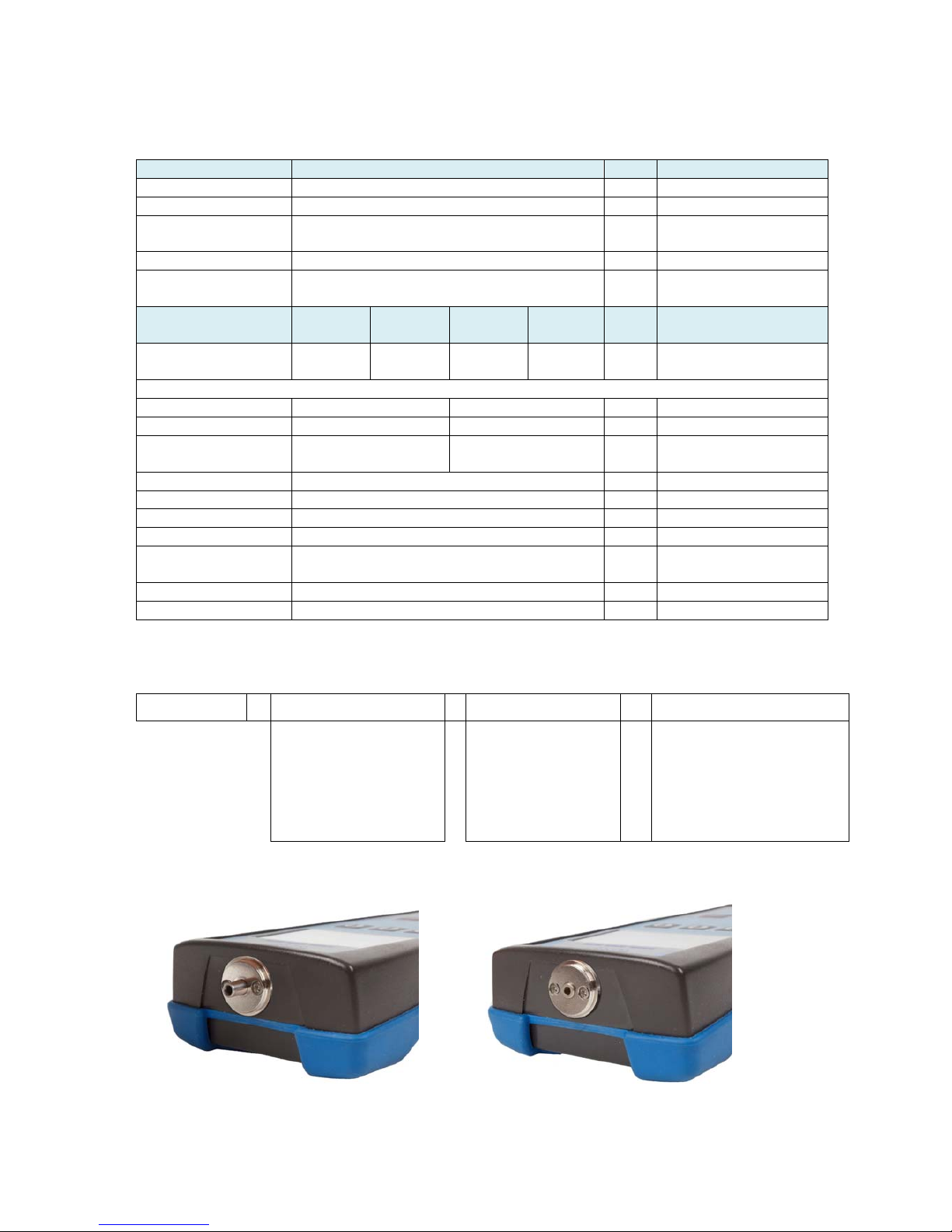
PM-800-GL INSTRUCTION MANUAL
8
classification system. The revised system is part of the revised IEC 60825 standard. From
2007, the revised system is also incorporated into the US-oriented ANSI Laser Safety
Standard (ANSI Z136.1). Since 2007, labeling according to the revised system is accepted
by the FDA on laser products imported into the US. The old and revised systems can be
distinguished by the 1M, 2M and 3R classes used only in the revised system and the 2A
and 3A classes used only in the old system. Class numbers were designated using Roman
numerals (I–IV) in the US under the old system and Arabic numerals (1–4) in the EU. The
revised system uses Arabic numerals (1–4) in all jurisdictions.
The classification of a laser is based on the concept of accessible emission limits (AEL) that
are defined for each laser class. This is usually a maximum power (in W) or energy (in J)
that can be emitted in a specified wavelength range and exposure time. For infrared
wavelengths above 4 μm, it is specified as a maximum power density (in W/m2). It is the
responsibility of the manufacturer to provide the correct classification of a laser, and to
equip the laser with appropriate warning labels and safety measures as prescribed by the
regulations. Safety measures used with the more powerful lasers include key-controlled
operation, warning lights to indicate laser light emission, a beam stop or attenuator, and
an electrical contact that the user can connect to an emergency stop or interlock
Below, the main characteristics and requirements for the classification system from 2002
are listed, along with typical required warning labels. Additionally, classes 2 and higher
must have the triangular warning label shown here and other labels are required in specific
cases indicating laser emission, laser apertures, skin hazards, and invisible wavelengths
Class 1
A class 1 laser is safe under all conditions of normal use. This means the maximum
permissible exposure (MPE) cannot be exceeded. This class includes high-power lasers
within an enclosure that prevents exposure to the radiation and that cannot be opened
without shutting down the laser. For example, a continuous laser at 600 nm can emit up to
0.39 mW, but for shorter wavelengths, the maximum emission is lower because of the
potential of those wavelengths to generate photochemical damage. The maximum
emission is also related to the pulse duration in the case of pulsed lasers and the degree of
spatial coherence.
Class 1M
A Class 1M laser is safe for all conditions of use except when passed through magnifying
optics such as microscopes and telescopes. Class 1M lasers produce large-diameter beams,
or beams that are divergent. The MPE for a Class 1M laser cannot normally be exceeded
unless focusing or imaging optics are used to narrow the beam. If the beam is refocused,
the hazard of Class 1M lasers may be increased and the product class may be changed. A
laser can be classified as Class 1M if the total output power is below class 3B but the
power that can pass through the pupil of the eye is within Class 1.
Class 2
A Class 2 laser is safe because the blink reflex will limit the exposure to no more than 0.25
seconds. It only applies to visible-light lasers (400–700 nm). Class-2 lasers are limited to 1
mW continuous wave, or more if the emission time is less than 0.25 seconds or if the light
is not spatially coherent. Intentional suppression of the blink reflex could lead to eye injury.
Many laser pointers are class 2.