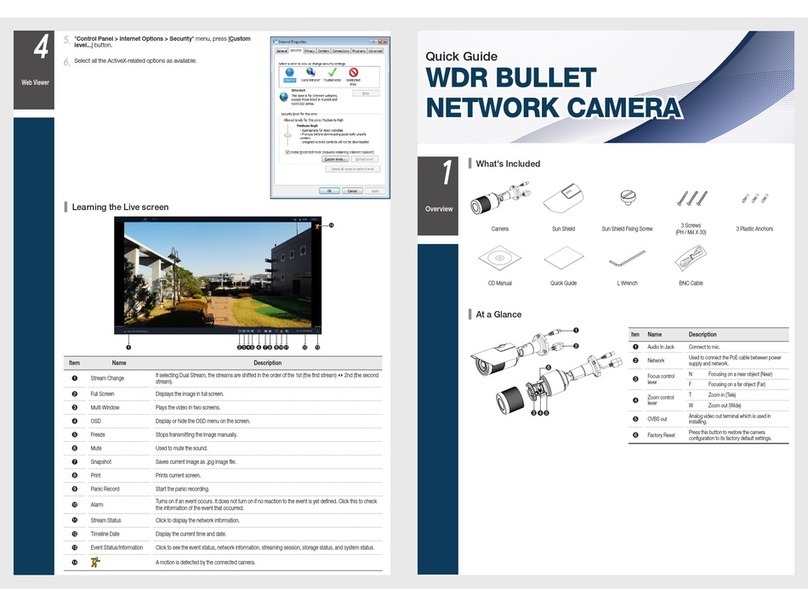
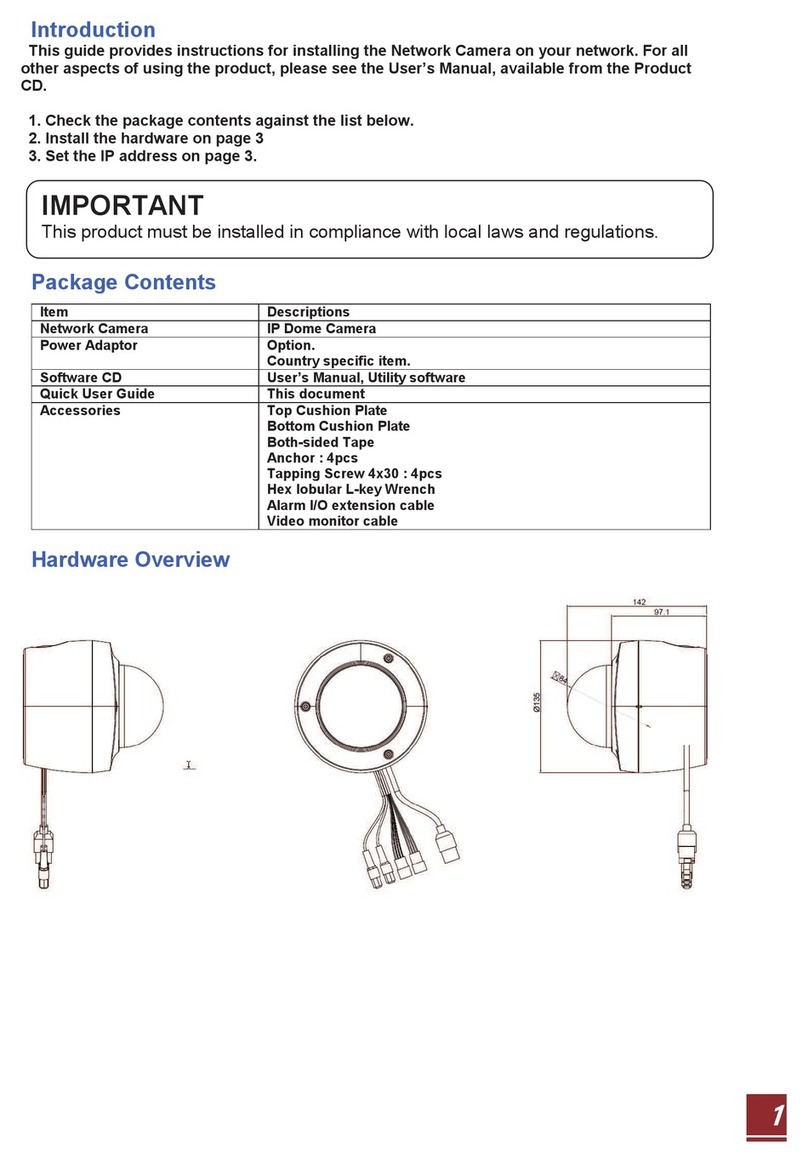
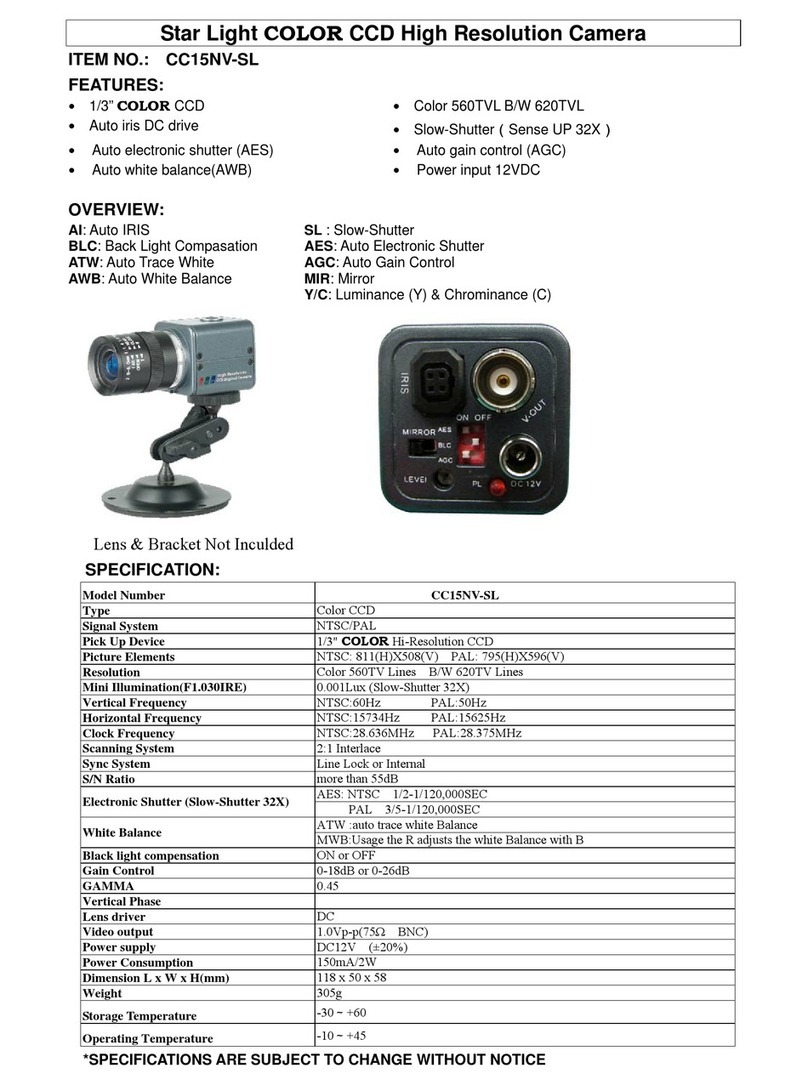
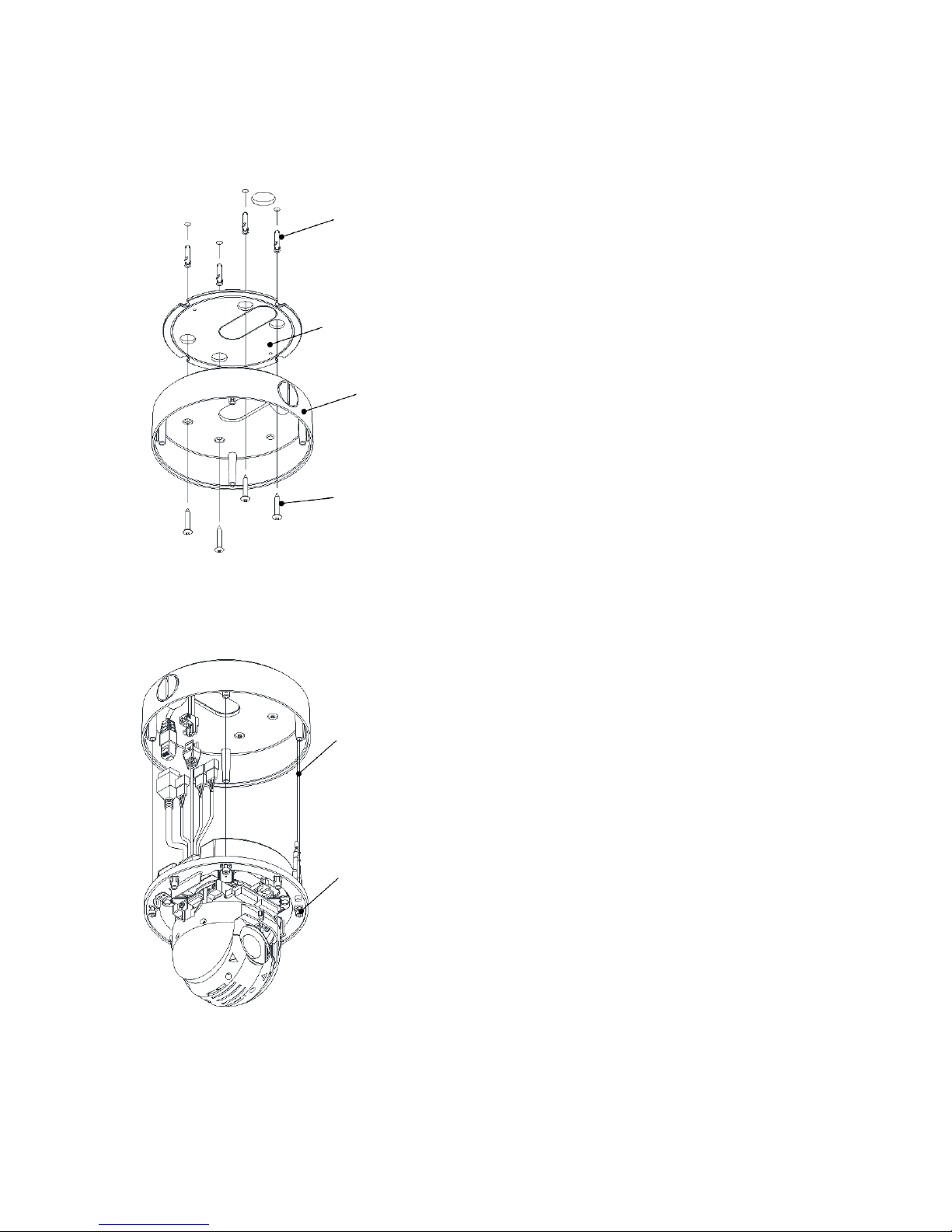
Contents
1. Product Features....................................................................................................... 4
2. Accessing the Camera.............................................................................................. 14
2.1 Access from a Browser........................................................................................ 15
2.2 Accessing the IP Camera from the Internet............................................................. 15
2.3 Adjusting the Image ............................................................................................ 15
2.4 Live View ........................................................................................................... 16
2.5 Video Stream Types ............................................................................................ 17
2.6 How to Stream H.264 .......................................................................................... 17
3. Setup..................................................................................................................... 18
3.1 Analog Output .................................................................................................... 18
3.2 Video ................................................................................................................ 18
3.2.1 Codec ...........................................................................................................18
3.2.2 Camera .........................................................................................................20
3.3 Audio ................................................................................................................ 21
3.4 Live .................................................................................................................. 22
