10
would be useful to plan for the mid-range of travel, or 3.4” +
½(1/2) = 3.6” as the target for A.
There are several ways to increase Band/or decrease Ato
arrive at focus.
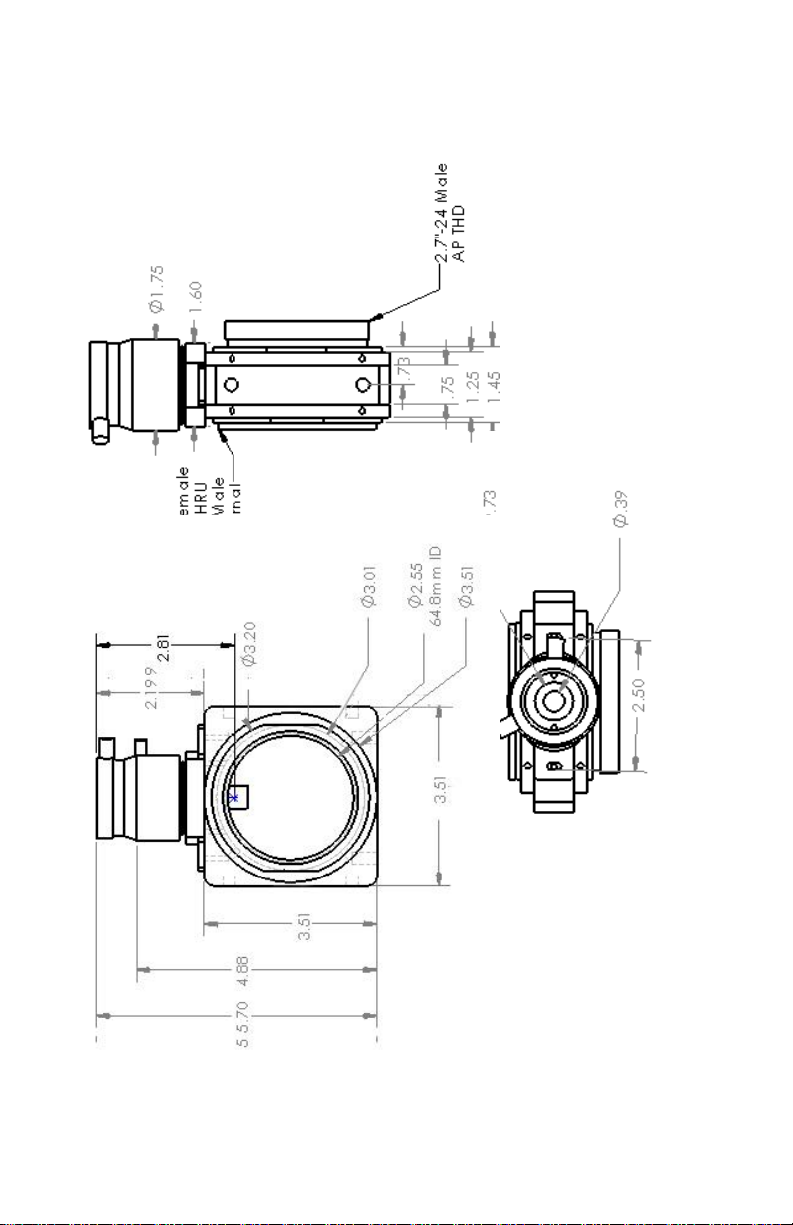
1. Use a 2.7” male fitting on your CFW. Add the
appropriate AP extension tube to achieve >3.65” for B.
Connect directly into the AP Female 2.7” adaptor
provided with the MMOAG. The guider nose piece does
not have to be placed flush into the focuser. It can be
retracted perhaps ¾”. Disadvantage –purchasing of a
2.7” male fitting for your CFW and AP extension tubes.
2. Replace the helical focuser with the provided 1.25”
nose-piece holder decreasing Afrom 3.6” to 2.7” AND
purchase the additional dovetail-to-3”male 0.75” long
adaptor. This makes Bfor YR, Apogee and FLI 3.08”,
3.24” and 3.51”, respectively. In this way, the guide
camera can be partially retracted from the nose piece
and then locked in place to achieve focus.
Disadvantage –losing the fine focus capability of the
helical focuser.
Another Way to Attach the Guide Camera
We have learned that the outside threads on the helical focuser
match the internal threads in SBIG remote guide head (RGH)
and ST-402 guide cameras. This allows the guider to be moved
closer to the prism by eliminating the 1.25” nose piece, if focus
cannot be achieved otherwise.