker, headphones, or the audio input of a transmitter.
Push-To-Talk (PTT)
The PTT input is active-low (ground for PTT) and is taken from J_ID pin 4. It is coupled
through a 2.2K resistor to the AUDO output. This arrangement is used for a combined
mic/PTT input on many handheld V/UHF transceivers from Yaesu, Alinco, Icom, ADI,
Radio Shack and several other manufacturers. If you do not wish to combine PTT and
audio, omit resistor R3 and use the solder pad marked PTT.
J_ID Connections and PCB Layout
Connector J_ID is intended to plug directly into the corresponding connector on an ID-O-
Matic, but can be used in other applications as well. The connections available are as
follows:
J_ID 1 No Connection
J_ID 2 INHIBIT output
J_ID 3 START output
J_ID 4 PTT input
J_ID 5 No Connection
J_ID 6 Ground
Table of contents
Other NOXAS Control Unit manuals
Popular Control Unit manuals by other brands

Harvia
Harvia sentiotec Professional Series Instructions for installation and use
FASTRON.
FASTRON. OZtherm F-312 Installation and commissioning manual

AMX
AMX MAX-AVM installation guide
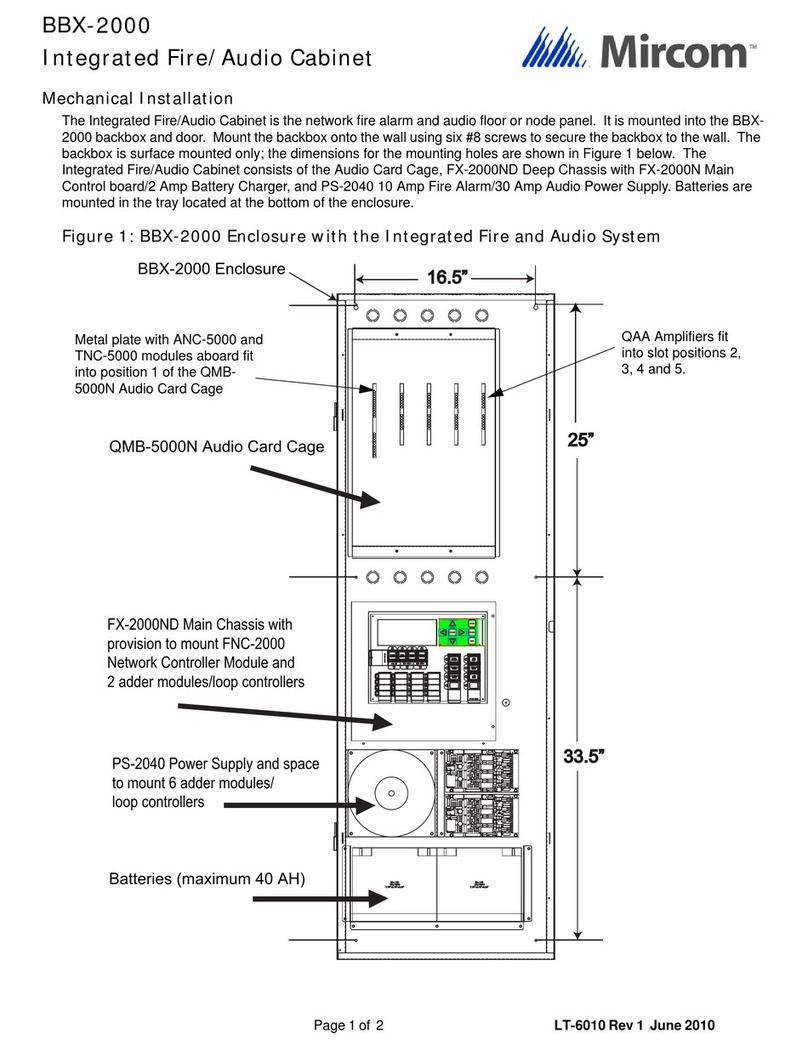
Mircom
Mircom BBX-2000 Mechanical installation

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS92410EVM-001 user guide

Emerson
Emerson Keystone Figure 320 Installation and maintenance instructions