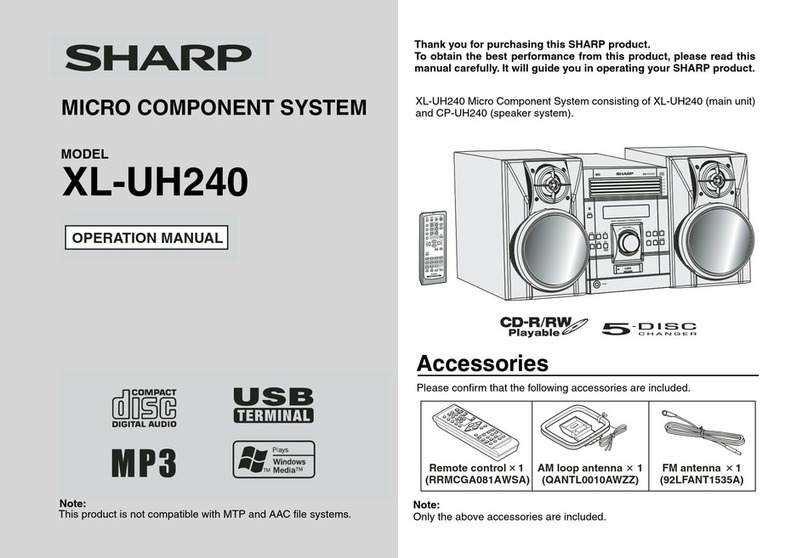
·
No sound is heard when the power is turned on.
·
Sound stops during a performance.
The function of this circuitry is to prevent circuitry damage if, for example, the positive and negative speaker connection wires are
“shorted”, or if speaker systems with an impedance less than the indicated rated impedance of the amplifier are used.
If this occurs, follow the procedure outlines below:
1. Turn off the power.
2. Determine the cause of the problem and correct it.
3. Turn on the power once again after one minute.
Note :
When the protection circuitry functions, the unit will not operate unless the power is first turned off and then on again.
1.5. Safety Part Information
Safety Parts List:
There are special components used in this equipment which are important for safety.
These parts are marked by in the Schematic Diagrams & Replacement Parts List. It is essential that these critical parts should
be replaced with manufacturer’s specified parts to prevent shock, fire or other hazards. Do not modify the original design without
permission of manufacturer.
Table 1
Reference No. Part No. Part name & Description Remarks
L5601 G0B9R5K00001 CHOKE COIL
L5602 G0B9R5K00001 CHOKE COIL
L5603 G0B9R5K00001 CHOKE COIL
L5604 G0B9R5K00001 CHOKE COIL
S5950 K0ABLB000003 SW VOLTAGE SELECTOR
T5950 G4CYAYY00135 MAIN TRANSFORMER
T5951 G4C2AAJ00005 SUB TRANSFORMER
Z5950 ERZV10V511CS ZENER
RL5950 K6B1AEA00015 POWER RELAY
F1 K5D402BLA013 FUSE
F2 K5D202BLA013 FUSE
FP5920 K5G702A00009 FUSE PROTECTOR
FP5940 K5G702Z00004 FUSE PROTECTOR
FP5950 K5G402A00025 FUSE PROTECTOR
JK5950 K2AA2B000011 JK AC INLET
A2 K2CQ2CA00006 AC CORD
C5920 ECA1JM102E 1000 63V
360 RAE0165A-V TRAVERSE UNIT
2 Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and
semiconductor “chip” components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage
caused by electro static discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equiped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equiped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as aluminium
foil, to prevent electrostatic charge build up or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder remover device. Some solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static (ESD protected)” can
generate electrical charge to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminium foil or
comparable conductive material).
5
SA-AK350GCP