3.4.1 Setup ............................................................................................................22
3.4.2 Privacy Mask ..................................................................................................22
3.5 SD Card ............................................................................................................ 23
3.5.1 Config...........................................................................................................23
3.5.2 Event ............................................................................................................23
3.5.3 Periodical ......................................................................................................24
3.6 FTP................................................................................................................... 24
3.6.1 Config...........................................................................................................25
3.6.2 Event ............................................................................................................26
3.6.3 Periodical ......................................................................................................27
3.7 Event ................................................................................................................ 27
3.7.1 Alarm Port......................................................................................................27
3.7.2 Motion...........................................................................................................28
3.7.3 Mapping ........................................................................................................28
3.8 Network............................................................................................................. 29
3.8.1 IP Setup ........................................................................................................29
3.8.2 Service Port ...................................................................................................30
3.8.3 RTP ..............................................................................................................31
3.8.4 E-mail...........................................................................................................32
3.8.5 DDNS............................................................................................................33
3.8.6 UPnP ............................................................................................................33
3.9 PTZ................................................................................................................... 34
3.9.1 Preset ...........................................................................................................34
3.9.2 Preset ...........................................................................................................35
3.9.3 Scan .............................................................................................................36
3.9.4 Tour..............................................................................................................36
3.9 System .............................................................................................................. 37
3.9.1 User..............................................................................................................37
3.9.2 Date/Time......................................................................................................37
3.9.3 Maintenance ..................................................................................................38
3.9.4 Information ....................................................................................................38
4. Accessory List......................................................................................................... 39