PSEN op4H-SL Series
Operating Manual PSEN op4H-SL Series
1004305-EN-01 10
Use of qualified personnel
The products may only be assembled, installed, programmed, commissioned, operated,
maintained and decommissioned by competent persons.
A competent person is a qualified and knowledgeable person who, because of their train-
ing, experience and current professional activity, has the specialist knowledge required. To
be able to inspect, assess and operate devices, systems and machines, the person has to
be informed of the state of the art and the applicable national, European and international
laws, directives and standards.
It is the company’s responsibility only to employ personnel who
}Are familiar with the basic regulations concerning health and safety / accident preven-
tion,
}Have read and understood the information provided in this description under "Safety"
}Have a good knowledge of the generic and specialist standards applicable to the spe-
cific application.
Warranty and liability
All claims to warranty and liability will be rendered invalid if
}The product was used contrary to the purpose for which it is intended
}Damage can be attributed to not having followed the guidelines in the manual
}Operating personnel are not suitably qualified
}Any type of modification has been made (e.g. exchanging components on the PCB
boards, soldering work etc.).
Disposal
}In safety-related applications, please comply with the mission time TM in the safety-re-
lated characteristic data.
}When decommissioning, please comply with local regulations regarding the disposal of
electronic devices (e.g. Electrical and Electronic Equipment Act).
Function description
Basic function
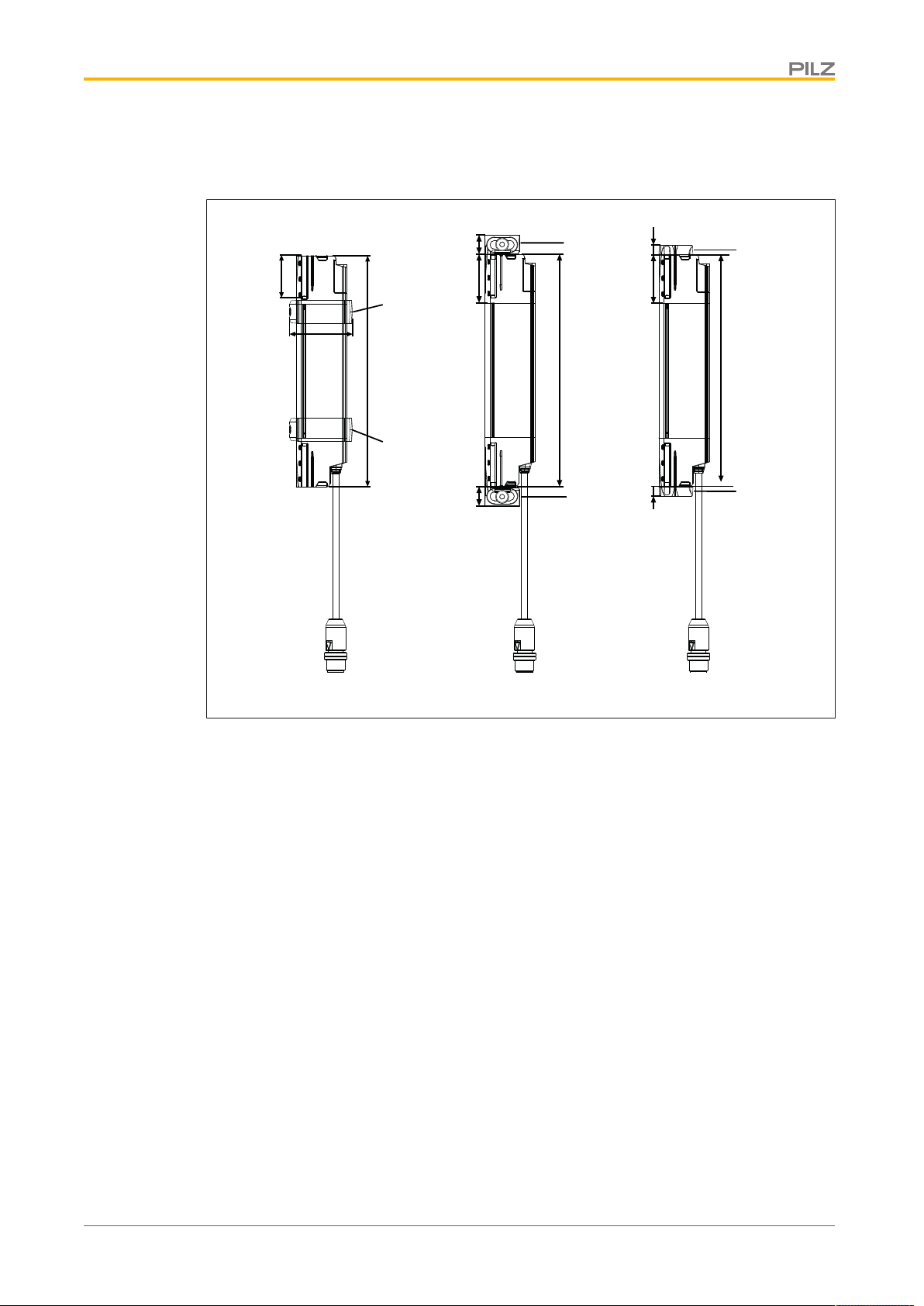
The safety light grid consists of a transmitter and a receiver.
Their shape and design
}protect the transmitter and receiver from external damage
}protect the safety light grid from malfunctions caused by vibration (see Technical de-
tails, environmental data section [ 43]).
The protected area is covered by infrared light beams, which are emitted from the transmit-
ter to the receiver. The protected field thus produced is able to detect an opaque object.
The control and monitoring of the transmitted and received infrared rays is performed by
microprocessors.